Abstract
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) may be one of the most common pathogen in gastrointestinal tract. Although several recent articles have reported a decline in the prevalence of H. pylori infection in both children and adults over the last several years, H. pylori infection usually occurs early in life and persists for a long time. The role of H. pylori in some digestive diseases, such as gastritis, ulcer and gastric cancer has been well established. And the possible role of H. pylori as a trigger for some extraintestinal diseases in children and adults has been considered in the last year. H. pylori infection might be associated with refractory iron deficiency anemia, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, growth retardation and obesity etc, directly or indirectly. Most of the studies are classified as epidemiological, clinical researches about effects on extraintestinal manifestations after eradication, or case reports. This review describes the possibility of association with several extraintestinal diseases and H. pylori infection and their possible mechanisms based on reported studies in the world and our several studies, even though there are still many conflicting results about that.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Schematic representation of the substances released by the immune system following gastric colonization by Helicobacter pylori2). TNF: tumor necrosis factor, PAF: platelet activating factor, LT: leukotriene, PG: prostaglandin, IL: interleukin, INF: interferon.
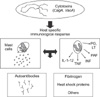
Fig. 2
Possible physiopathologic mechanism of the anemia7). Lf: lactoferrin, Tf: transferring, R: outer membrane receptor.
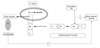
Table 1
Potential Association between Helicobacter pylori Infection and Iron-deficiency Anemia according to the Six Parameters in Infants and Children13)

References
1. Gasbarrini A, Carloni E, Gasbarrini G, Menard A. Helicobacter pylori and extragastric disease-other Helicobacters. Helicobacter. 2003. 8:68–76.

2. Gasbarrini A, Franceschi F, Armuzzi A, Ojetti V, Candelli M, Torre ES, et al. Extradigestive manifestations of Helicobacter pylori gastric infection. Gut. 1999. 45:Suppl 1. I9–I12.
3. Sherman PM, Lin FY. Extradigestive manifestations of Helicobacter infection in children and adolescents. Can J Gastroenterol. 2005. 19:421–424.

4. Fagan RP, Dunaway CE, Bruden DL, Parkinson AJ, Gessner BD. Controlled, household-randomized, openlabel trial of the effect of treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection on iron deficiency among children in rural Alaska: results at 40 months. J Infect Dis. 2009. 199:652–660.

5. Baysoy G, Ertem D, Ademoglu E, Kotiloglu E, Keskin S, Pehlivanoglu E. Gastric histopathology, iron status and iron deficiency anemia in children with Helicobacter pylori infection. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2004. 38:146–151.

6. Hershko C, Ianculovich M, Souroujon M. A hematologist's view of unexplained iron deficiency anemia in males: impact of Helicobacter pylori eradication. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2007. 38:45–53.

7. Barabino A. Helicobacer pylori-related iron deficiency anemia: a review. Helicobacter. 2002. 7:71–75.

8. DuBois S, Kearney DJ. Iron-deficiency anemia and Helicobacter pylori infection: a review of the evidence. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005. 100:453–459.

9. Choi JW. Does Helicobacter pylori infection relate to iron deficiency anemia in prepubescent children under 12 years of age? Acta Paediatr. 2003. 92:970–972.

10. Choi JW, Son BK. Soluble transferrin receptor concentration is not superior to log ferritin for evaluating erythropoiesis in adolescents with iron deficiency anemia. Clin Chim Acta. 2005. 355:83–89.

11. Choi JW. Sensitivity, specificity, and predictive value of serum soluble transferrin receptor at different stages of iron deficiency. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2005. 35:435–439.
12. Goo SI. Relationship between complete blood cell count profiles and histopatholoigic changes of gastric mucosa in children(dissertation). 2005. Jinju: Gyeongsang National Univ..
13. Son MH, Yeom JS, Park JS, Park ES, Seo JH, Lim JY, et al. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and iron-deficiency anemia in infants and children. Korean J Pediatr. 2009. 52:544–548.

14. Arnold DM, Bernotas A, Nazi I, Stasi R, Kuwana M, Liu Y, et al. Platelet count response to H. pylori treatment in patients with immune thrombocytopenic purpura with and without H. pylori infection: a systematic review. Haematologica. 2009. 94:850–856.

15. Treepongkaruna S, Sirachainan N, Kanjanapongkul S, Winaichatsak A, Sirithorn S, Sumritsopak R, et al. Absence of platelet recovery following Helicobacter pylori eradication in childhood chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: a multi-center randomized controlled trial. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2009. 53:72–77.

16. Ferrara M, Capozzi L, Russo R. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on platelet count in children with chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Hematology. 2009. 14:282–285.

17. Scandellari R, Allemand E, Vettore S, Plebani M, Randi ML, Fabris F. Platelet response to Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy in adult chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura seems to be related to the presence of anticytotoxin-associated gene A antibodies. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2009. 20:108–113.

18. Bai Y, Wang Z, Bai X, Yu Z, Cao L, Zhang W, et al. Cross-reaction of antibody against Helicobacter pylori urease B with platelet glycoprotein IIIa and its significance in the pathogenesis of immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Int J Hematol. 2009. 89:142–149.

