Abstract
Purpose:
This study aimed to evaluate the outcomes, including the complications, of open reduction and internal fixation using a headless cannulated compression screw for a fifth metatarsal base fracture.
Materials and Methods:
We retrospectively investigated 11 patients with 5th metatarsal base fracture who were treated with a headless cannulated compression screw. The mean follow-up period was 13 months (8∼15 months), and the mean age was 46.5 years (21∼70 years). We analyzed the patients’ sex, age, time to union, amount of fracture displacement, and complications. The American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) midfoot score was used for clinical assessment.
Results:
The average amount of displacement decreased significantly from 3.4 mm (2.1∼5.2 mm), preoperatively, to 0.4 mm (0∼1.3 mm), postoperatively (p<0.001). The average bone union time was 54.1 days (41∼68 days). There were no complications, such as a metal failure, irritation, and loss of a reduction. The mean AOFAS midfoot score was 97.7 (90∼100) at 6 months, postoperatively.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Early JS. Fractures and dislocations of the midfoot and forefoot. In: Buckhols RW, Heckman JD, editors1 Fractures in adults. 5th ed.Philadelphia: Lippincott William and Wilkins;2001. p. 2215–28.
2.Hatch RL., Alsobrook JA., Clugston JR. Diagnosis and management of metatarsal fractures. Am Fam Physician. 2007. 76:817–26.
3.Lawrence SJ., Botte MJ. Jones’ fractures and related fractures of the proximal fifth metatarsal. Foot Ankle. 1993. 14:358–65.

5.Thomas JL., Davis BC. Three-wire fixation technique for displaced fifth metatarsal base fractures. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2011. 50:776–9.

6.Sung KS., Koh KH., Koo KH., Park JC. Conservative treatment of nondisplaced fifth metatarsal base zone I and II fractures. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2008. 12:185–8.
7.Wiener BD., Linder JF., Giattini JF. Treatment of fractures of the fifth metatarsal: a prospective study. Foot Ankle Int. 1997. 18:267–9.

9.Jones R. I1 Fracture of the base of the fifth metatarsal bone by indirect violence. Ann Surg. 1902. 35:697–700. .2.
10.Pietropaoli MP., Wnorowski DC., Werner FW., Fortino MD. Intramedullary screw fixation of Jones fractures: a biomechanical study. Foot Ankle Int. 1999. 20:560–3.

11.Suh JS., Kim JH., Choi JY. Operative treatment of fractures of the fifth metatarsal base. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2008. 12:189–96.
12.Ahn JK., Chung HJ., Bae SY., Park JY. Treatment of fifth metatarsal base fracture using tension band wiring. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2011. 15:18–21.
Go to : 
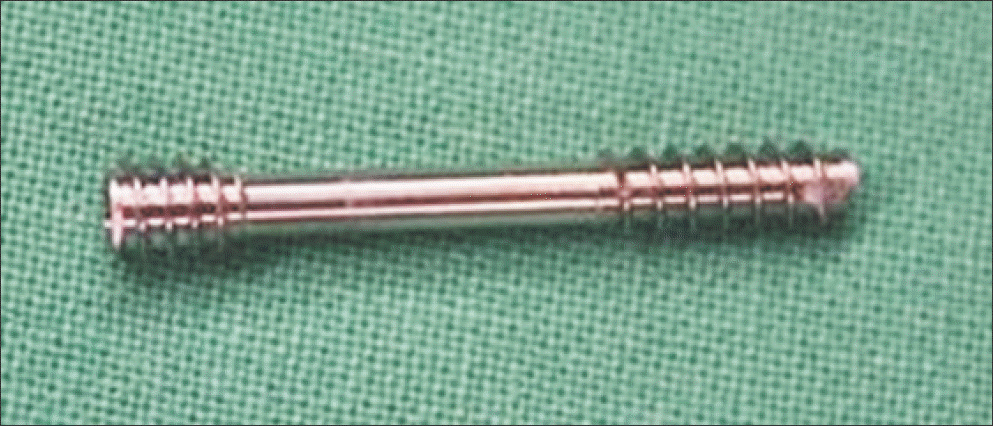 | Figure 1.A 3.0 mm headless cannulated compression screw with a low profile head to prevent soft tissue irritation and to facilitate countersinking, particularly in small bone was used. |
 | Figure 2.(A) A 50-year-old woman with 5th metatarsal base fracture. Initial oblique view with 3.1 mm displacement. (B) Immediate postoperative oblique view after open reduction and headless cannulated compression screw fixation. (C) Follow-up oblique view on her postoperative 6 months. |
Table 1.
Patients’ Data




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download