Abstract
Purpose:
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical and radiologic outcome of syndesmosis fixation using TightRopeTM (Arthrex, Naples, FL, USA) in acute syndesmosis injuries.
Materials and Methods:
Twenty-five consecutive patients with acute syndesmosis injuries, treated using TightRopeTM, were reviewed. Patients were evaluated preoperatively and at the last follow-up (at least 12 months postoperatively). Clinical outcomes were assessed using American Orthopaedics Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) ankle-hindfoot score and self-subjective satisfaction survey. Three radiologic parameters were evaluated two times at the preoperative and final follow up from the nonweightbearing ankle anteroposterior radiographs.
Results:
The mean AOFAS ankle-hindfoot score was 95.5 at the final follow-up. According to the satisfaction survey, 21 patients chose excellent, and four patients chose good. All radiologic parameters, including the mean tibiofibular clear space, mean tibiofibular overlap, and mean medial clear space on nonweightbearing ankle anteroposterior view, significantly improved after surgery. Complications occurred in only one patient who experienced knot irritation with infection.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Wagener ML., Beumer A., Swierstra BA. Chronic instability of the anterior tibiofibular syndesmosis of the ankle. Arthroscopic findings and results of anatomical reconstruction. BMC Muscu-loskelet Disord1. 2011. 12:212.

3.Leeds HC., Ehrlich MG. Instability of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis after bimalleolar and trimalleolar ankle fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984. 66:490–503.

4.Lui TH. Tri-ligamentous reconstruction of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis: a minimally invasive approach. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2010. 49:495–500.

5.Peter RE., Harrington RM., Henley MB., Tencer AF. Biomechanical effects of internal fixation of the distal tibiofibular syndesmotic joint: comparison of two fixation techniques. J Orthop Trauma. 1994. 8:215–9.
6.Klitzman R., Zhao H., Zhang LQ., Strohmeyer G., Vora A. Suture-button versus screw fixation of the syndesmosis: a biomechanical analysis. Foot Ankle Int. 2010. 31:69–75.

7.Thordarson DB., Samuelson M., Shepherd LE., Merkle PF., Lee J. Bioabsorbable versus stainless steel screw fixation of the syndesmosis in pronation-lateral rotation ankle fractures: a prospective randomized trial. Foot Ankle Int. 2001. 22:335–8.

8.Coetzee JC., Ebeling PB. Treatment of syndesmoses disruptions: a prospective, randomized study comparing conventional screw fixation vs TightRope® fiber wire fixation - medium term re-sults. SA Orthop J. 2009. 33:32–7.
9.Forsythe K., Freedman KB., Stover MD., Patwardhan AG. Comparison of a novel FiberWire-button construct versus metallic screw fixation in a syndesmotic injury model. Foot Ankle Int. 2008. 29:49–54.

10.Manjoo A., Sanders DW., Tieszer C., MacLeod MD. Functional and radiographic results of patients with syndesmotic screw fixation: implications for screw removal. J Orthop Trauma. 2010. 24:2–6.

11.Bava E., Charlton T., Thordarson D. Ankle fracture syndesmosis fixation and management: the current practice of orthopedic surgeons. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2010. 39:242–6.
12.Weening B., Bhandari M. Predictors of functional outcome following transsyndesmotic screw fixation of ankle fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2005. 19:102–8.

13.Jordan TH., Talarico RH., Schuberth JM. The radiographic fate of the syndesmosis after trans-syndesmotic screw removal in displaced ankle fractures. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2011. 50:407–12.

14.Cottom JM., Hyer CF., Philbin TM., Berlet GC. Transosseous fixation of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis: comparison of an interosseous suture and endobutton to traditional screw fixation in 50 cases. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2009. 48:620–30.

15.Cottom JM., Hyer CF., Philbin TM., Berlet GC. Treatment of syndesmotic disruptions with the Arthrex Tightrope: a report of 25 cases. Foot Ankle Int. 2008. 29:773–80.

16.Qamar F., Kadakia A., Venkateswaran B. An anatomical way of treating ankle syndesmotic injuries. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2011. 50:762–5.

17.Degroot H., Al-Omari AA., El Ghazaly SA. Outcomes of suture button repair of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis. Foot Ankle Int. 2011. 32:250–6.

