Abstract
Purpose:
To evaluate the radiological and clinical effects of early weightbearing after distal reverse oblique osteotomy of bunionette.
Materials and Methods:
Between 2009 and 2015, 52 patients who underwent surgical treatment at our hospital for bunionette deformity with a minimum follow up of one year were included in the study. Postoperatively, foot cast was applied and full weightbearing was permitted in 28 patients. And short leg splint was applied with only partial weightbearing using crutches allowed in 24 patients. Clinical scores were evaluated. Radiologically, the 4th∼5th intermetatarsal angle (IMA), and 5th metatarsophalangeal angle (MPA) were analyzed preoperatively and at the final follow up visit.
Results:
The visual analogue scale and American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society scores improved in the partial weightbearing group and full weightbearing group, but without significant differences. The average 4th∼5th IMA and average 5th MPA correction also did not showed significant differences between the partial weightbearing group and full weightbearing group. Moreover, the full weightbearing group did not encourage non-union rate compared with the partial weightbearing group.
REFERENCES
4.Kim YC., Ahn JH. Bunionette deformity. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2013. 17:1–10.
5.Coughlin MJ. Treatment of bunionette deformity with longitudinal diaphyseal osteotomy with distal soft tissue repair. Foot Ankle. 1991. 11:195–203.

6.Kitaoka HB., Holiday AD Jr. Metatarsal head resection for bunionette: long-term follow-up. Foot Ankle. 1991. 11:345–9.

7.Cooper MT., Coughlin MJ. Subcaptial oblique fifth metatarsal osteotomy versus distal chevron osteotomy for correction of bunionette deformity: a cadaveric study. Foot Ankle Spec. 2012. 5:313–7.
8.Lee KT., Young KW., Kim JY., Cha SD., Kim ES., Ahn YJ. Treatment of bunionette deformity with distal chevron osteotomy. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2006. 41:14–8.

9.Glover JP., Weil L Jr., Weil LS Sr. Scarfette osteotomy for surgical treatment of bunionette deformity. Foot Ankle Spec. 2009. 2:73–8.

10.Guha AR., Mukhopadhyay S., Thomas RH. ‘Reverse’ scarf osteotomy for bunionette correction: initial results of a new surgical technique. Foot Ankle Surg. 2012. 18:50–4.

11.Seide HW., Petersen W. Tailor’s bunion: results of a scarf osteotomy for the correction of an increased intermetatarsal IV/V angle. A report on ten cases with a 1-year follow-up. Arch Or-thop Trauma Surg. 2001. 121:166–9.
12.Ahn JH., Kim HY., Kang JW., Choy WS., Kim YI. Treatment of bunionette deformity with diaphyseal oblique osteotomy. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2008. 12:31–5.
13.Kim SK., Kim J., Lee JI., Rhee SH. Treatment of bunionette deformity with diaphyseal oblique osteotomy. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2014. 18:19–23.

14.London BP., Stern SF., Quist MA., Lee RK., Picklesimer EK. Long oblique distal osteotomy of the fifth metatarsal for correction of tailor’s bunion: a retrospective review. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2003. 42:36–42.

15.Okuda R., Kinoshita M., Morikawa J., Jotoku T., Abe M. Proximal dome-shaped osteotomy for symptomatic bunionette. Clin Or-thop Relat Res. 2002. 396:173–8.

16.Coughlin MJ. Etiology and treatment of the bunionette defor-mity. Instr Course Lect. 1990. 39:37–48.
17.Fallat LM. Pathology of the fifth ray, including the tailor’s bunion deformity. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 1990. 7:689–715.
18.Jørgensen L., Jacobsen BK., Wilsgaard T., Magnus JH. Walking after stroke: does it matter? Changes in bone mineral density within the first 12 months after stroke. A longitudinal study. Os-teoporos Int. 2000. 11:381–7.

