Abstract
Eosinophil is one of the most enigmatic leukocytes that plays pleiotropic roles in initiation and propagation of inflammatory conditions, modulation of innate and adaptive immune responses, homeostasis, and remodeling and repair of diverse tissues in health and disease. Eosinophils arise from CD34+ hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow under the influence of transcription factors (C/EBPα and GATA-1) and hematopoietic cytokines (IL-5, IL-3, and GM-CSF). The unusually high numbers of eosinophils in blood and/or tissues, so-called hypereosinophilia, are often critically involved in pathophysiology of a wide variety of inflammatory diseases in many organs, including many allergic diseases (asthma, rhinitis, conjunctivitis, atopic dermatitis), gastrointestinal diseases (eosinophilic eosophagitis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, Duchenne's muscular dystrophy, idiopathic myositis), cancers (pancreas, bladder, liver, kidney, breast, melanoma, colon, glioblastoma, gastric, uterine, oral/nasal, lung), infectious diseases (helminth, bacteria, virus, fungi), transplantation rejection (lung, cardiac, corneal, skin, liver, and renal), reproduction, and autoimmune diseases. A dozen of therapeutic agents, notably including humanized anti-IL-5 monoclonal antibodies, that directly and indirectly target eosinophils have been developed and are studied extensively under clinical and preclinical trials. Some agents have been shown to have promising perspectives to hypereosinophilic diseases, especially against asthma exacerbations and hypereosinophilic syndromes. Further studies are required for discovery of the specific mechanisms of actions of the different eosinophil-targeted therapies, dosing strategies and treatment options with identification of biomarkers that can monitor and predict the responses.
Figures and Tables
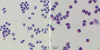 | Fig. 1Purified neutrophils and eosinophils from human peripheral blood. After RBC had been precipitated in 6% dextran-dextrose in 0.1 M EDTA (pH 7.4), the leukocyte-rich cell suspension was layered on a Percoll solution (1.070 g/mL) and centrifuged at 3,500×rpm for 30 min at 4℃. The enriched polymorphonuclear fraction were incubated with anti-CD16 monoclonal antibody-conjugated microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec), and neurophils (A) and eosinophils (B) were isolated through positively and negative selection, respectively, using a MACS (BD PharMingen). |
References
1. Lee JJ, Jacobsen EA, McGarry MP, Schleimer RP, Lee NA. Eosinophils in health and disease: the LIAR hypothesis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010. 40:563–575.

2. Lee JJ, Jacobsen EA, Ochkur SI, McGarry MP, Condjella RM, Doyle AD, et al. Human versus mouse eosinophils: "that which we call an eosinophil, by any other name would stain as red". J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012. 130:572–584.

3. Meeusen EN, Balic A. Do eosinophils have a role in the killing of helminth parasites? Parasitol Today. 2000. 16:95–101.

4. Gleich GJ. The eosinophil and bronchial asthma: current understanding. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990. 85:422–436.

5. Liu LY, Sedgwick JB, Bates ME, Vrtis RF, Gern JE, Kita H, et al. Decreased expression of membrane IL-5 receptor alpha on human eosinophils: I. Loss of membrane IL-5 receptor alpha on airway eosinophils and increased soluble IL-5 receptor alpha in the airway after allergen challenge. J Immunol. 2002. 169:6452–6458.

6. Jacobsen EA, Helmers RA, Lee JJ, Lee NA. The expanding role(s) of eosinophils in health and disease. Blood. 2012. 120:3882–3890.

7. Muller C, Kowenz-Leutz E, Grieser-Ade S, Graf T, Leutz A. NF-M (chicken C/EBP beta) induces eosinophilic differentiation and apoptosis in a hematopoietic progenitor cell line. EMBO J. 1995. 14:6127–6135.

8. Zhang DE, Zhang P, Wang ND, Hetherington CJ, Darlington GJ, Tenen DG. Absence of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor signaling and neutrophil development in CCAAT enhancer binding protein alpha-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. 94:569–574.

