Abstract
Syndesmotic injury can either be isolated or associated with bony or ligamentous ankle injury. When it is not associated with an ankle fracture, it may not be easy to diagnose, especially when there is no franck diastasis on a plain radiograph. Without proper treatment, syndesmotic injury can lead to chronic pain due to impingement of scar tissues and instability. It may further lead to ankle arthritis. Early diagnosis with appropriate management is a prerequisite to avoid these problems. Herein, we review and discuss the mechanism of injury, classification, diagnosis, and treatment of isolated syndesmotic injury.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.van Dijk CN., Longo UG., Loppini M., Florio P., Maltese L., Ciuf-freda M, et al. Classification and diagnosis of acute isolated syndesmotic injuries: ESSKA-AFAS consensus and guidelines. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016. 24:1200–16.

2.van Dijk CN., Longo UG., Loppini M., Florio P., Maltese L., Ciuf-freda M, et al. Conservative and surgical management of acute isolated syndesmotic injuries: ESSKA-AFAS consensus and guidelines. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016. 24:1217–27.

3.Hopkinson WJ., St Pierre P., Ryan JB., Wheeler JH. Syndesmosis sprains of the ankle1 Foot Ankle. 1990. 10:325–30.
4.Gwak HC., Kwon YW. Ankle syndesmotic injury. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2011. 15:187–94.
6.Miller TL., Skalak T. Evaluation and treatment recommendations for acute injuries to the ankle syndesmosis without associated fracture. Sports Med. 2014. 44:179–88.

7.Edwards GS Jr., DeLee JC. Ankle diastasis without fracture1 Foot Ankle. 1984. 4:305–12.
8.Frick H. Diagnosis, therapy and results of acute instability of the syndesmosis of the upper ankle joint (isolated anterior rupture of the syndesmosis). Orthopade. 1986. 15:423–6.
10.Gerber JP., Williams GN., Scoville CR., Arciero RA., Taylor DC. Persistent disability associated with ankle sprains: a prospective examination of an athletic population. Foot Ankle Int. 1998. 19:653–60.

11.Ogilvie-Harris DJ., Gilbart MK., Chorney K. Chronic pain following ankle sprains in athletes: the role of arthroscopic surgery. Arthroscopy. 1997. 13:564–74.

12.Van Heest TJ., Lafferty PM. Injuries to the ankle syndesmosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014. 96:623–13.

13.Ostrum RF., De Meo P., Subramanian R. A critical analysis of the anterior-posterior radiographic anatomy of the ankle syndes-mosis. Foot Ankle Int. 1995. 16:128–31.

14.Rammelt S., Zwipp H., Grass R. Injuries to the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis: an evidence-based approach to acute and chronic lesions. Foot Ankle Clin. 2008. 13:611–33.

15.Degroot H., Al-Omari AA., El Ghazaly SA. Outcomes of suture button repair of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis. Foot Ankle Int1. 2011. 32:250–6.

16.Sikka RS., Fetzer GB., Sugarman E., Wright RW., Fritts H., Boyd JL, et al. Correlating MRI findings with disability in syndesmotic sprains of NFL players. Foot Ankle Int. 2012. 33:371–8.

17.van den Bekerom MP., de Leeuw PA., van Dijk CN. Delayed operative treatment of syndesmotic instability1 Current concepts review1 Injury1. 2009. 40:1137–42.
18.Espinosa N., Smerek JP., Myerson MS. Acute and chronic syndesmosis injuries: pathomechanisms, diagnosis and management. Foot Ankle Clin. 2006. 11:639–57.

19.Ebraheim NA., Lu J., Yang H., Mekhail AO., Yeasting RA. Radiographic and CT evaluation of tibiofibular syndesmotic diastasis: a cadaver study. Foot Ankle Int. 1997. 18:693–8.

20.Harper MC., Keller TS. A radiographic evaluation of the tibiofibular syndesmosis. Foot Ankle. 1989. 10:156–60.

21.Lee HS., Park SS., Kim JW., Shin MJ., Kim SM., Lee SH, et al. Diagnostic value of ultrasonography for acute tear of tibiofibular syndesmosis in ankle. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2004. 8:1–6.
22.Reckling FW., McNamara GR., DeSmet AA. Problems in the diagnosis and treatment of ankle injuries. J Trauma. 1981. 21:943–50.

23.Han SH., Lee JW., Kim S., Suh JS., Choi YR. Chronic tibiofibular syndesmosis injury: the diagnostic efficiency of magnetic resonance imaging and comparative analysis of operative treatment. Foot Ankle Int. 2007. 28:336–42.

24.Vogl TJ., Hochmuth K., Diebold T., Lubrich J., Hofmann R., Stöckle U, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of acute injured distal tibiofibular syndesmosis. Invest Radiol. 1997. 32:401–9.

25.Magan A., Golano P., Maffulli N., Khanduja V. Evaluation and management of injuries of the tibiofibular syndesmosis. Br Med Bull. 2014. 111:101–15.

26.Ogilvie-Harris DJ., Reed SC. Disruption of the ankle syndesmosis: diagnosis and treatment by arthroscopic surgery. Arthroscopy. 1994. 1:.: 561-8.

27.Heim D., Schmidlin V., Ziviello O. Do type B malleolar fractures need a positioning screw? Injury. 2002. 33:729–34.

28.Kaukonen JP., Lamberg T., Korkala O., Pajarinen J. Fixation of syndesmotic ruptures in 38 patients with a malleolar fracture: a randomized study comparing a metallic and a bioabsorbable screw. J Orthop Trauma. 2005. 19:392–5.
29.Naqvi GA., Cunningham P., Lynch B., Galvin R., Awan N. Fixation of ankle syndesmotic injuries: comparison of tightrope fixation and syndesmotic screw fixation for accuracy of syndesmotic reduction. Am J Sports Med. 2012. 40:2828–35.
30.Needleman RL., Skrade DA., Stiehl JB. Effect of the syndesmotic screw on ankle motion. Foot Ankle. 1989. 10:17–24.

