Abstract
With the increasing use of magnets in toys, magnet ingestion is becoming a serious problem in children. Two or more magnets may attract across the gastrointestinal tract leading to pressure necrosis, perforation, fistula, volvulus or obstruction. We report a case of a 12-year-old boy with autism who presented with vomiting during seven days due to ingestion of 14 magnetic rods. Under general anesthesia, 5 of 14 magnets were removed from the second portion of the duodenum using a magnetic probe during endoscopy. The remaining magnets were not visible in the duodenum. A plain radiograph taken the next day revealed that the remaining magnets were impacted in the descending-sigmoid junction. One magnet passed spontaneously. However the other 8 magnets did not pass through the junction for 7 days. Five of 8 impacted magnets were removed by a colonoscopic procedure. After 2 hours of colonoscopy, one by one, the remaining three magnets spontaneously passed.
Figures and Tables
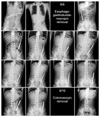 | Fig. 1Serial plain radiographs of the abdomen demonstrate foreign bodies. Five magnetic rods were found in the 2nd portion of the duodenum and removed by endoscopy performed on the 6th of August. After ten days, colonoscopy was performed and 5 of the remaining magnets were successfully removed; they were linearly stuck to each other and firmly impacted in the descending sigmoid junction. |
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Gastrointestinal injuries from magnet ingestion in children - United States, 2003-2006. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2006. 55:1296–1300.
2. Lee WH, Min YD, Moon KR. A case of gastroduodenal fistula caused by ingested magnetic foreign bodeis. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008. 11:84–88.

3. Kwak BG, Moon JS, Jang HO, Nam SY, Kim DW, Lee CG, et al. Small bowel-mesentery-small bowel fistula caused by ingested magnets. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005. 8:60–63.

4. Kim MJ, Kwak AJ, Choi KH. Gastric ulcer due to three magnets ingestion in a 37-month-old girl. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2002. 5:68–72.

5. Seo JK. Endoscopic management of gastrointestinal foreign bodies in children. Indian J Pediatr. 1999. 66:1 Suppl. S75–S80.
6. Ohno Y, Yoneda A, Enjoji A, Furui J, Janematsu T. Gastroduodenal fistula caused by ingested magnets. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005. 61:109–110.

7. Seo JK. Endoscopic management of gastrointestinal foreign bodies in children:a clinical practice guideline. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007. 10:Suppl 1. 64–69.
8. Hwang JB, Park MH, Choi SO, Park WH, Kim AS. How strong construction toy magnets are! A gastro-gastro-duodenal fistula formation. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007. 44:291–292.

9. Chung JH, Kim JS, Song YT. Small bowel complication caused by magnetic foreign body ingestion of children. J Pediatr Surg. 2003. 38:1548–1550.

10. Cauchi JA, Shawis RN. Multiple magnet ingestion and gastrointestinal morbidity. Arch Dis Child. 2002. 87:539–540.

11. Kubota Y, Tokiwa K, Tanaka S, Iwai N. Intestinal obstruction in an infant due to magnet ingestion. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 1995. 5:119–120.

12. Nui A, Hirama T, Katsuramaki T, Maeda T, Meguro M, Nagayama M, et al. An intestinal volvulus caused by multiple magnet ingestion: an unexpected risk in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2005. 40:e9–e11.

13. Chang YS, Song JY, Choi SI. Ileal perforation caused by ingestion of multiple magnets. J Korean Surg Soc. 2009. 76:270–272.

14. Shah SK, Tieu KK, Tsao K. Intestinal complications of magnet ingestion in children from the pediatric surgery perspective. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2009. 19:334–337.

15. Canadian Paediatric Surveillance Program. Magnets in the bowel: a sticky problem! Paediatr Child Health. 2008. 13:118.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download