Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to assess changes in neuropeptide Y (NPY) immunoreactivity in the hypothalamus and interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) in the small intestine of rats fed high-fat diets (HFD).
Methods
Male Sprague-Dawley rats (200~250 g body weight) were randomly divided into two groups, which were the control group (normal chow diet for 6 weeks), and the HFD group (rodent diet with 60% kcal fat for 6 weeks). The immunoreactivity of NPY in the hypothalamus and ICC in the small intestine was evaluated after every feed for 6 weeks.
Results
NPY immunoreactivity was observed strongly in the hypothalamic nuclei in the HFD group compared to the control group. The numbers of NPY-immunoreactive (IR) cells were significantly higher in the paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus in the HFD group than in the control group. In the region of Auerbach's plexus (AP) of small intestine, the staining intensity of the ICC-IR cells was reduced in the HFD group compared to the control group. The numbers of ICC in the small intestine with HFD, including ICC in the inner circular and outer longitudinal muscle were significantly lower than in the control group.
Figures and Tables
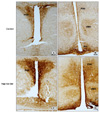 | Fig. 1NPY immunoreactivity from a control (A, B) and a high-fat diet (HFD; C, D) group in the rat hypothalamus. NPY immunoreactivity was observed in the PVH, VMH and Arc in both groups. NPY immunoreactivity was strongly detected in these hypothalamic nuclei from the HFD compared to the control group. Arc: arcuate nucleus, PVH: paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, VMH: ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus, HFD: high-fat diet. Scale bars=100µm. |
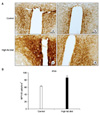 | Fig. 2(A) Representative photomicrographs of the NPY immunoreactivity from a control (a, b) and a HFD (c, d) group in the PVH. The PVH contained large numbers of NPY-IR cell bodies and axon terminals in both groups. The staining intensity of NPY-IR cells was increased in the HFD group compared to the control group. Scale bars=100µm. (B) The numbers of NPY-IR cells in the PVH of the control and the HFD group. PVH: paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, HFD: high-fat diet. *p<0.05. |
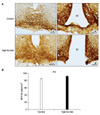 | Fig. 3(A) Representative photomicrographs of the NPY immunoreactivity from a control (a, b) and a HFD (c, d) group in the Arc. Strong stained NPY-IR cells were observed in the Arc in both groups. Scale bars= 100µm. (B) The numbers of NPY-IR cells in the Arc of the control and the HFD group. Arc: arcuate nucleus, HFD: high-fat diet. |
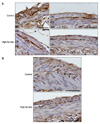 | Fig. 4(A) Representative photomicrographs of the c-kit immunoreactivity from the control and the HFD group in the small intestine. In the region of Auerbach's plexus (AP), the staining intensity of the c-kit IR cells was reduced in the HFD group compared to the control group. (B) Small arrows indicate c-kit IR cells within the AP in the control group. AP: Auerbach's (myenteric) plexus, CM: circular muscle layer, LM: longitudinal muscle layer, SM: submucosa, HFD: high-fat diet. Scale bars=100µm. |
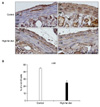 | Fig. 5(A) Representative photomicrographs of the c-kit immunoreactivity from the control and the HFD group in the whole musculature of small intestine. In the inner CM and outer LM, the staining intensity of the c-kit IR cells was reduced in the HFD group compared to the control group. Scale bars=100µm. (B) Quantification of the c-kit-IR cell proportions in the small intestine from the controls and the HFD groups. *p<0.05. AP: Auerbach's (myenteric) plexus, CM: circular muscle layer, LM: longitudinal muscle layer, SM: submucosa, HFD: high-fat diet. |
References
1. Schwartz MW, Woods SC, Porte D Jr, Seeley RJ, Baskin DG. Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature. 2000. 404:661–671.

2. Stanley BG, Anderson KC, Grayson MH, Leibowitz SF. Repeated hypothalamic stimulation with neuropeptide Y increases daily carbohydrate and fat intake and body weight gain in female rats. Physiol Behav. 1989. 46:173–177.

3. Kotz CM, Briggs JE, Grace MK, Levine AS, Billington CJ. Divergence of the feeding and thermogenic pathways influenced by NPY in the hypothalamic PVN of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1998. 275:R471–R477.

4. Lin EJ, Sainsbury A, Lee NJ, Boey D, Couzens M, Enriquez R, et al. Combined deletion of Y1, Y2, and Y4 receptors prevents hypothalamic neuropeptide Y overexpression-induced hyperinsulinemia despite persistence of hyperphagia and obesity. Endocrinology. 2006. 147:5094–5101.

5. MacLean PS, Higgins JA, Johnson GC, Fleming-Elder BK, Peters JC, Hill JO. Metabolic adjustments with the development, treatment, and recurrence of obesity in obesity-prone rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2004. 287:R288–R297.

6. Klem ML, Wing RR, Lang W, McGuire MT, Hill JO. Does weight loss maintenance become easier over time? Obes Res. 2000. 8:438–444.

7. Julan L, Guan H, van Beek JP, Yang K. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta suppresses 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 gene expression in human placental trophoblast cells. Endocrinology. 2005. 146:1482–1490.

8. Ordög T, Hayashi Y, Gibbons SJ. Cellular pathogenesis of diabetic gastroenteropathy. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2009. 55:315–343.
9. Marchesini G, Brizi M, Bianchi G, Tomassetti S, Bugianesi E, Lenzi M, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a feature of the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes. 2001. 50:1844–1850.

10. Krssak M, Falk Petersen K, Dresner A, DiPietro L, Vogel SM, Rothman DL, et al. Intramyocellular lipid concentrations are correlated with insulin sensitivity in humans: a 1H NMR spectroscopy study. Diabetologia. 1999. 42:113–116.

11. Lara-Castro C, Garvey WT. Intracellular lipid accumulation in liver and muscle and the insulin resistance syndrome. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2008. 37:841–856.

12. Petersen KF, Dufour S, Shulman GI. Decreased insulin-stimulated ATP synthesis and phosphate transport in muscle of insulin-resistant offspring of type 2 diabetic parents. PLoS Med. 2005. 2:e233.

14. Nguyen AD, Herzog H, Sainsbury A, Neuropeptide Y, Peptide YY. Important regulators of energy metabolism. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2011. 18:56–60.
15. Allen YS, Adrian TE, Allen JM, Tatemoto K, Crow TJ, Bloom SR, et al. Neuropeptide Y distribution in the rat brain. Science. 1983. 221:877–879.

16. Morris BJ. Neuronal localisation of neuropeptide Y gene expression in rat brain. J Comp Neurol. 1989. 290:358–368.

17. Hanson ES, Dallman MF. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) may integrate responses of hypothalamic feeding systems and the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis. J Neuroendocrinol. 1995. 7:273–279.

18. White BD, Dean RG, Edwards GL, Martin RJ. Type II corticosteroid receptor stimulation increases NPY gene expression in basomedial hypothalamus of rats. Am J Physiol. 1994. 266:R1523–R1529.

19. Kuo LE, Czarnecka M, Kitlinska JB, Tilan JU, Kvetňanský R, Zukowska Z. Chronic stress, combined with a high-fat/high-sugar diet, shifts sympathetic signaling toward neuropeptide Y and leads to obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008. 1148:232–237.

20. Ordog T, Takayama I, Cheung WK, Ward SM, Sanders KM. Remodeling of networks of interstitial cells of Cajal in a murine model of diabetic gastroparesis. Diabetes. 2000. 49:1731–1739.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download