Figure 1.
(A) The oblique osteotomy is started at the fifth metatarsal neck, and angled 40° to 45° in a proximal direction. (B) The distal fragment is removed and used for bone graft at the osteotomy site. (C) Finally, metatarsal head was translated proximally and medially.
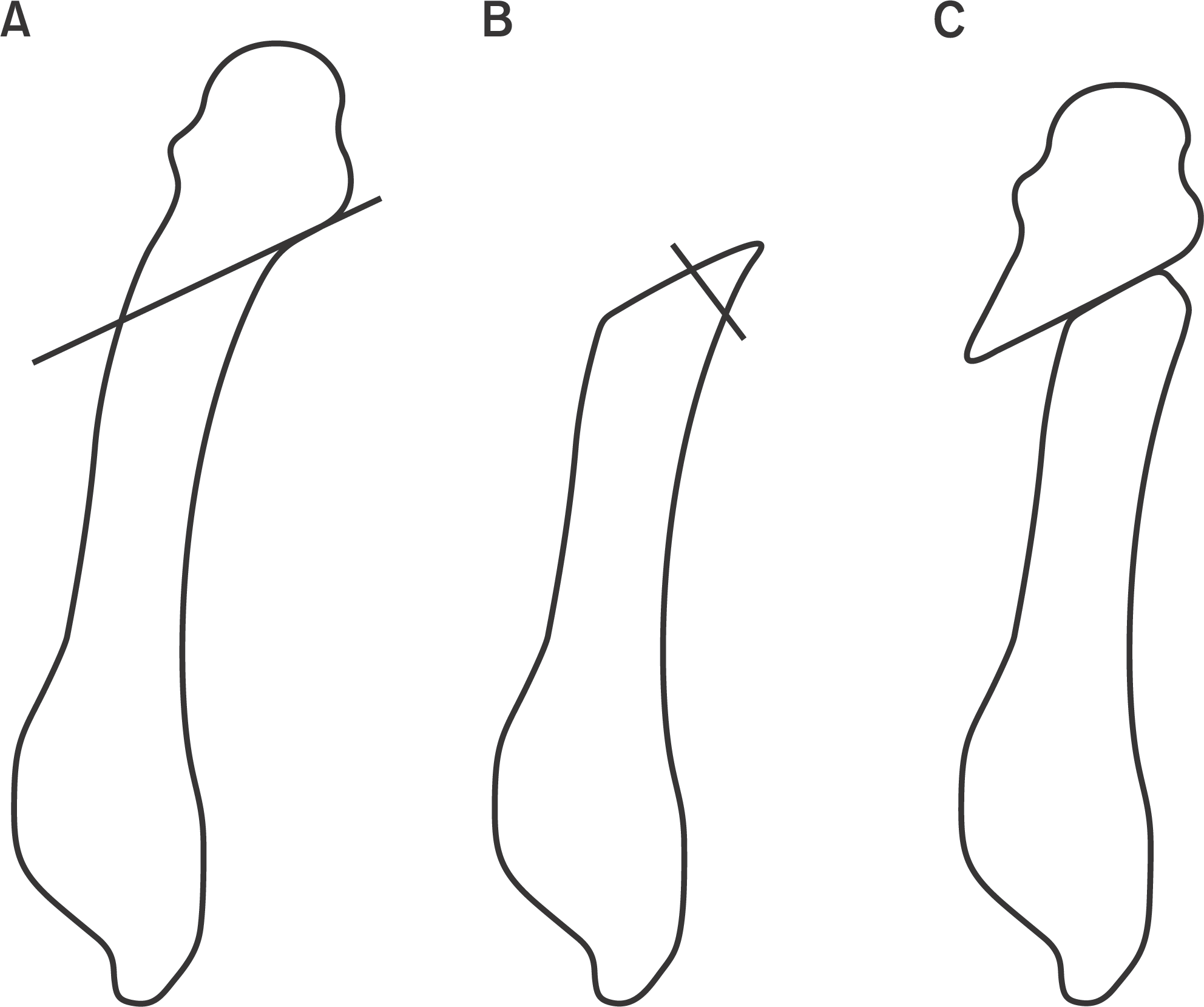
