Abstract
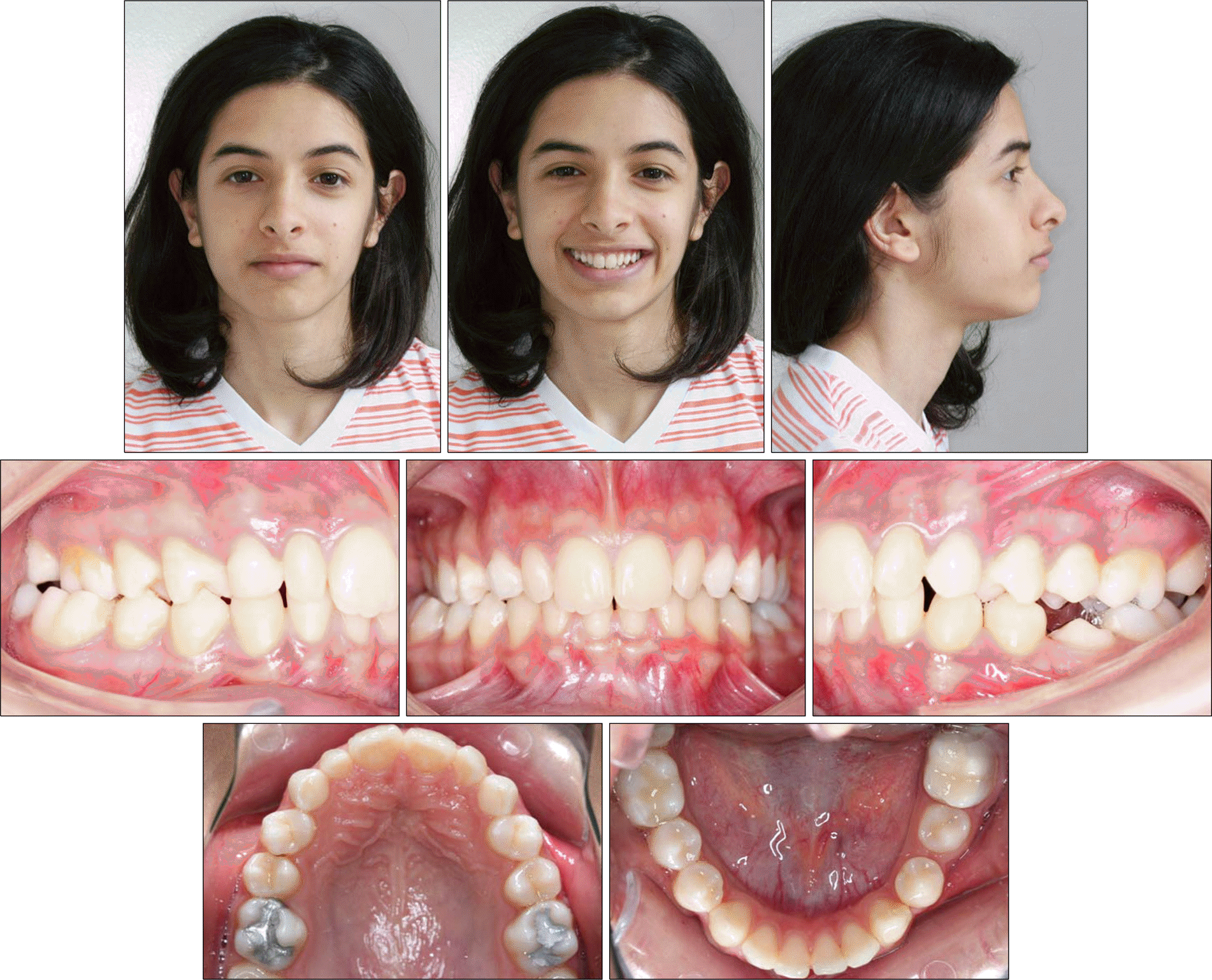
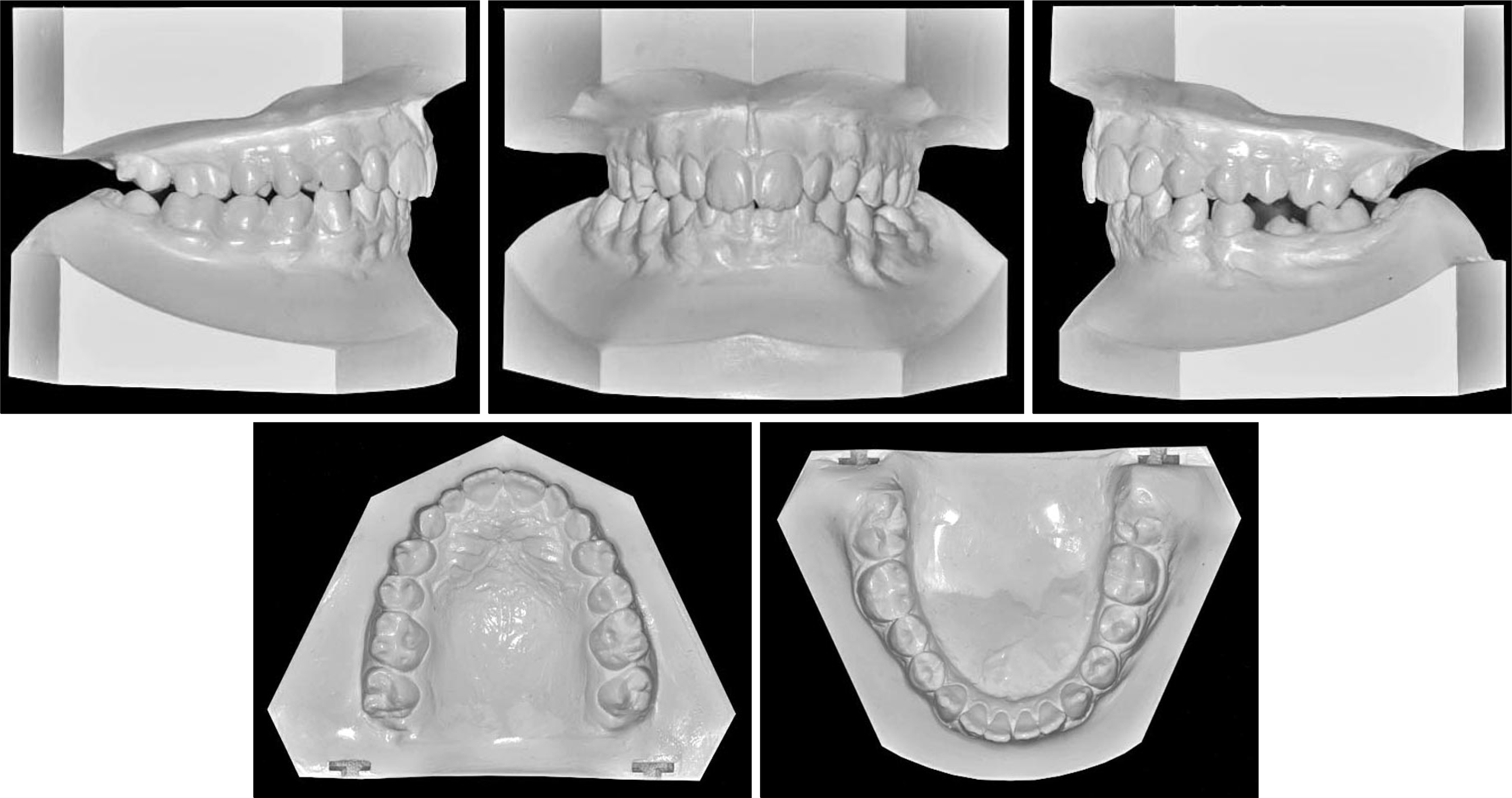
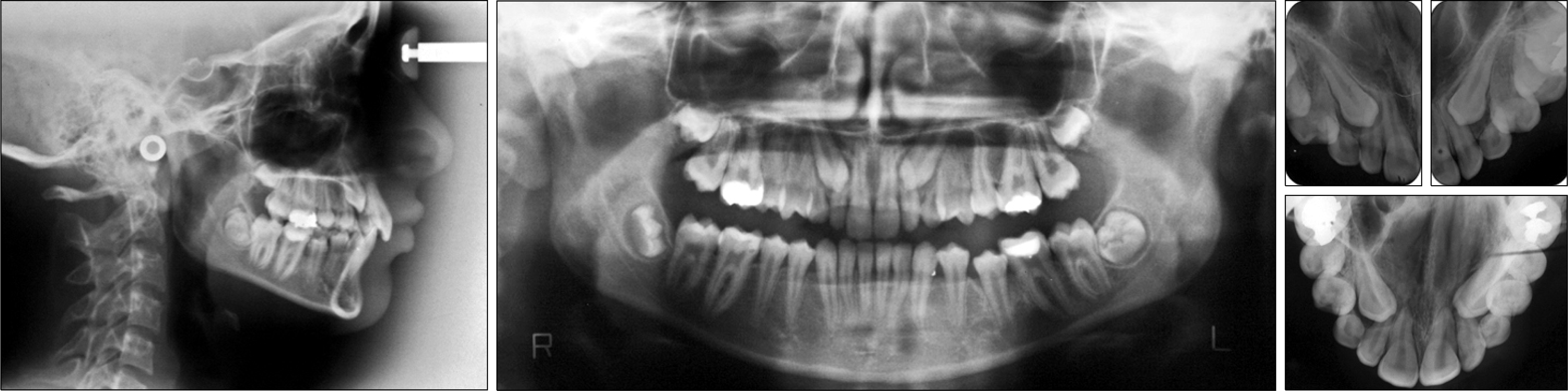
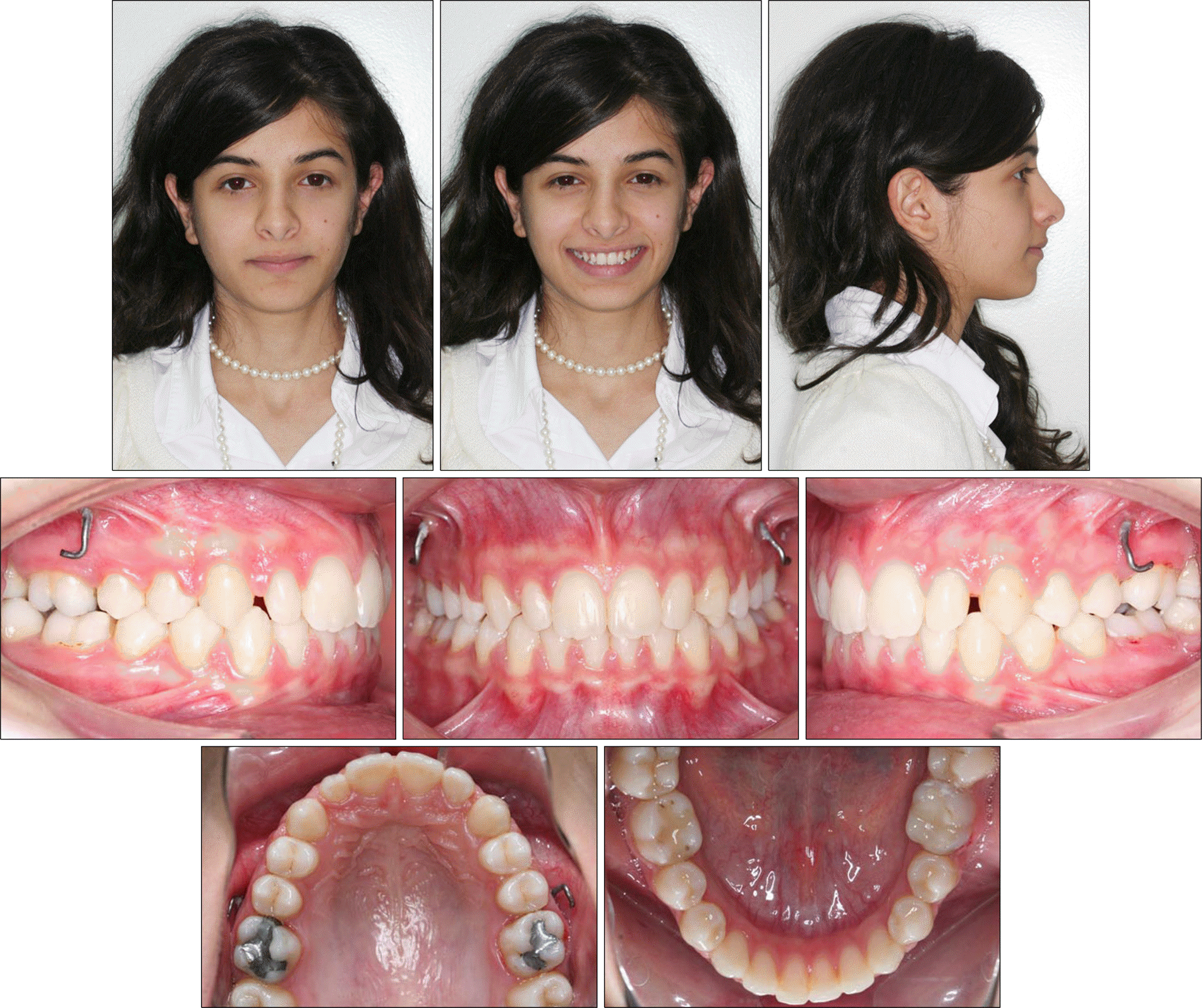
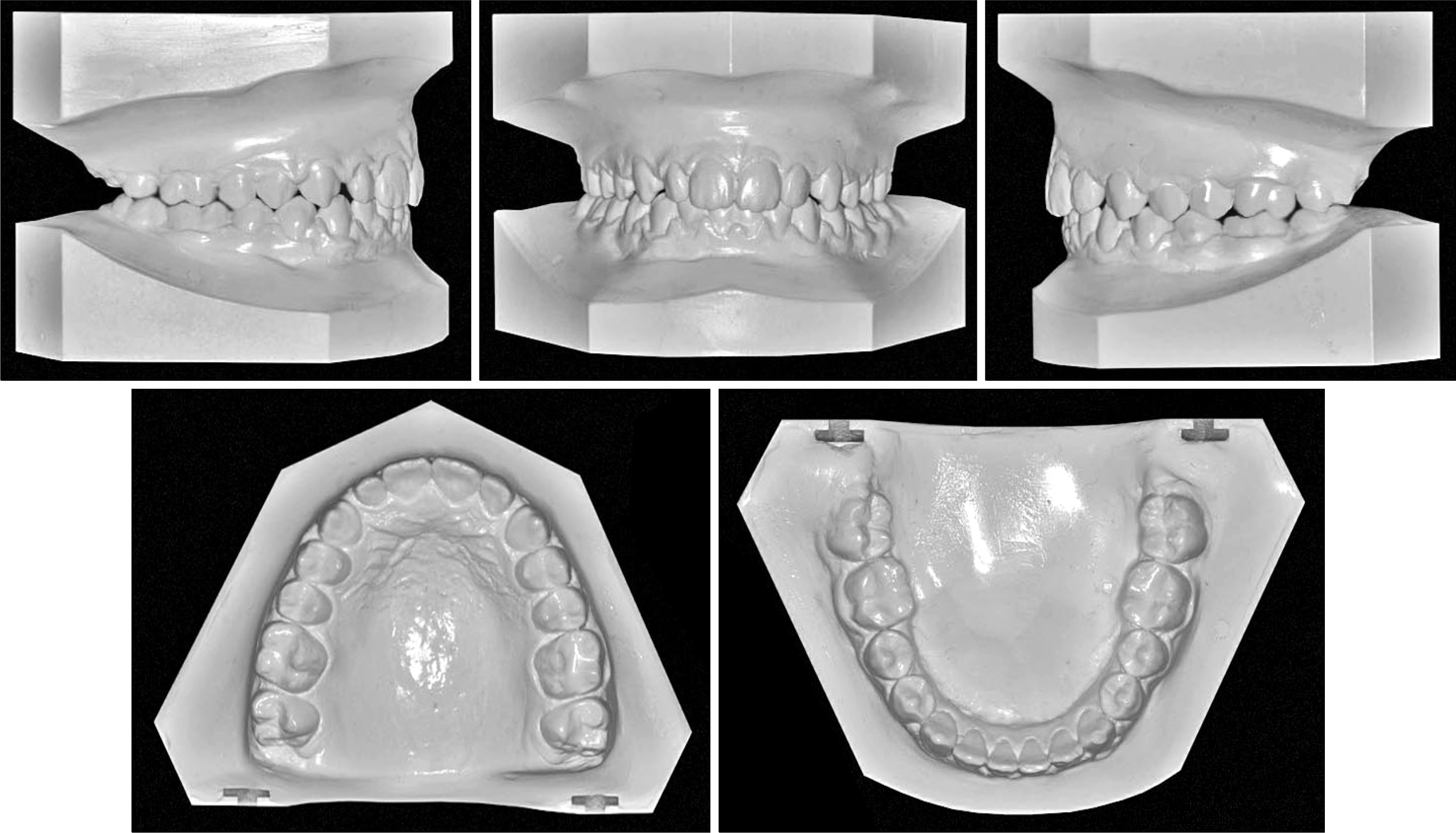
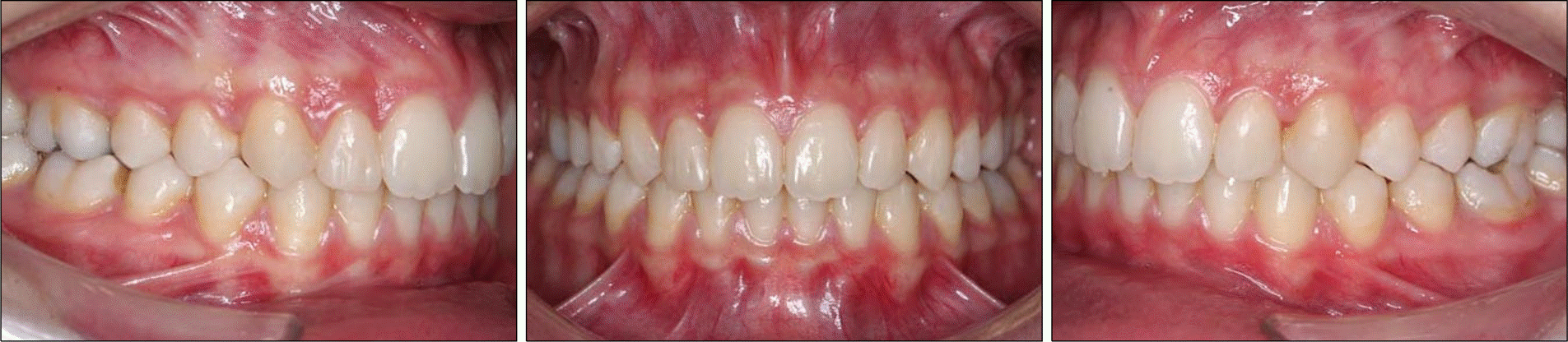
The aim of this report is to present an intraoral upper molar distalization system supported with zygomatic anchorage plates (Zygoma-gear Appliance, ZGA). This system was used for a 16-year-old female patient with a Class II molar relationship requiring molar distalization. The system consisted of bilateral zygomatic anchorage plates, an inner-bow and heavy intraoral elastics. Distalization of the upper molars was achieved in 3 months and the treatment results were evaluated from lateral cephalometric radiographs. According to the results of the cephalometric analysis, the maxillary first molars showed a distalization of 4 mm, associated with a distal axial inclination of 4.5°. The results of this study show that an effective upper molar distalization without anchorage loss can be achieved in a short time using the ZGA. We suggest that this new system may be used in cases requiring molar distalization in place of extraoral appliances.
REFERENCES
1.Cangialosi TJ., Meistrell ME Jr., Leung MA., Ko JY. A cephalometric appraisal of edgewise Class II nonextraction treatment with extraoral force. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1988. 93:315–24.

2.Wilson WL., Wilson RC. Modular 3D appliances. Problem solving in edgewise, straightwire and lightwire treatment. J Clin Orthod. 1984. 18:272–81.