18.Klossner O. Late results of operative and non-operative treatment of severe ankle fractures. A clinical study. Acta Chir Scand Suppl. 1962. (Suppl 293):1–93.
19.Fanter NJ., Inouye SE., McBryde AM Jr. Safety of ankle trans-syndesmotic fixation. Foot Ankle Int. 2010. 31:433–40.

20.Landis JR., Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977. 33:159–74.

21.Scranton PE Jr., McMaster JG., Kelly E. Dynamic fibular function: a new concept. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976. 118:76–81.
22.Hart DP., Dahners LE. Healing of the medial collateral ligament in rats. The effects of repair, motion, and secondary stabilizing ligaments. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987. 69:1194–9.

23.Rigby RB., Cottom JM. Does the Arthrex TightRope® provide maintenance of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis? A 2-year follow-up of 64 TightRopes® in 37 patients. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2013. 52:563–7.

24.Thornes B., McCartan D. Ankle syndesmosis injuries treated with the TightRopeTM suture-button kit. Techn Foot Ankle Surg. 2006. 5:45–53.
25.Naqvi GA., Cunningham P., Lynch B., Galvin R., Awan N. Fixation of ankle syndesmotic injuries: comparison of tightrope fixation and syndesmotic screw fixation for accuracy of syndesmotic reduction. Am J Sports Med. 2012. 40:2828–35.
26.Kortekangas TH., Pakarinen HJ., Savola O., Niinimäki J., Lepojärvi S., Ohtonen P, et al. Syndesmotic fixation in supination-external rotation ankle fractures: a prospective randomized study. Foot Ankle Int. 2014. 35:988–95.
Go to : 
Table 1.
Demographics and Patient Summary Results
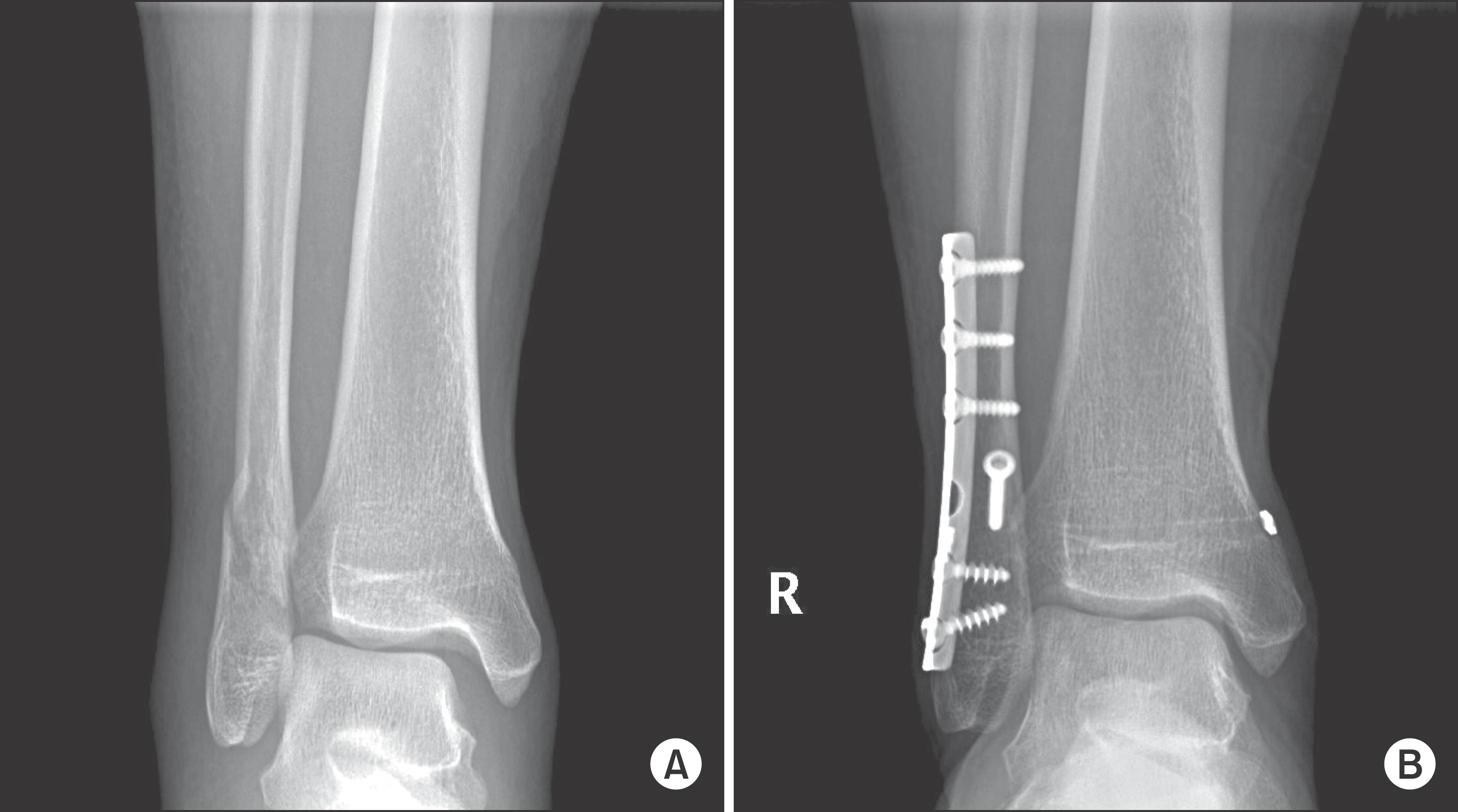 | Figure 1.(A) Preoperative nonweightbearing anteroposterior radiograph of a right ankle demonstrates supination-external rotation type ankle fracture. (B) Final non-weightbearing anteroposterior radiograph show no evidence of syndesmosis widening. |