Figure 2.
(A) A lateral radiograph of a foot shows a short leg splint applied postoperatively. (B) A lateral radiograph of another foot shows a foot cast applied postoperatively.
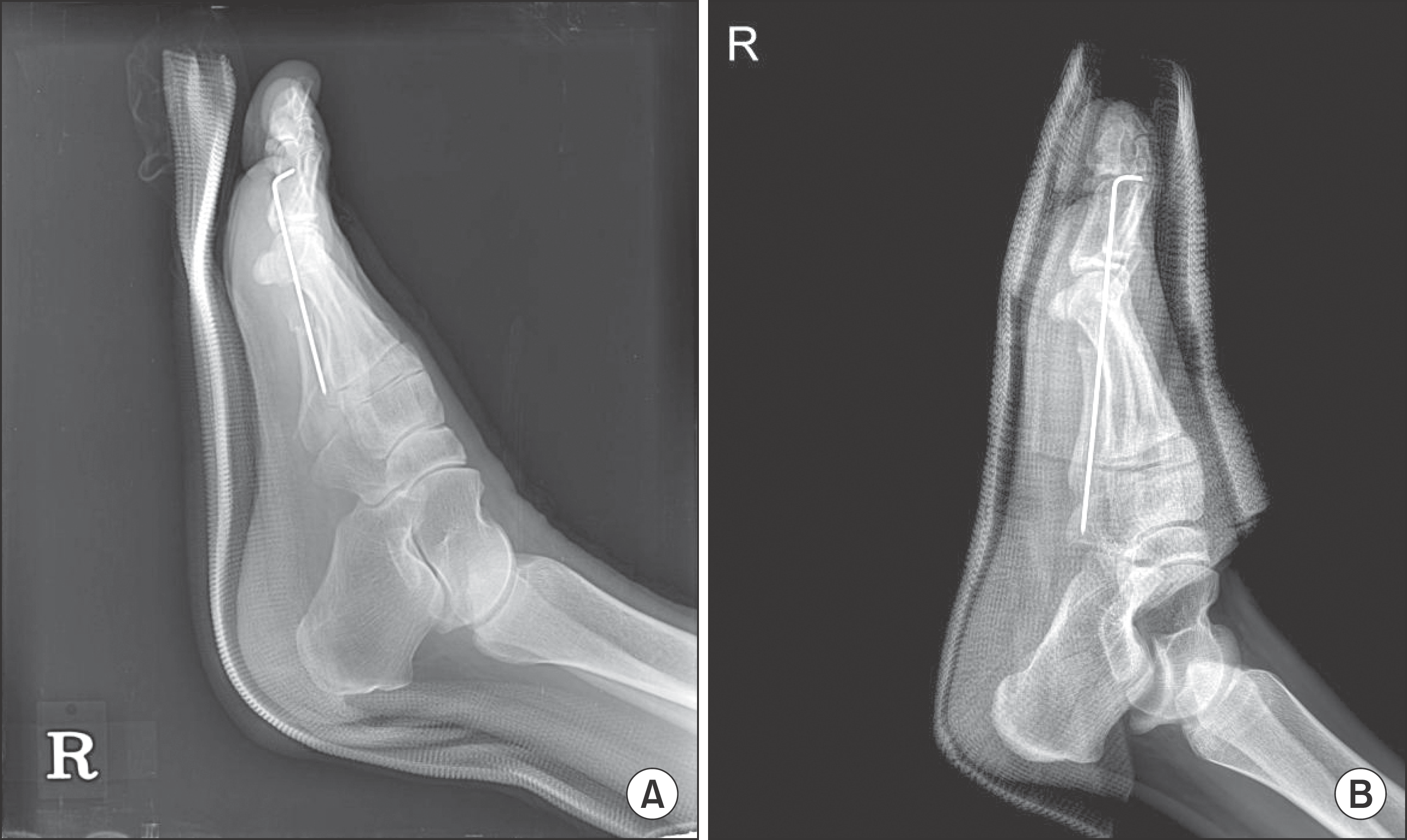
Figure 3.
(A) Preoperative standing anteroposterior radiograph shows a foot with bunionette