3.Blechman AM. Magnetic force systems in orthodontics. Clinical results of a pilot study. Am J Orthod. 1985. 87:201–10.
4.Hilgers JJ. The pendulum appliance for Class II non-compliance therapy. J Clin Orthod. 1992. 26:706–14.
5.Byloff FK., Darendeliler MA. Distal molar movement using the pendulum appliance. Part 1: clinical and radiological evaluation. Angle Orthod. 1997. 67:249–60.
6.Taner TU., Yukay F., Pehlivanoglu M., Cakirer B. A comparative analysis of maxillary tooth movement produced by cervical headgear and pend-x appliance. Angle Orthod. 2003. 73:686–91.
7.Haydar S., Uner O. Comparison of Jones jig molar distalization appliance with extraoral traction. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2000. 117:49–53.

8.Carano A., Testa M. The distal jet for upper molar distali-zation. J Clin Orthod. 1996. 30:374–80.
9.Keles A., Pamukcu B., Tokmak EC. Bilateral maxillary molar distalization with sliding mechanics: keles slider. World J Orthod. 2002. 3:57–66.
10.Fortini A., Lupoli M., Giuntoli F., Franchi L. Dentoskeletal effects induced by rapid molar distalization with the first class appliance. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2004. 125:697–705.

11.Kärcher H., Byloff FK., Clar E. The Graz implant supported pendulum, a technical note. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2002. 30:87–90.

12.Keles A., Erverdi N., Sezen S. Bodily distalization of molars with absolute anchorage. Angle Orthod. 2003. 73:471–82.
13.Gelgör IE., Büyükyilmaz T., Karaman AI., Dolanmaz D., Kalayci A. Intraosseous screw-supported upper molar distali-zation. Angle Orthod. 2004. 74:838–50.
14.Kircelli BH., Pektas ZO., Kircelli C. Maxillary molar distalization with a bone-anchored pendulum appliance. Angle Orthod. 2006. 76:650–9.
15.Kinzinger GS., Diedrich PR., Bowman SJ. Upper molar distalization with a miniscrew-supported distal jet. J Clin Orthod. 2006. 40:672–8.
16.Escobar SA., Tellez PA., Moncada CA., Villegas CA., Latorre CM., Oberti G. Distalization of maxillary molars with the bone-supported pendulum: a clinical study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2007. 131:545–9.

17.Bayram M., Nur M., Kilkis D. The frog appliance for upper molar distalization: a case report. Korean J Orthod. 2010. 40:50–60.

18.Kim SJ., Chun YS., Jung SH., Park SH. Three dimensional analysis of tooth movement using different types of maxillary molar distalization appliances. Korean J Orthod. 2008. 38:376–87.

19.De Clerck H., Geerinckx V., Siciliano S. The zygoma anchorage system. J Clin Orthod. 2002. 36:455–9.
20.Sugawara J., Kanzaki R., Takahashi I., Nagasaka H., Nanda R. Distal movement of maxillary molars in nongrowing patients with the skeletal anchorage system. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006. 129:723–33.

21.Kaya B., Arman A., Uckan S., Yazici AC. Comparison of the zygoma anchorage system with cervical headgear in buccal segment distalization. Eur J Orthod. 2009. 31:417–24.

22.Burstone CJ. Application of bioengineering to clinical orthodontics. In: Graber TM, Vanarsdall RJ editors. Orthodontics. Current principles and techniques. 3rd ed.St Louis: CV Mosby;2000. p. 259–92.
Fig 1.
Schematic illustration of components (A) and the effective distalizing force vector of the ZGA (Zygoma-Gear Appliance) (B).
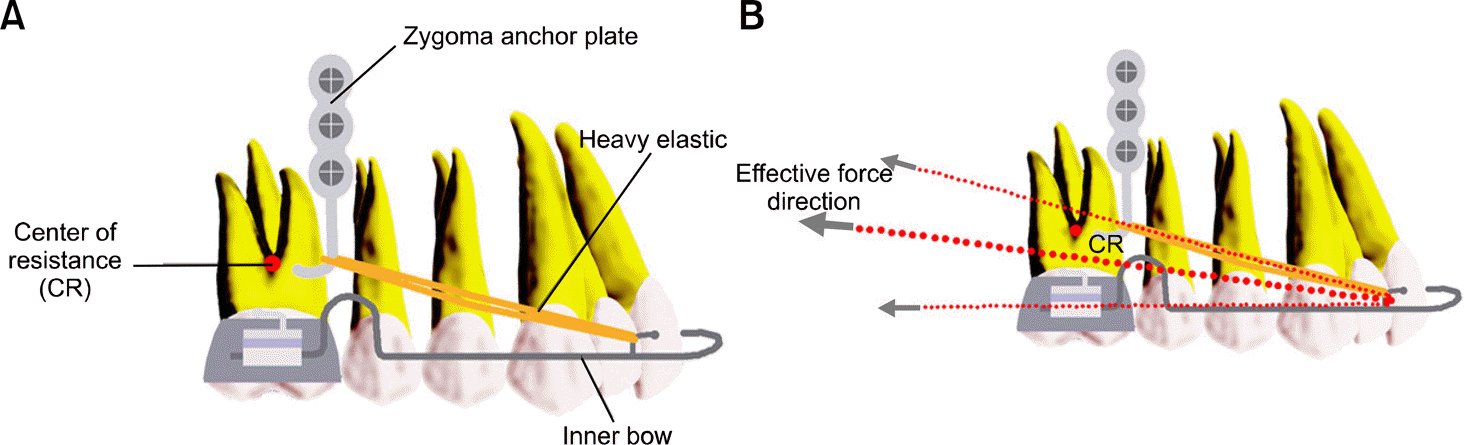
Fig 6.
