Abstract
Swelling is a body’s natural reaction to foot and ankle injury to mount a healing inflammatory response. To some degree, swelling is necessary for healing and is something that cannot be avoided following injury. However, post-traumatic swelling may have an adverse effect on wound healing and surgery can often be delayed due to preoperative swelling. We report on a unique technique of making multiple meshed stab incisions around the site of injury to reduce soft tissue swelling and promote wound healing.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Carati CJ., Anderson SN., Gannon BJ., Piller NB. Treatment of postmastectomy lymphedema with low-level laser therapy: a double blind, placebo-controlled trial. Cancer. 2003. 98:1114–22.
2.Burkhardt A., Joachim L. Clinical options in edema control. J Hand Ther. 1993. 6:337–8.
3.Faghri PD. The effects of neuromuscular stimulation-induced muscle contraction versus elevation on hand edema in CVA patients. J Hand Ther. 1997. 10:29–34.

4.Vasudevan SV., Melvin JL. Upper extremity edema control: rationale of the techniques. Am J Occup Ther. 1979. 33:520–3.
5.Matsen FA 3rd., Krugmire RB Jr. The effect of externally applied pressure on post-fracture swelling. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974. 56:1586–91.

7.Howard SB., Krishnagiri S. The use of manual edema mobilization for the reduction of persistent edema in the upper limb. J Hand Ther. 2001. 14:291–301.
8.Casley-Smith JR., Gaffney RM. Excess plasma proteins as a cause of chronic inflammation and lymphodema: quantitative electron microscopy. J Pathol. 1981. 133:243–72.
Go to : 
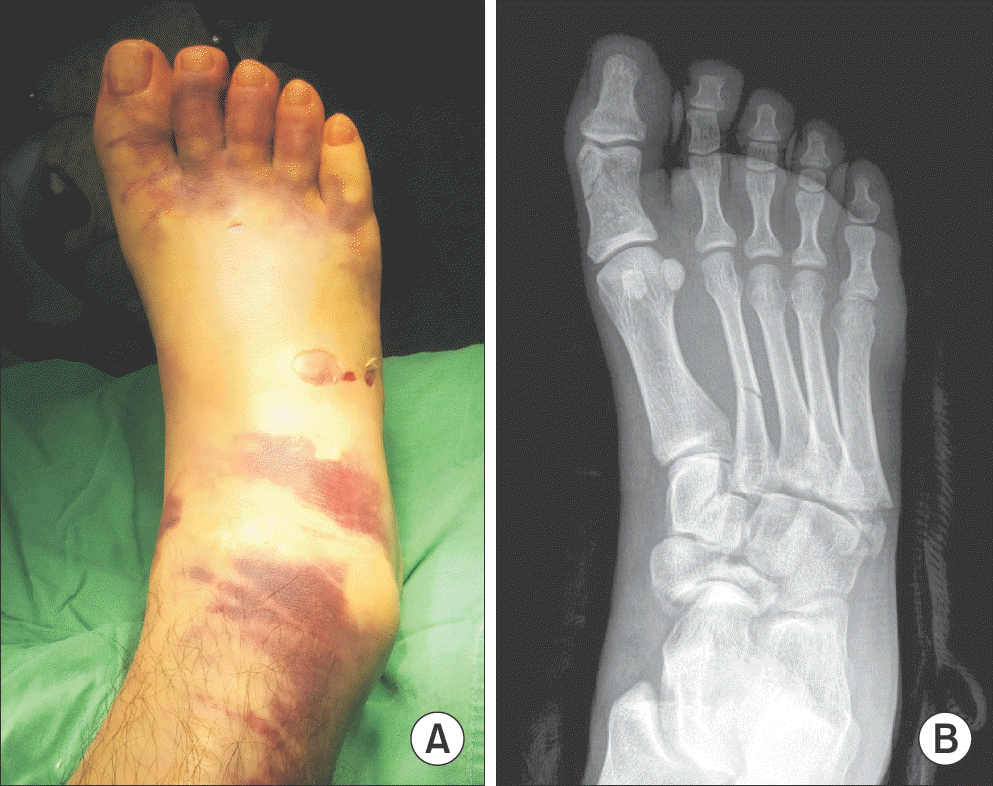 | Figure 1.(A) A 22-year-old male patient had severe swelling with blister formation on his right foot. (B) Simple radiograph shows multiple fracture on his right foot. |
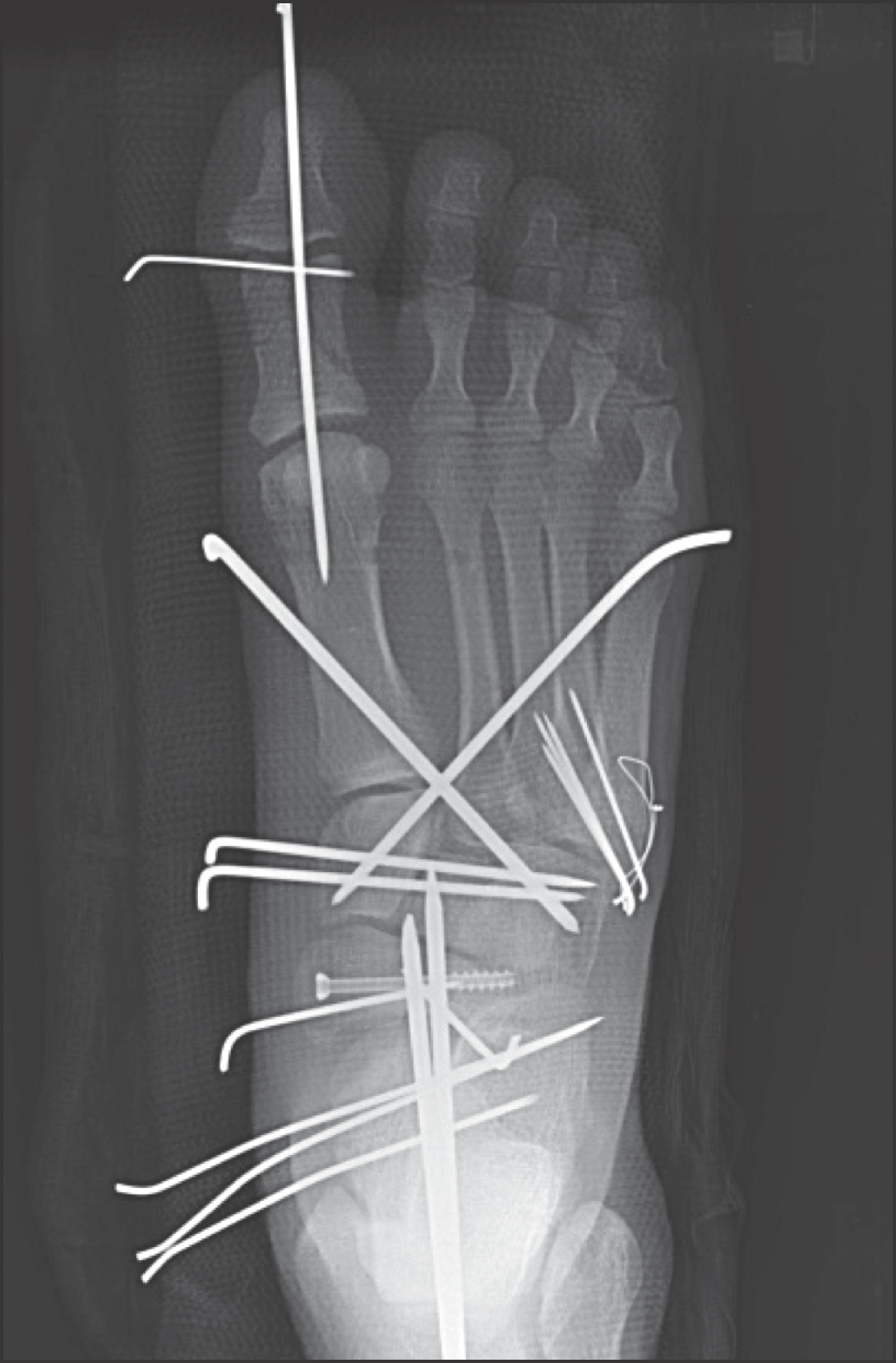 | Figure 2.Postoperative radiograph shows reduction and internal fixation of the multiple fractures. |
 | Figure 3.Intraoperative clinical photos show widening of multiple stab incisions by mosquito (A), irrigation using a 50 mL syringe (B), and the final state of meshed stab incision with number 11 scalpel blade (C). (D) Clinical photo taken 7 days after surgery shows decreased swelling without any signs of infection. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download