9. Tsai FY, Orkin SH. Transcription factor GATA-2 is required for proliferation/survival of early hematopoietic cells and mast cell formation, but not for erythroid and myeloid terminal differentiation. Blood. 1997. 89:3636–3643.

10. Hirasawa R, Shimizu R, Takahashi S, Osawa M, Takayanagi S, Kato Y, et al. Essential and instructive roles of GATA factors in eosinophil development. J Exp Med. 2002. 195:1379–1386.

11. Yu C, Cantor AB, Yang H, Browne C, Wells RA, Fujiwara Y, et al. Targeted deletion of a high-affinity GATA-binding site in the GATA-1 promoter leads to selective loss of the eosinophil lineage in vivo. J Exp Med. 2002. 195:1387–1395.

12. Clutterbuck EJ, Hirst EM, Sanderson CJ. Human interleukin-5 (IL-5) regulates the production of eosinophils in human bone marrow cultures: comparison and interaction with IL-1, IL-3, IL-6, and GMCSF. Blood. 1989. 73:1504–1512.

13. Wechsler ME, Fulkerson PC, Bochner BS, Gauvreau GM, Gleich GJ, Henkel T, et al. Novel targeted therapies for eosinophilic disorders. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012. 130:563–571.

14. Yamaguchi Y, Zon LI, Ackerman SJ, Yamamoto M, Suda T. Forced GATA-1 expression in the murine myeloid cell line M1: induction of c-Mpl expression and megakaryocytic/erythroid differentiation. Blood. 1998. 91:450–457.

15. Uhm TG, Kim BS, Chung IY. Eosinophil development, regulation of eosinophil-specific genes, and role of eosinophils in the pathogenesis of asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012. 4:68–79.

16. Leckie MJ, ten Brinke A, Khan J, Diamant Z, O'Connor BJ, Walls CM, et al. Effects of an interleukin-5 blocking monoclonal antibody on eosinophils, airway hyper-responsiveness, and the late asthmatic response. Lancet. 2000. 356:2144–2148.

17. Pavord ID, Korn S, Howarth P, Bleecker ER, Buhl R, Keene ON, et al. Mepolizumab for severe eosinophilic asthma (DREAM): a multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2012. 380:651–659.

18. Nair P, Pizzichini MM, Kjarsgaard M, Inman MD, Efthimiadis A, Pizzichini E, et al. Mepolizumab for prednisone-dependent asthma with sputum eosinophilia. N Engl J Med. 2009. 360:985–993.

19. Harlin SL, Ansel DG, Lane SR, Myers J, Kephart GM, Gleich GJ. A clinical and pathologic study of chronic sinusitis: the role of the eosinophil. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1988. 81:867–875.

20. Leiferman KM, Ackerman SJ, Sampson HA, Haugen HS, Venencie PY, Gleich GJ. Dermal deposition of eosinophil-granule major basic protein in atopic dermatitis. Comparison with onchocerciasis. N Engl J Med. 1985. 313:282–285.

21. Oldhoff JM, Darsow U, Werfel T, Katzer K, Wulf A, Laifaoui J, et al. Anti-IL-5 recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody (mepolizumab) for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Allergy. 2005. 60:693–696.

22. Bonini S, Magrini L, Rotiroti G, Lambiase A, Tomassini M, Rumi C, et al. The eosinophil and the eye. Allergy. 1997. 52:44–47.

23. Forbes E, Smart VE, D'Aprile A, Henry P, Yang M, Matthaei KI, et al. T helper-2 immunity regulates bronchial hyperresponsiveness in eosinophil-associated gastrointestinal disease in mice. Gastroenterology. 2004. 127:105–118.

24. Carvalho AT, Elia CC, de Souza HS, Elias PR, Pontes EL, Lukashok HP, et al. Immunohistochemical study of intestinal eosinophils in inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003. 36:120–125.