31.Thompson MC., Gesink D., Hamson K. Biomechanical evaluation of syndesmosis fixation with 315- and 415-millimeter stainless steel screws. J Orthop Trauma. 2002. 14:144.
32.Kukreti S., Faraj A., Miles JN. Does position of syndesmotic screw affect functional and radiological outcome in ankle fractures? Injury. 2005. 36:1121–4.

33.Sinisaari IP., Lüthje PM., Mikkonen RH. Ruptured tibio-fibular syndesmosis: comparison study of metallic to bioabsorbable fixation1 Foot Ankle Int. 2002. 23:744–8.
34.Thordarson DB., Hedman TP., Gross D., Magre G. Biomechanical evaluation of polylactide absorbable screws used for syndesmosis injury repair. Foot Ankle Int. 1997. 18:622–7.

35.van den Bekerom MP., Hogervorst M., Bolhuis HW., van Dijk CN. Operative aspects of the syndesmotic screw: review of current concepts. Injury. 2008. 39:491–8.

36.Parlamas G., Hannon CP., Murawski CD., Smyth NA., Ma Y., Kerk-hoffs GM, et al. Treatment of chronic syndesmotic injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013. 21:1931–9.

37.Yasui Y., Takao M., Miyamoto W., Innami K., Matsushita T. Anatomical reconstruction of the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament for chronic disruption of the distal tibiofibular syndesmo-sis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011. 19:691–5.

38.Zamzami MM., Zamzam MM. Chronic isolated distal tibiofibular syndesmotic disruption: diagnosis and management. Foot Ankle Surg1. 2009. 15:14–9.

39.Olson KM., Dairyko GH Jr., Toolan BC. Salvage of chronic instability of the syndesmosis with distal tibiofibular arthrodesis: functional and radiographic results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011. 93:66–72.
Go to : 
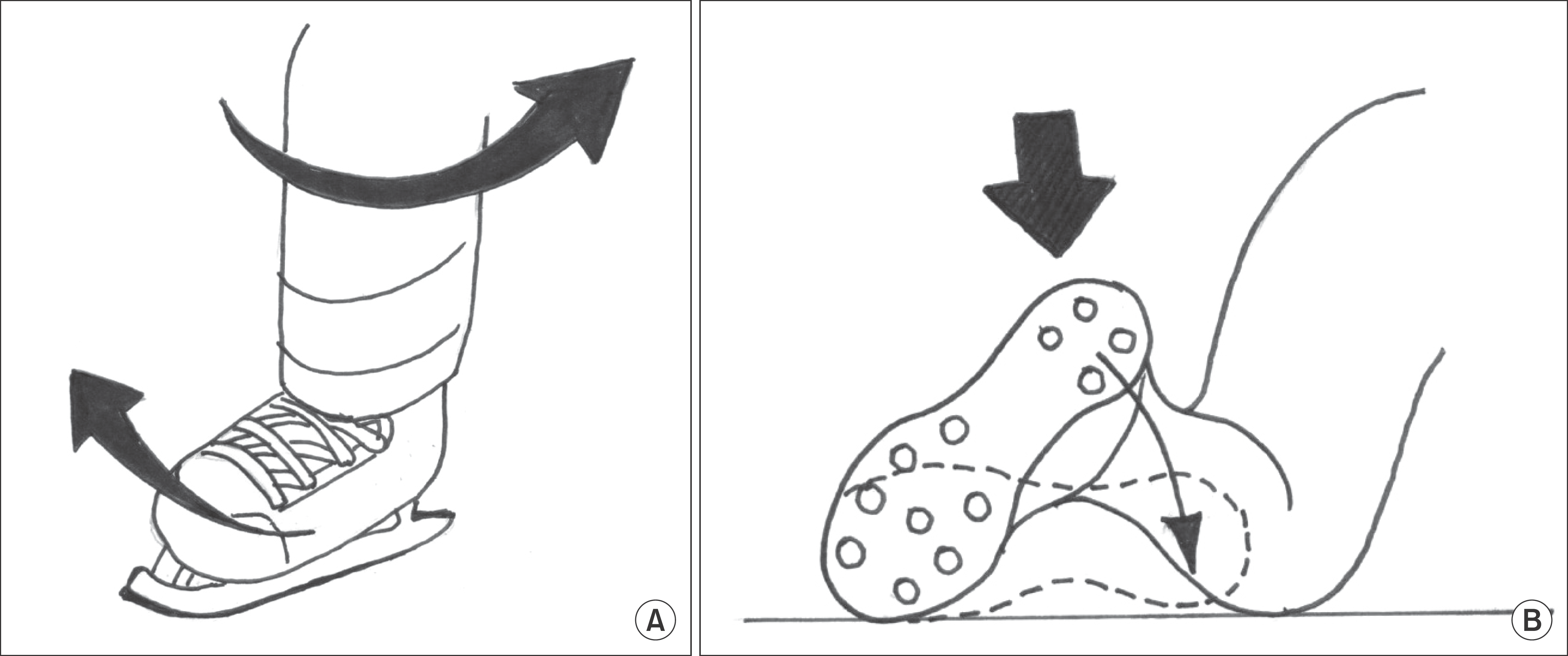 | Figure 1.The mechanism of syndesmotic injury is described. (A) A direct blow down to the leg of a football player external rotates the ankle to give syndesmotic injury. (B) External rotating force is applied to the ankle of an ice hockey player when the player’s foot is planted and the knee internal rotated. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download