Abstract
Materials and Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 312 patients with plantar fasciitis between March 2008 and February 2013. We investigated age, sex, site, visual analogue scale (VAS), body mass index (BMI), characteristics of pain, awareness of rupture, and duration of symptoms. Acute rupture was defined as a rupture that occurred during exercise; chronic rupture was defined as a degenerative rupture after plantar fasciitis. We investigated the frequency of acute and chronic rupture.
Results
Among 312 patients, 38 patients (12.2%) were diagnosed with plantar fascia rupture. Thirty-eight patients consisted of 14 men (36.8%) and 24 women (63.2%). The mean age of plantar fascia rupture was 58.29±12.54 years. The mean VAS score was 5.92 points (3~9 points). The mean BMI was 25.92±1.59 kg/m2. Among the 38 patients, 2 patients had acute plantar fascia rupture and 36 had chronic plantar fascia rupture. In 34 patients—out of 36 chronic plantar fascia rupture, there were no subjective symptoms.
Conclusion
Chronic rupture of the plantar fascia that occurred after plantar fasciitis was more common than acute rupture. Chronic rupture occurred at approximately 12% of patients treated with plantar fasciitis. In chronic rupture of the plantar fascia, there were no subjective symptoms of rupture. Therefore, we should doubt chronic rupture of plantar fascia when plantar fasciitis is prolonged.
Figures and Tables
 | Figure 1Plantar fascia rupture was diagnosed with palpation in full dorsiflexion of the ankle and metatarsophalangeal joints. |
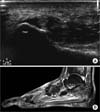 | Figure 3The ultrasonography (A) was diagnosed partial rupture of plantar fascia (PF) or chronic plantar fasciits. But, magnetic resonance imaging (B) showed plantar fascia complete rupture. |
Table 1
Characteristics of Plantar Fascia Rupture

References
1. Leach R, Jones R, Silva T. Rupture of the plantar fascia in athletes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978; 60:537–539.

2. Coughlin MJ, Mann RA, Saltzman CL. Surgery of the foot and ankle. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Mosby;2007. p. 689–705.
3. Sellman JR. Plantar fascia rupture associated with corticosteroid injection. Foot Ankle Int. 1994; 15:376–381.

5. Wright DG, Rennels DC. A study of the elastic properties of plantar fascia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1964; 46:482–492.

6. Buchbinder R. Clinical practice. Plantar fasciitis. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:2159–2166.
8. Balasubramaniam P, Prathap K. The effect of injection of hydrocortisone into rabbit calcaneal tendons. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1972; 54:729–734.

9. Riddle DL, Pulisic M, Pidcoe P, Johnson RE. Risk factors for plantar fasciitis: a matched case-control study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85:872–877.
10. Wearing SC, Smeathers JE, Urry SR, Hennig EM, Hills AP. The pathomechanics of plantar fasciitis. Sports Med. 2006; 36:585–611.

11. Herrick RT, Herrick S. Rupture of the plantar fascia in a middle-aged tennis player. A case report. Am J Sports Med. 1983; 11:95.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download