Intraoral occlusal views of the mechanics for erupting of the impacted canines (A), and of the erupted canines (B).
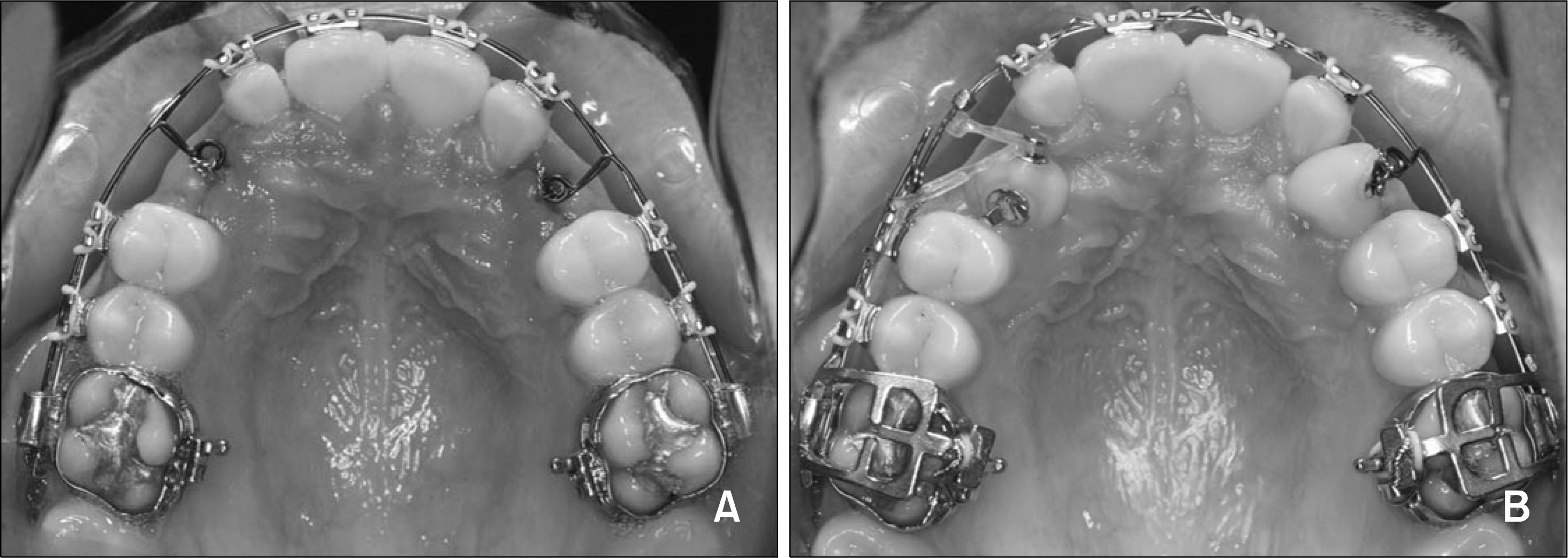
Fig 7.
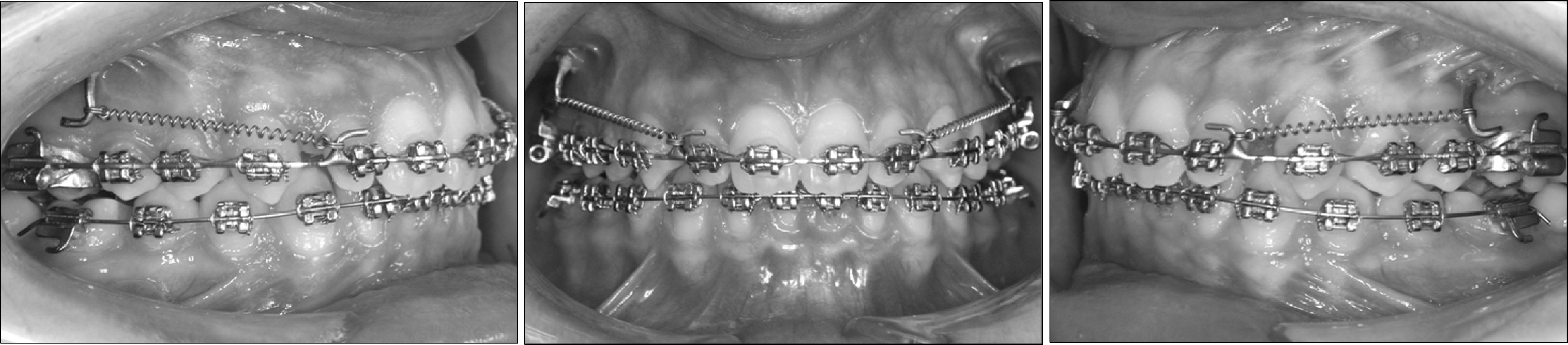
Application of the ZGA (Zygoma-Gear Appliance) at the beginning of distalization (A), and the views of the patient immediately after the distalization (B).