25. Masterson JC, McNamee EN, Jedlicka P, Fillon S, Ruybal J, Hosford L, et al. CCR3 Blockade Attenuates Eosinophilic Ileitis and Associated Remodeling. Am J Pathol. 2011. 179:2302–2314.

26. Sewry CA. Muscular dystrophies: an update on pathology and diagnosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2010. 120:343–358.

27. Krahn M, Lopez de Munain A, Streichenberger N, Bernard R, Pécheux C, Testard H, et al. CAPN3 mutations in patients with idiopathic eosinophilic myositis. Ann Neurol. 2006. 59:905–911.
28. Riise GC, Scherstén H, Nilsson F, Ryd W, Andersson BA. Activation of eosinophils and fibroblasts assessed by eosinophil cationic protein and hyaluronan in BAL. Association with acute rejection in lung transplant recipients. Chest. 1996. 110:89–96.

29. Gatault S, Legrand F, Delbeke M, Loiseau S, Capron M. Involvement of eosinophils in the anti-tumor response. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2012. 61:1527–1534.

30. Simon HU, Rothenberg ME, Bochner BS, Weller PF, Wardlaw AJ, Wechsler ME, et al. Refining the definition of hypereosinophilic syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. 126:45–49.

31. Cools J, DeAngelo DJ, Gotlib J, Stover EH, Legare RD, Cortes J, et al. A tyrosine kinase created by fusion of the PDGFRA and FIP1L1 genes as a therapeutic target of imatinib in idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:1201–1214.

32. Wong CK, Cheung PF, Ip WK, Lam CW. Intracellular signaling mechanisms regulating toll-like receptor-mediated activation of eosinophils. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2007. 37:85–96.

33. Klion AD, Nutman TB. The role of eosinophils in host defense against helminth parasites. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004. 113:30–37.

34. Gebreselassie NG, Moorhead AR, Fabre V, Gagliardo LF, Lee NA, Lee JJ, et al. Eosinophils preserve parasitic nematode larvae by regulating local immunity. J Immunol. 2012. 188:417–425.

35. Dimova-Yaneva D, Russell D, Main M, Brooker RJ, Helms PJ. Eosinophil activation and cysteinyl leukotriene production in infants with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004. 34:555–558.

36. Rosenberg HF, Domachowske JB. Eosinophils, eosinophil ribonucleases, and their role in host defense against respiratory virus pathogens. J Leukoc Biol. 2001. 70:691–698.
37. Yousefi S, Gold JA, Andina N, Lee JJ, Kelly AM, Kozlowski E, et al. Catapult-like release of mitochondrial DNA by eosinophils contributes to antibacterial defense. Nat Med. 2008. 14:949–953.

38. Feger TA, Rupp NT, Kuhn FA, Ford JL, Dolen WK. Local and systemic eosinophil activation in allergic fungal sinusitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1997. 79:221–225.

39. Romero R, Kusanovic JP, Gomez R, Lamont R, Bytautiene E, Garfield RE, et al. The Clinical significance of eosinophils in the amniotic fluid in preterm labor. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010. 23:320–329.

40. Blumenthal RD, Samoszuk M, Taylor AP, Brown G, Alisauskas R, Goldenberg DM. Degranulating eosinophils in human endometriosis. Am J Pathol. 2000. 156:1581–1588.

41. Abraham SC, Leach S, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Murakata LA, Boitnott JK, et al. Eosinophilic pancreatitis and increased eosinophils in the pancreas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003. 27:334–342.

42. Wang Q, Lu CM, Guo T, Qian JM. Eosinophilia associated with chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2009. 38:149–153.

43. Correale J, Fiol M. Activation of humoral immunity and eosinophils in neutromyelitis optica. Neurology. 2004. 63:2363–2370.

44. Jarratt M, Bybee JD, Ramsdell W. Eosinophilic fasciitis: an early variant of scleroderma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1979. 1:221–226.

