Abstract
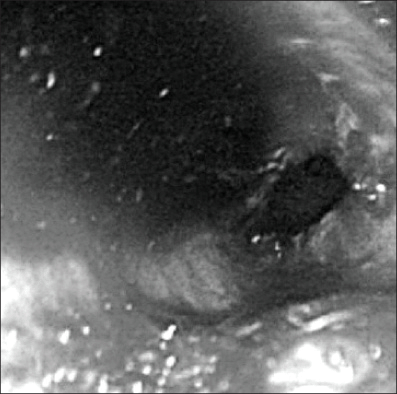
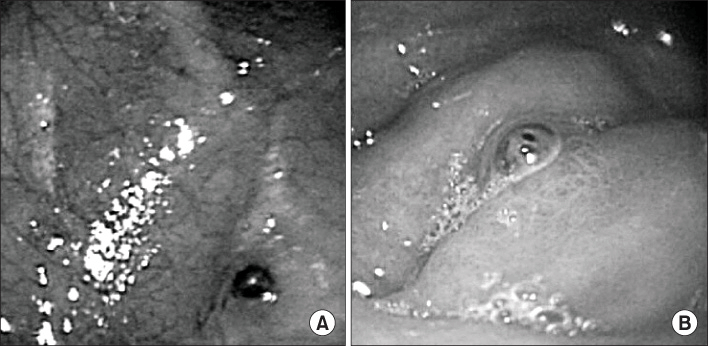
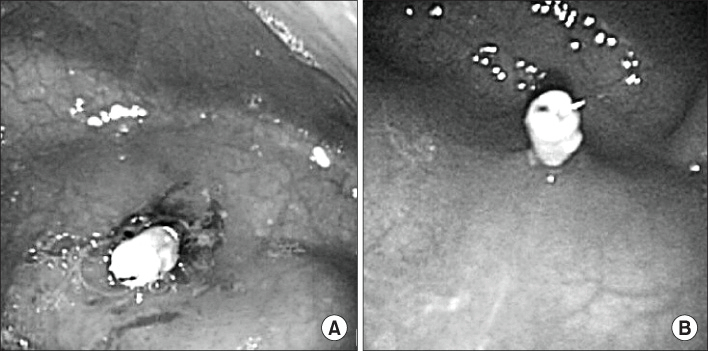
Dieulafoy's lesion is defined as a small mucosal defect overlying an abnormal, large caliber submucosal artery that protrudes through the gastrointestinal mucosa. This lesion is a rare cause of massive upper gastrointestinal bleeding in the pediatric population and extremely rare in neonates. We report a 1-day-old neonate who presented with massive gastrointestinal bleeding caused by a gastric Dieulafoy lesion, which was successfully treated by endoscopic hemoclipping without any complications.
REFERENCES
1. Veldhuyzen van Zanten SJ, Bartelsman JF, Schipper ME, Tytgat GN. Recurrent massive haematemesis from Dieulafoy vascular malformations a review of 101 cases. Gut. 1986; 27:213–222.
2. Stockwell JA, Werner HA, Marsano LS. Dieulafoy\'s lesion in an infant: a rare cause of massive gastrointestinal bleeding. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2000; 31:68–70.

3. Lee ES, Oh CH, Kim JW, Chung KS, Han SJ. A case of Dieulafoy\'s disease in a child. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999; 2:80–84.

4. Kim HJ, Shin JS, Seo JW. Endoscopic management with ethanol injection in a child with gastric Dieulafoy lesion. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2003; 6:187–191.

5. Lee YJ, Oh JM, Park SE, Park JH. Successful treatment of a gastric Dieulafoy\'s lesion with a hemoclip in a newborn infant. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 57:435–436.

6. Koo YH, Jang JS, Cho JH, Han SH, Ryu SH, Lee SW, et al. Endoscopic injection treatment for gastric Dieulafoy lesion in two newborn infants. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2005; 46:413–417.
7. Schmulewitz N, Baillie J. Dieulafoy lesions: a review of 6 years of experience at a tertiary referral center. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001; 96:1688–1694.

8. Miko TL, Thomazy VA. The caliber persistent artery of the stomach: A unifying approach to gastric aneurysm, Dieulafoy\'s lesion, and submucosal arterial malformation. Hum Pathol. 1988; 19:914–921.

9. Reilly HF, Al-Kawas FH. Dieulafoy\'s lesion: diagnosis and management. Dig Dis Sci. 1991; 36:1702–1707.
10. Durham JD, Kumpe DA, Rothbarth LJ, Van Stiegmann G. Dieulafoy disease: arteriographic findings and treatment. Radiology. 1990; 174:937–941.

11. Baettig B, Haecki W, Lammer F, Jost R. Dieulafoy\'s disease: Endoscopic treatment and follow up. Gut. 1993; 34:1418–1421.

12. Grisendi A, Lonardo A, Della casa G, Frazzoni M, Pulvirenti M, Ferrari AM, et al. Combined endoscopic and surgical management of Dieulafoy vascular malformation. J Am Coll Surg. 1994; 179:182–186.
13. Lee JH, Lee SH, Bae WY, Park JH, Park DH, Chung IK, et al. The usefulness of positional change in endoscopic hemostasis for bleeding Dieulafoy\'s lesion. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 32:168–172.
14. Lee YT, Walmsley RS, Leong RW, Sung JJ. Dieulafoy\'s lesion. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 58:236–243.

15. Parra-Blanco A, Takahashi H, Méndez Jerez PV, Kojima T, Aksoz K, Kirihara K, et al. Endoscopic management of Dieulafoy lesions of the stomach: a case study of 26 patients. Endoscopy. 1997; 29:834–839.

16. Kim YS, Choung RS, Kim KO, Koh DW, Cho YJ, Kim HJ, et al. A case of Dieulafoy\'s lesion of the terminal ileum treated by colonoscopic electro coagulation. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 23:499–502.
17. Jeong EJ, Bae YM, Kim KH, Heo J, Heo JH, Chu HJ, et al. Clinical feature and the effects of endoscopic band ligation of Dieulafoy-like lesion. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 24:267–272.
18. Bedford RA, van Stolk R, Sivak MV Jr, Chung RS, Van Dam J. Gastric perforation after endoscopic treatment of a Dieulafoy\'s lesion. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992; 87:244–247.
19. Ko JH, Lee KJ, Jeoung ST, Kwon OY, Ko YY, Jee SB, et al. Comparison of various endoscopic injection therapy and hemoclipping for bleeding peptic ulcers. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 1998; 18:817–824.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download