Fig 14.
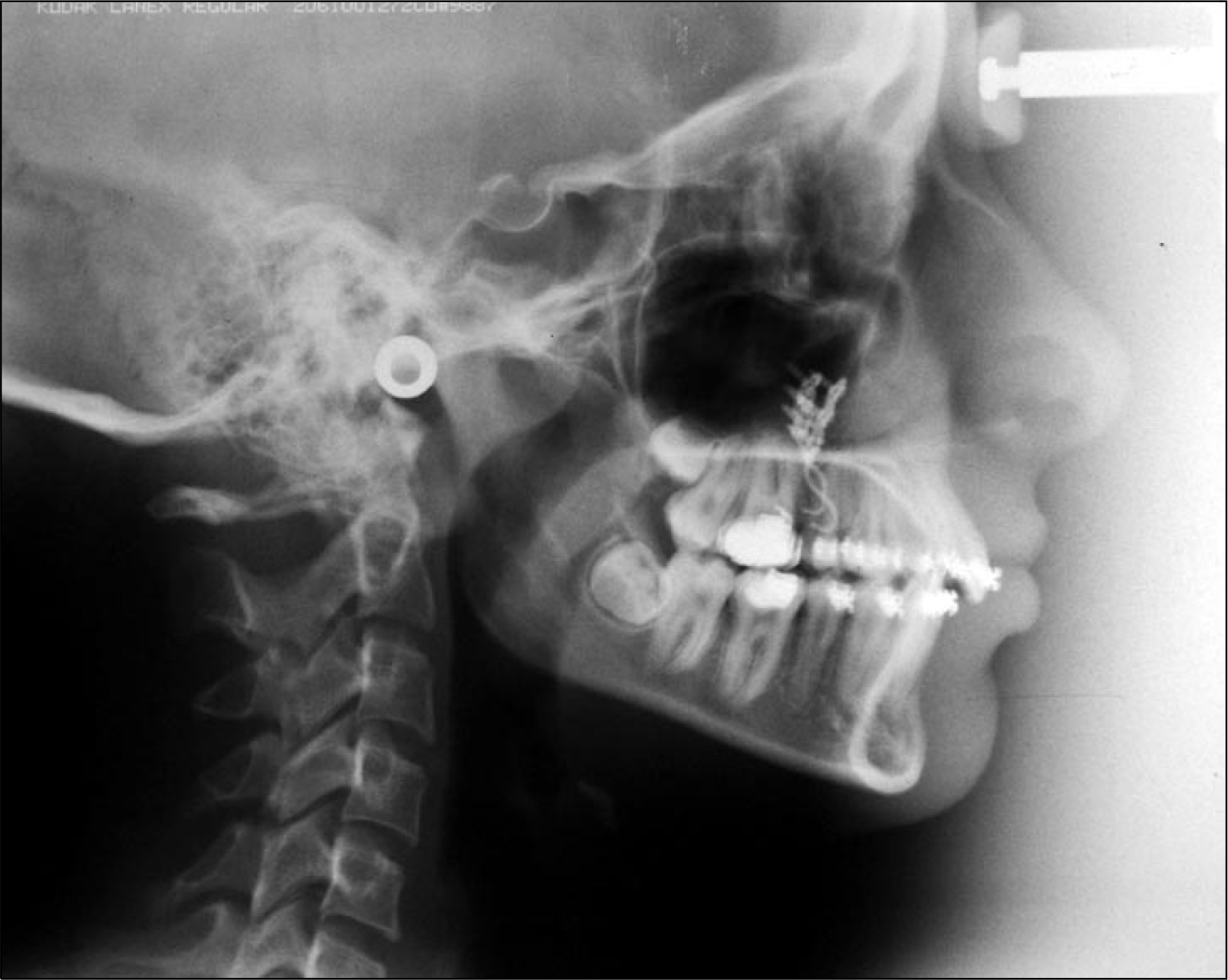
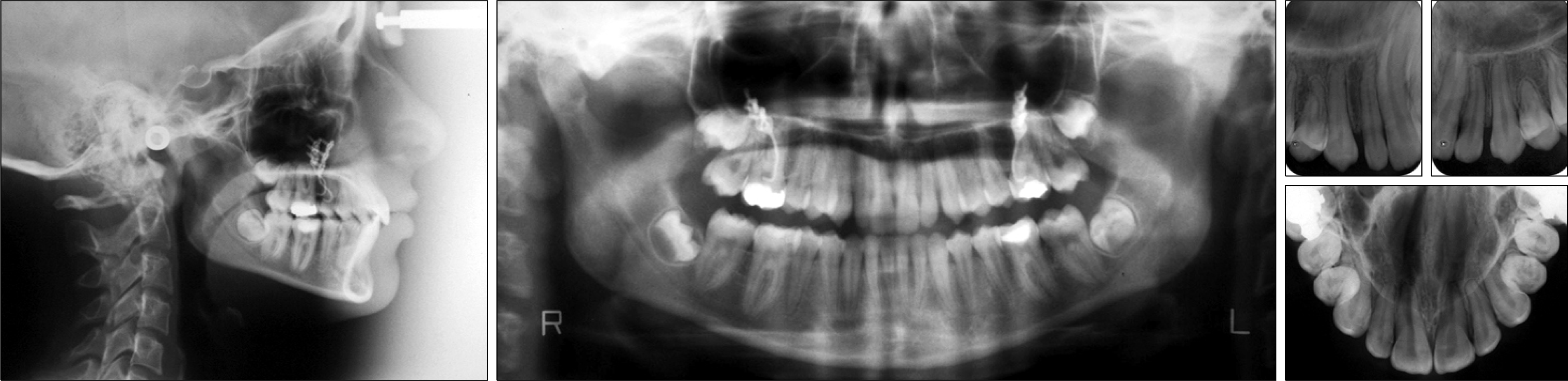
Superimpositions of pre- and post-distalization (A), and pre- and post-treatment cephalometric tracings (B).
