Abstract
Purpose
Since there are few studies involving acute pancreatitis in children, we reviewed our experience with this medical condition to describe the clinical features.
Methods
A retrospective analysis was conducted by reviewing the medical records of 41 patients with AP who were admitted to the Department of Pediatrics of Pusan National University Hospital between January 1996 and June 2007.
Results
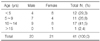
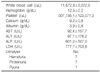
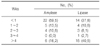
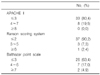
Twenty males and 21 females (mean age, 8.7±4.5 years) were included. In 22 patients (53.7%), no definitive causes were found. The most common etiologies were choledochal cysts (22.0%). Necrotizing pancreatitis was diagnosed in 5 patients (12.2%), and recurrent acute pancreatitis in 4 patients (9.8%). CT findings included pancreatic swelling (43.9%), peripancreatic fluid collection (29.3%), ascites (24.4%), and peripancreatic fat necrosis (12.2%). Serum amylase and lipase levels at diagnosis were 535.3±553.2 and 766.2±723.6 U/L, respectively, and were normalized within 1 week in 22 and 14 patients, respectively. On the basis of the Balthazar scale, 2 patients were diagnosed with severe AP. In 4 patients (9.8%), a surgical procedure was indicated. Major complications included ascites (32.3%), sepsis (16.1%), and pseudocyst and renal impairments (12.9%). Two patients died from multi-organ failure.
Conclusion
The etiologies of AP in children are varied. Most children have a single episode and a self-limited course. However, AP of childhood still carries significant morbidity and mortality. Early diagnosis, appropriate treatment according to disease severity, and management of complications are important.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Lopez MJ. The changing incidence of acute pancreatitis in children: a single-institution perspective. J Pediatr. 2002. 140:622–624.

2. Nydegger A, Hein RG. Changing incidence of acute pancreatitis: 10-year experience at the Royal Children's Hospital, Melbourne. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. 22:1313–1316.

3. Werlin SL, Kugathasan S, Frautschy BC. Pancreatitis in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2003. 37:591–595.

5. Cho JH, Lee TS, Ko YG, Oh SM. Acute pancreatitis in children. J Korean Assoc Pediatr Surg. 1996. 2:17–25.

6. Choi YI, Seo JK. Evaluation of severity of childhood pancreatitis with multiple factor scoring systems. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1995. 38:1653–1663.
7. Park JE, Kim KM. Etiology and analysis of severity in childhood pancreatitis. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999. 2:194–203.

8. Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE. APACHE II: A severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med. 1985. 13:818–829.
9. Balthazar EJ, Robinson DL, Megibow AJ, Ranson JH. Acute pancreatitis: value of CT in establishing prognosis. Radiology. 1990. 174:331–336.

10. Haddock G, Youngson CG. Acute pancreatitis in children: a 15-year review. J Pediatr Surg. 1994. 29:719–722.

11. Nydegger A, Couper RT, Oliver MR. Childhood pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006. 21:499–509.

12. Choi WI, Ahn YH, Park CS, Jo J, Yoo BD, Lee DP. A clinical study of acute pancreatitis. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 1998. 9:277–285.
13. Eichelberger MR, Hoelzer DJ, Koop CE. Acute pancreatitis: the difficulties of diagnosis and therapy. J pediatr Surg. 1983. 17:244–254.

14. Blamey Sl, Imrie CW, D'Neil J, Gilmour WH, Carter DC. Prognostic factors in acute pancreatitis. Gut. 1984. 25:1340–1346.

15. Ranson JHC, Rifkind KM, Roses DF, Fink SO, Eng K, Spencer FC. Prognostic signs and the roles of operative management in acute pancreatitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1974. 139:69–81.
16. Wilson C, Heath DI, Imrie CW. Prediction of outcome in acute pancreatitis comparative study of APACHE II, clinical assessment and multiple factor scoring systems. Br J Surg. 1990. 77:1260–1264.

17. Tran DD, Cuesta MA. Evaluation of severity in patients with acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992. 87:604–608.
18. Chatzicostas C, Roussomoustakaki M, Vardas E, Romanos J, Kouroumalis EA. Balthazar computed tomography severity index is superior to Ranson criteria and APACHE II and III scoring systems in predicting acute pancreatitis outcome. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003. 36:253–260.

19. Singer MV, Gyr K, Sarles H. Revised classification of pancreatitis. Report of the Second International Symposium on the Classification of Pancreatitis in Marseille, France, March 28-30, 1984. Gastroenterology. 1985. 89:683–685.
20. Marik PE, Zaloga GP. Meta-analysis of parenteral nutrition versus enteral nutrition in patients with acute pancreatitis. BMJ. 2004. 328:1407.

21. Frank AW, Maik K, Ina H, Thomas F, Christoph AJ, Hans G, et al. Effects of octreotide in acute hemorrhagic necrotizing pancreatitis in rats. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. 22:1872–1876.

22. Seta T, Noguchi Y, Shimada T, Shikata S, Fukui T. Treatment of acute pancreatitis with protease inhibitors: a meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004. 16:1287–1293.
23. Stefan H, Markus S, Valentin R, Pierre AC. Evidence-based treatment of acute pancreatitis; a look at established paradigms. Ann Surg. 2006. 243:154–168.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download