Abstract
Intestinal duplication cysts are characterized by the attachment to some part of the gastrointestinal tract with which a blood supply is shared, and have an epithelial lining resembling some part of the alimentary tract. A 15-month-old female was admitted to our hospital with cyclic irritability, vomiting, and blood-tinged stool. The results of an ultrasound showed an ileocolic intussusception and a 1.3 cm cystic mass had double-wall sign and a Y-configuration with an adjacent ileal loop. She had a past history of two ileocolic intussusceptions. The cystic mass was considered to be a pathologic lead point, so resection and end-to-end anastomosis was performed. The gross and histologic evaluation of the specimen demonstrated a 2.4×2.4 cm cystic mass containing yellow mucoid fluid and the cyst wall was lined with intestinal and gastric mucosa and enclosed by a layer of muscle, which was shared with the adjacent ileum.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
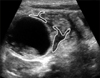
(A) Ultrasound shows a cystic mass with a double-layered wall consisting of an echogenic inner layer (black arrow) and a hypoechoic outer layer (white arrow). (B) A Y-configuration is shown at the junction of the cyst and adjacent small bowel (oval line).

Fig. 2
On a contrast-enhanced CT scan, a 2.4 cm cystic-like mass with an enhancing wall (arrow) is demonstrated in the left lower peritoneal cavity adjacent to an ileal loop.
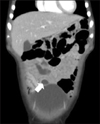
Fig. 4
(A) Low-power histologic photomicrograph demonstrates the cyst with a layer of muscle (arrowhead) is shared with adjacent ileum, and the white box represents a low magnification lesion of (B) (H&E, ×12.5). (B) The cystic outer wall is lined with shared normal intestinal mucosa (yellow arrow) and the inner wall is lined with ectopic gastric mucosa (black arrow; H&E, ×40).

Fig. 5
The cystic wall consists of inner hyperechoic and outer hypoechoic layers, known as the double-wall sign, and two Y-configurations (white line) are visible at the junctions of the cyst and adjacent small bowel loop (ref. 14).
References
1. Lee SH, Kim KH, Jung SE, Lee SC, Park KW, Kim WK. Clinical Characteristics and Management of Congenital Intestinal Duplication. J Korean Surg Soc. 2001. 61:530–536.
2. Park SY, Park JY. Intestinal Duplication in Childhood. J Korean Surg Soc. 2008. 75:262–267.
3. Kim HK, Woo ZH, Sohn JH. A report of 2 cases of duplication of the alimentary tract. J Korean Surg Soc. 1971. 13:456–459.
4. Choi GW, Kang GS, Park BU, Lee WM, Jeen YS, Lee TW. A case ileal duplication with intussusception. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1992. 35:563–568.
5. Cheng G, Soboleski D, Daneman A, Poenaru D, Hurlbut D. Sonographic pitfalls in the diagnosis of enteric duplication cysts. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005. 184:521–525.

6. Milbrandt K, Sigalet D. Intussusception associated with a Meckel's diverticulum and a duplication cyst. J Pediatr Surg. 2008. 43:e21–e23.

7. Srivastava P, Gangopadhyay AN, Kumar V, Upadhyaya VD, Sharma SP, Jaiman R, et al. Noncommunicating isolated enteric duplication cyst in childhood. J Pediatr Surg. 2009. 44:e9–e10.

8. Chung JY, Park DC. A Case of Intra-Abdominal Esophageal Duplication Cyst. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2001. 4:224–227.

9. Navarro O, Daneman A. Intussusception. Part 3: Diagnosis and management of those with an identifiable or predisposing cause and those that reduce spontaneously. Pediatr Radiol. 2004. 34:305–312.
10. Lee KS, Park YJ. Clinical analysis of recurrent intussusception and the pathologic lead point in a single center. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2009. 12:163–170.

11. De Roeck A, Vervloessem D, Mattelaer C, Schwagten K. Isolated enteric duplication cyst with respiratory epithelium: case report and review of the literature. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2008. 18:337–339.

12. Kim YJ, Kim YK, Jeong YJ, Moon WS, Gwak HJ. Ileal duplication cyst: Y-configuration on in vivo sonography. J Pediatr Surg. 2009. 44:1462–1464.

13. Dias AR, Lopes RI, do Couto RC, Bonafe WW, D'Angelo L, Salvestro ML. Ileal duplication causing recurrent intussusception. J Surg Educ. 2007. 64:51–53.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download