deformity. (B) Bunionette deformity was corrected postoperatively. (C) At one year postoperatively, complete bony union was confirmed.
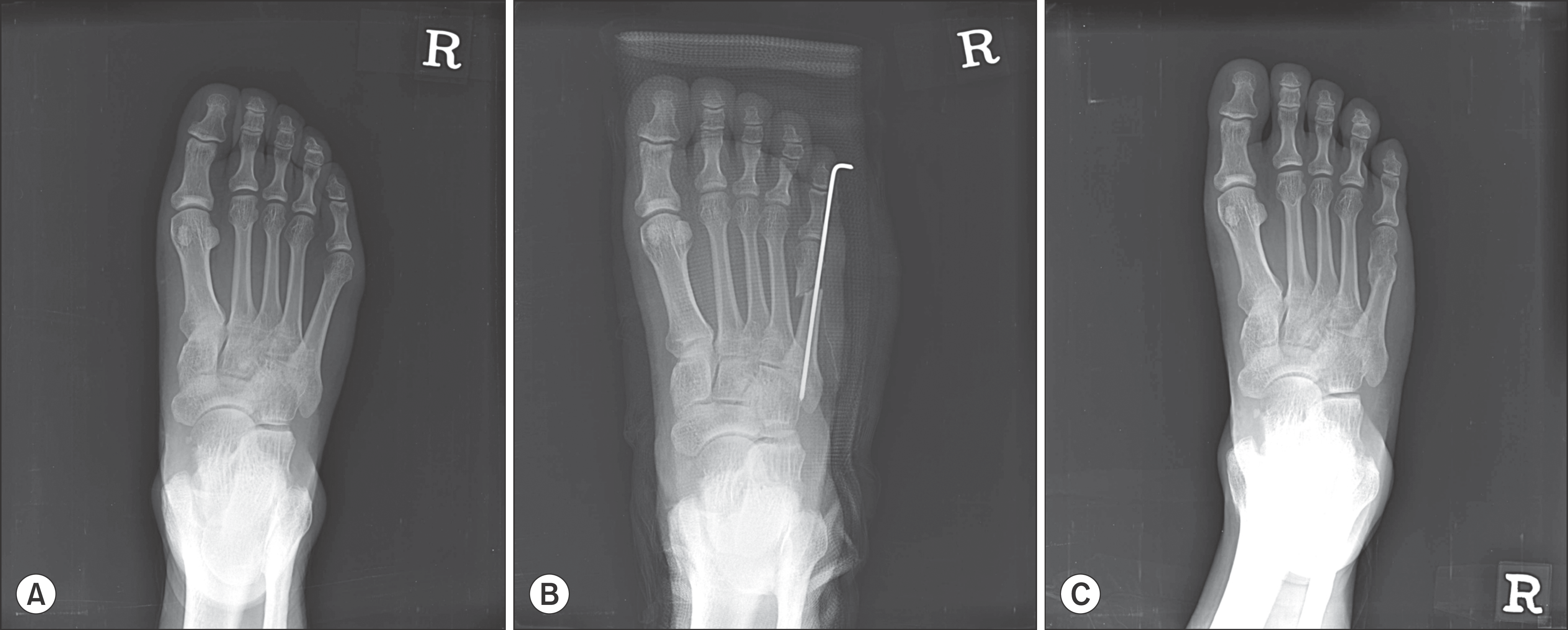
Table 1.
Comparison of Partial Weightbearing Group and Full Weightbearing Group




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download