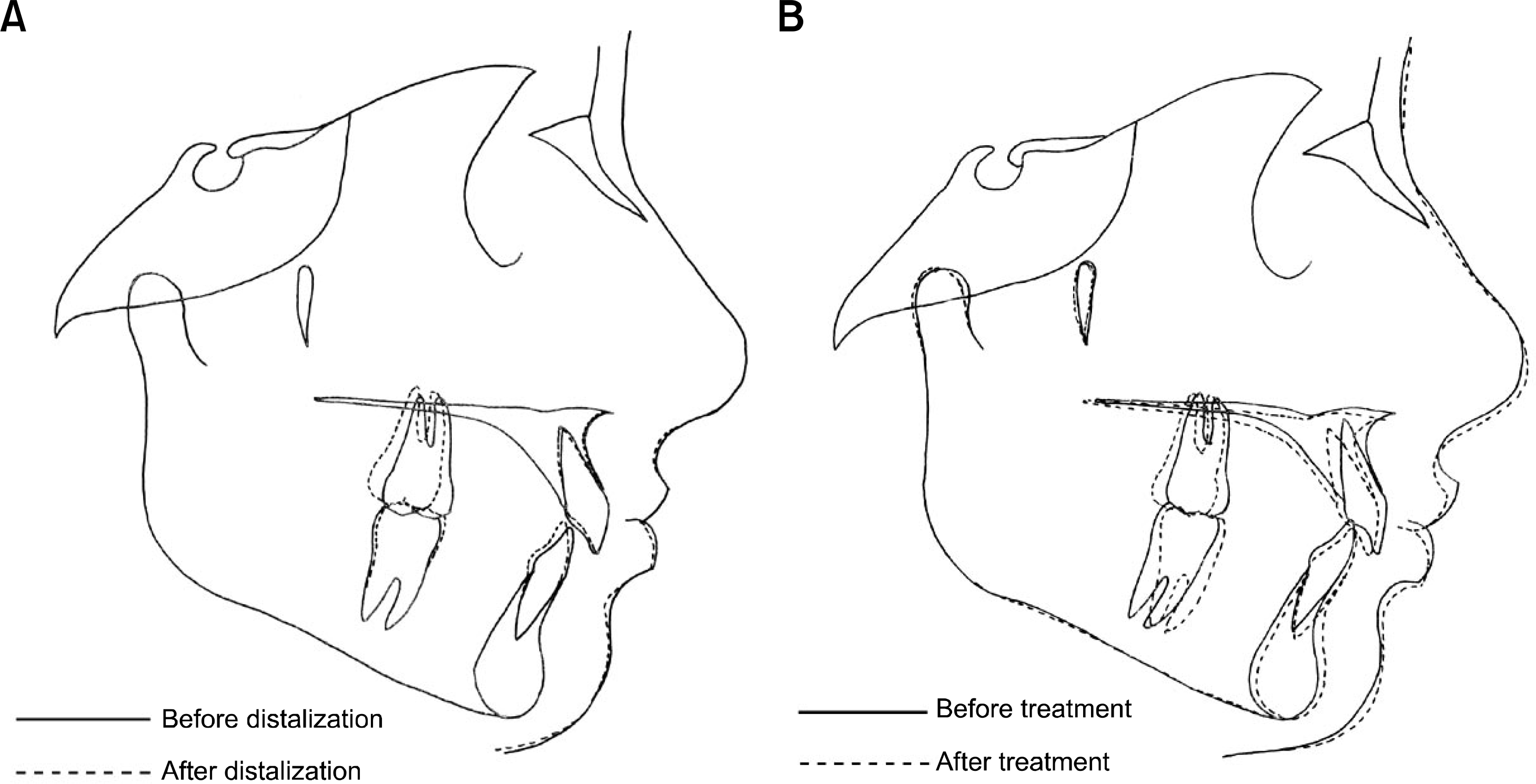
Table 1.
Cephalometric measurements of the patient




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download