19. Gasbarrini A, De Luca A, Fiore G, Ojetti V, Franceschi F, Di Campli C, et al. Helicobacter pylori and primary headache. Gastroenterol Int. 1997. 10:11–13.
20. Yiannopoulou KG, Efthymiou A, Karydakis K, Arhimandritis A, Bovaretos N, Tzivras M. Helicobacter pylori infection as an environmental risk factor for migraine without aura. J Headache Pain. 2007. 8:329–333.

21. Realdi G, Dore MP, Fastame L. Extradigestive manifestations of Helicobacter pylori infection: fact and fiction. Dig Dis Sci. 1999. 44:229–236.
22. Pinessi L, Savi L, Pellicano R, Rainero I, Valfrè W, Gentile S, et al. Chronic Helicobacter pylori infection and migraine: a case-control study. Headache. 2000. 40:836–839.

23. Mavromichalis I, Zaramboukas T, Giala MM. Migraine of gastrointestinal origin. Eur J Pediatr. 1995. 154:406–410.

24. Choi MB. Cellular changes in the gastroduodenal mucosa associated with Helicobacter pylori infection in children with headache(dissertation). 2003. Jinju: Gyeongsang National Univ..
25. Soylu OB, Ozturk Y. Helicobacter pylori infection: effect on malnutrition and growth failure in dyspeptic children. Eur J Pediatr. 2008. 167:557–562.

26. Bravo LE, Mera R, Reina JC, Pradilla A, Alzate A, Fontham E, et al. Impact of Helicobacter pylori infection on growth of children: a prospective cohort study. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2003. 37:614–619.

27. Passaro DJ, Taylor DN, Meza R, Cabrera L, Gilman RH, Parsonnet J. Acute Helicobacter pylori infection is followed by an increase in diarrheal disease among Peruvian children. Pediatrics. 2001. 108:E87.
28. Choe YH, Kim SK, Hong YC. Helicobacter pylori infection with iron deficiency anaemia and subnormal growth at puberty. Arch Dis Child. 2000. 82:136–140.

29. Pacifico L, Anania C, Osborn JF, Ferrara E, Schiavo E, Bonamico M, et al. Long-term effects of Helicobacter pylori eradication on circulating ghrelin and leptin concentrations and body composition in prepubertal children. Eur J Endocrinol. 2008. 158:323–332.

30. Wedi B, Raap U, Kapp A. Chronic urticaria and infections. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004. 4:387–396.

31. Abdou AG, Elshayeb EI, Farag AG, Elnaidany NF. Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with chronic urticaria: correlation with pathologic findings in gastric biopsies. Int J Dermatol. 2009. 48:464–469.

32. Magen E, Mishal J, Schlesinger M, Scharf S. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection equally improves chronic urticaria with positive and negative autologous serum skin test. Helicobacter. 2007. 12:567–571.

33. Fukuda S, Shimoyama T, Umegaki N, Mikami T, Nakano H, Munakata A. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication in the treatment of Japanese patients with chronic idiopathic urticaria. J Gastroenterol. 2004. 39:827–830.

34. Hernando-Harder AC, Booken N, Goerdt S, Singer MV, Harder H. Helicobacter pylori infection and dermatologic diseases. Eur J Dermatol. 2009. 19:431–444.
35. Dauden E, Jimenez-Alonso I, Garcia-Diez A. Helicobacter pylori and idiopathic chronic urticaria. Int J Dermatol. 2000. 39:446–452.

36. Başkan EB, Türker T, Gülten M, Tunali S. Lack of correlation between Helicobacter pylori infection and autologous serum skin test in chronic idiopathic urticaria. Int J Dermatol. 2005. 44:993–995.

37. Sackesen C, Sekerel BE, Orhan F, Kocabas CN, Tuncer A, Adalioglu G. The etiology of different forms of urticaria in childhood. Pediatr Dermatol. 2004. 21:102–108.

38. Kilic G, Guler N, Suleyman A, Tamay Z. Chronic urticaria and autoimmunity in children. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010. 21:837–842.

39. Saulsbury FT. Henoch-Schonlein purpura in children: report of 100 pateints and review of the literature. Medicine. 1999. 78:395–409.

40. Hernando-Harder AC, Nina B, Sergij G, Manfred VS, Herman H. Helicobacter pylori infection and dermatologic disease. Eur J Dermatol. 2009. 19:431–444.
41. Mytinger JR, James WP, Erin ST, Jeffrey W, Frank TS. Henoch-Schonlein purpura associated with Helicobacter pylori infection in a child. Pediatr Dermatol. 2008. 25:630–632.

42. Kellerman P. Henoch-Schonlein purpura in adults. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006. 48:1009–1016.
43. Davin JC, ten Berg IJ, Weeining JJ. What is the difference between IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schonlein purpura nephritis? Kidney Int. 2001. 59:823–834.

44. Barratt J, Bailey EM, Buck KS, Mailley J, Moayyedi P, Feehally J, et al. Exaggerated systemic antibody response to mucosal Helicobacter pylori infection in IgA nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 1999. 33:1049–1057.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download