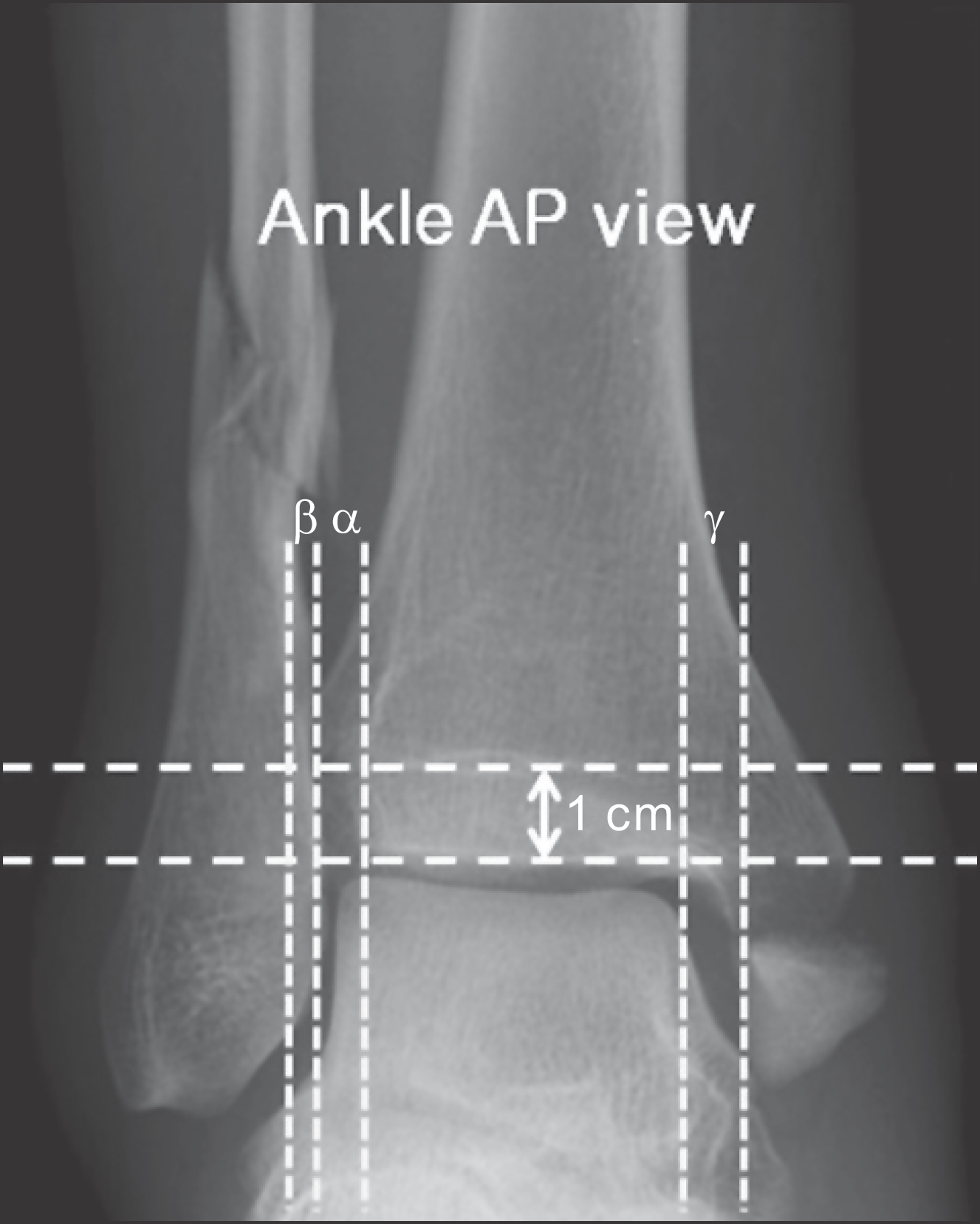 | Figure 2.Three radiographic parameters were measured from non-weightbearing anteroposterior (AP) radiographs. Tibiofibular clear space (TFCS, α) is distance between the medial border of the fibula and the lateral border of the tibia. The TFCS is measured 1 cm proximal to the plafond. Tibiofibular overlap (β) is the overlap of the lateral malleolus and the anterior tibial tubercle measured 1 cm proximal to the plafond. Medial clear space (γ) is distance between the articular surfaces of the talus and the medial malleolus. |
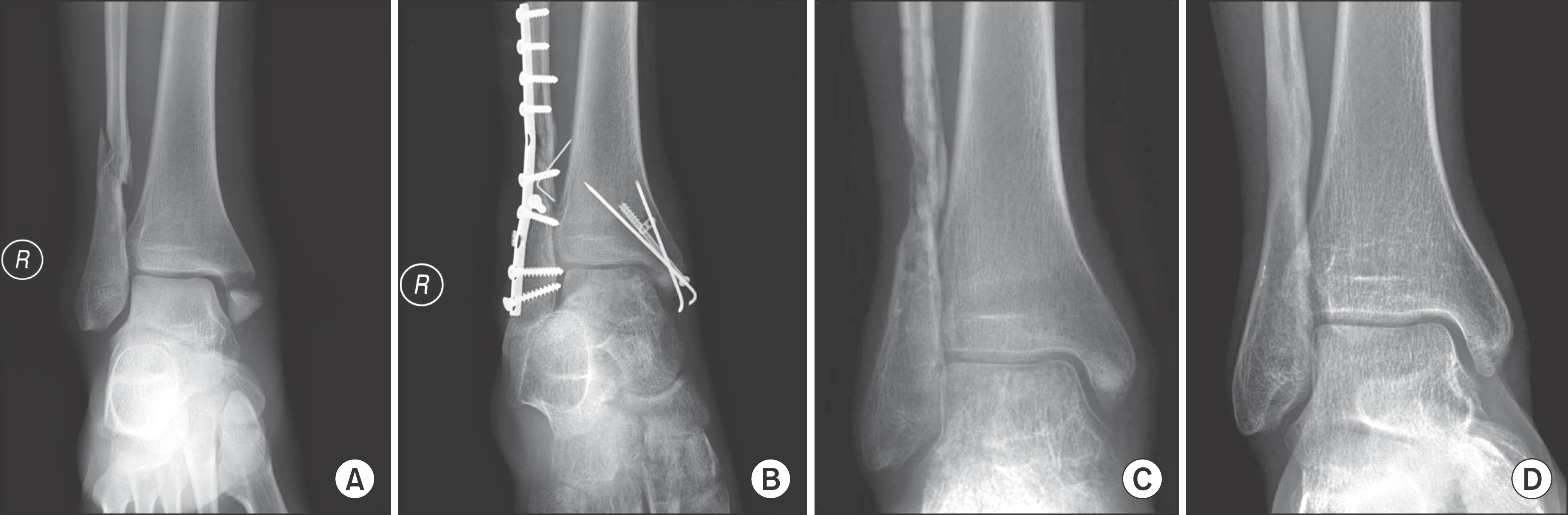 | Figure 3.(A) Preoperative anteroposterior radiograph of a right ankle demonstrates pronation-external rotation type ankle fracture. (B) Open reduction and internal fixation with syndesmosis fixation was performed. (C) All implants were removed at 4 months due to soft tissue irritation and deep infection. (D) At one-year follow up after implant removal, radiograph show complete bone union and adequately maintained ankle mortise. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download