Abstract
Food allergy is an adverse immune response to foods. The prevalence of food allergy vary by age, diet, and many other factors. Based on the immunological mechanism, food allergies may be classified in a IgE-mediated diseases, which are the best-characterized food allergy reactions, non-IgE-medicated diseases, and mixed type diseases. In children, the GI tract seems to be the most common target organ. Generally, IgE-mediated reactions have an acute onset, whereas non-IgE-mediated reactions have a late onset. The most food allergy with GI manifestation involve non-IgE-mediated reactions. The evaluation of a child with suspected food allergy includes medical history, physical examination, screening test and the response to elimination diet and to oral food challenge. The diagnosis of non-IgE-mediated food allergies using a screening test is difficult. In this review, investigate the diagnostic criteria and manifestations of several non-IgE-mediated allergic diseases and the diagnostic method in the field of a pediatric gastroenterology.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 4
Algorithm after oral cow's milk challenge for diagnosis of typical cow's milk protein-induced enterocolitis. Adapted from ref. 26.
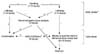
Table 8
Clinical Features Suggestive of Food Protein-Induced Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders In Infants and Young Children

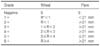
Table 9
Grading System for Skin Prick Test
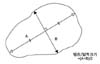
A: allergen, H: histamine, R: ratio of wheal of allergen and histamine (1 mg/ml). Adapted from ref. 21.
Table 10
Predictive Values of Food Allergen-Specific Immunoglobulin E Levels

PL: prodictive level, PPV: positive predictive value. *Infants<2 years. Adapted from ref. 22.
Table 12
Histologic Features Associated with EE

None of the features are pathognomonic of EE. Adapted from ref. 23.
Table 13
Oral food challenge in food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome

*Lower dose recommended in children with history of previous severe reaction. Adapted from ref. 25.
References
2. Hong SJ, Ahn KM, Lee SY, Kim KE. The prevalences of asthma and allergic diseases in Korean children. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2008. 18:15–25.

3. Cianferoni A, Spergel JM. Food allergy: review, classification and diagnosis. Allergol Int. 2009. 58:457–466.

4. Husby S. Food allergy as seen by a paediatric gastroenterologist. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008. 47:Suppl 2. S49–S52.

5. Chehade M. IgE and non-IgE-mediated food allergy: treatment in 2007. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007. 7:264–268.

6. Garcia-Careaga M Jr, Kerner JA Jr. Gastrointestinal manifestations of food allergies in pediatric patients. Nutr Clin Pract. 2005. 20:526–535.

7. Sampson HA, Anderson JA. Summary and recommendations: classification of gastrointestinal manifestations due to immunologic reactions to foods in infants and young children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2000. 30:Suppl. S87–S94.

8. Hwang JB, Choi SY, Kwon TC, Oh HK, Kam S. Clinical observations of gastrointestinal cow milk allergy in children according to a new classification. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2004. 7:40–47.

9. Mansueto P, Montalto G, Pacor ML, Esposito-Pellitteri M, Ditta V, Lo Bianco C, et al. Food allergy in gastroenterologic diseases: review of literature. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. 12:7744–7752.

12. Boné J, Claver A, Guallar I, Plaza AM. Allergic proctocolitis, food-induced enterocolitis: immune mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2009. 37:36–42.

13. Chung HL, Hwang JB, Park JJ, Kim SG. Expression of transforming growth factor beta1, transforming growth factor type I and II receptors, and TNF-alpha in the mucosa of the small intestine in infants with food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002. 109:150–154.

14. Pratt CA, Demain JG, Rathkopf MM. Food allergy and eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders: guiding our diagnosis and treatment. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 2008. 38:170–188.

15. Bischoff SC. Food allergy and eosinophilic gastroenteritis and colitis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. 10:238–245.

16. Furuta GT, Forbes D, Boey C, Dupont C, Putnam P, Roy S, et al. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases (EGIDs). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008. 47:234–238.

17. Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGID). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004. 113:11–28. quiz 9.

18. King J, Khan S. Eosinophilic esophagitis: perspectives of adult and pediatric gastroenterologists. Dig Dis Sci. 2010. 55:973–982.

19. Chehade M, Aceves SS. Food allergy and eosinophilic esophagitis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. 10:231–237.

20. Heine RG. Allergic gastrointestinal motility disorders in infancy and early childhood. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2008. 19:383–391.

22. Berni Canani R, Ruotolo S, Discepolo V, Troncone R. The diagnosis of food allergy in children. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2008. 20:584–589.

23. Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Collins MH, Gupta SK, Justinich C, Putnam PE, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: a systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology. 2007. 133:1342–1363.

25. Nowak-Wegrzyn A, Muraro A. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009. 9:371–377.

26. Hwang JB. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome: an update on clinical approaches and its pathophysiology. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007. 10:117–128.

27. Nam SY. Food allergy; diagnosis and treatment. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2004. 14:119–126.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print










 XML Download
XML Download