45. Rothenberg ME, Klion AD, Roufosse FE, Kahn JE, Weller PF, Simon HU, et al. Treatment of patients with the hypereosinophilic syndrome with mepolizumab. N Engl J Med. 2008. 358:1215–1228.

46. Kim S, Marigowda G, Oren E, Israel E, Wechsler ME. Mepolizumab as a steroid-sparing treatment option in patients with Churg-Strauss syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. 125:1336–1343.

47. Oldhoff JM, Darsow U, Werfel T, Bihari IC, Katzer K, Laifaoui J, et al. No effect of anti-interleukin-5 therapy (mepolizumab) on the atopy patch test in atopic dermatitis patients. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2006. 141:290–294.

48. Kips JC, O'Connor BJ, Langley SJ, Woodcock A, Kerstjens HA, Postma DS, et al. Effect of SCH55700, a humanized anti-human interleukin-5 antibody, in severe persistent asthma: a pilot study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003. 167:1655–1659.

49. Gevaert P, Lang-Loidolt D, Lackner A, Stammberger H, Staudinger H, Van Zel T, et al. Nasal IL-5 levels determine the response to anti-IL-5 treatment in patients with nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006. 118:1133–1141.

50. Klion AD, Law MA, Noel P, Kim YJ, Haverty TP, Nutman TB. Safety and efficacy of the monoclonal anti-interleukin-5 antibody SCH55700 in the treatment of patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome. Blood. 2004. 103:2939–2941.

51. Kolbeck R, Kozhich A, Koike M, Peng L, Andersson CK, Damschroder MM, et al. MEDI-563, a humanized anti-IL-5 receptor alpha mAb with enhanced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity function. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. 125:1344–1353.
52. Busse WW, Katial R, Gossage D, Sari S, Wang B, Kolbeck R, et al. Safety profile, pharmacokinetics, and biologic activity of MEDI-563, an anti-IL-5 receptor alpha antibody, in a phase I study of subjects with mild asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. 125:1237–1244.
53. Sefcick A, Sowter D, DasGupta E, Russell NH, Byrne JL. Alemtuzumab therapy for refractory idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Br J Haematol. 2004. 124:558–559.

54. Simon D, Wittwer J, Kostylina G, Buettiker U, Simon HU, Yawalkar N. Alefacept (lymphocyte function-associated molecule 3/IgG fusion protein) treatment for atopic eczema. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008. 122:423–424.

55. van Rensen EL, Evertse CE, van Schadewijk WA, van Wijngaarden S, Ayre G, Mauad T, et al. Eosinophils in bronchial mucosa of asthmatics after allergen challenge: effect of anti-IgE treatment. Allergy. 2009. 64:72–80.

56. Wenzel S, Wilbraham D, Fuller R, Getz EB, Longphre M. Effect of an interleukin-4 variant on late phase asthmatic response to allergen challenge in asthmatic patients: results of two phase 2a studies. Lancet. 2007. 370:1422–1431.

57. Gauvreau GM, Boulet LP, Cockcroft DW, Baatjes A, Cote J, Deschesnes F, et al. Antisense therapy against CCR3 and the common beta chain attenuates allergen-induced eosinophilic responses. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008. 177:952–958.

58. Blanchard C, Wang N, Stringer KF, Mishra A, Fulkerson PC, Abonia JP, et al. Eotaxin-3 and a uniquely conserved gene-expression profile in eosinophilic esophagitis. J Clin Invest. 2006. 116:536–547.

59. Okigami H, Takeshita K, Tajimi M, Komura H, Albers M, Lehmann TE, et al. Inhibition of eosinophilia in vivo by a small molecule inhibitor of very late antigen (VLA)-4. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. 559:202–209.

60. Bloomgren G, Richman S, Hotermans C, Subramanyam M, Goelz S, Natarajan A, et al. Risk of natalizumab-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2012. 366:1870–1880.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download