Abstract
Purpose
The aim of the current study is to report on the clinical and radiographic results after calcaneo-stop procedure in Korean children with symptomatic flexible flatfoot.
Materials and Methods
Twenty-two children suffering pain along the medial aspect of midfoot with flexible flatfoot whose symptoms did not improve with conservative measures and therefore underwent calcaneo-stop procedure were identified retrospectively. Clinically, American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) ankle-hindfoot scale and visual analogue scale (VAS) were evaluated. Radiographically, standing anteroposterior and lateral radiographs of the foot and Saltzman's alignment views were taken and talonavicular coverage angle, lateral talo-first metatarsal angle, and hindfoot alignment angles were measured and analyzed.
Results
Clinically, AOFAS ankle-hindfoot scale improved from 70.3±5.6 to 97.3±2.5 and VAS improved from 6.4±1.6 to 0.2±0.4. Radiographically, talonavicular coverage angle improved from 28.3o±12.3o to 10.9o±8.1o, lateral talo-first metatarsal angle improved from –19.3o±9.0o to –2.4o±8.1o, and hindfoot alignment angle improved from valgus 11.9o±10.0o to 3.5o±4.3o at minimum 2-year follow-up. No complications occurred postoperatively.
References
1. Staheli LT. Evaluation of planovalgus foot deformities with special reference to the natural history. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 1987; 77:2–6.

2. Nelson SC, Haycock DM, Little ER. Flexible flatfoot treatment with arthroereisis: radiographic improvement and child health survey analysis. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2004; 43:144–55.

4. Giannini S, Ceccarelli F. The flexible flat foot. Foot Ankle Clin. 1998; 3:573–92.
5. Jerosch J, Schunck J, Abdel-Aziz H. The stop screw technique: a simple and reliable method in treating flexible flatfoot in children. Foot Ankle Surg. 2009; 15:174–8.
7. Harris EJ, Vanore JV, Thomas JL, Kravitz SR, Mendelson SA, Mendicino RW, et al. Clinical Practice Guideline Pediatric Flatfoot Panel of the American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons. Diagnosis and treatment of pediatric flatfoot. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2004; 43:341–73.

8. Needleman RL. A surgical approach for flexible flatfeet in adults including a subtalar arthroereisis with the MBA sinus tarsi implant. Foot Ankle Int. 2006; 27:9–18.

9. Smith SD, Millar EA. Arthrorisis by means of a subtalar polyethylene peg implant for correction of hindfoot pronation in children. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983; 181:15–23.

10. Forg P, Feldman K, Flake E, Green DR. Flake-Austin modification of the STA-Peg arthroereisis: a retrospective study. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2001; 91:394–405.
11. Magnan B, Baldrighi C, Papadia D. Flatfeet: comparison of surgical techniques. Result of study group into retrograde endorthesis with calcaneus-stop. Ital J Pediatr Orthop. 1997; 13:28–33.
12. Smith PA, Millar EA, Sullivan RC. Sta-Peg arthroereisis for treatment of the planovalgus foot in cerebral palsy. Clin Podiatr Med Surg1. 2000; 17:459–69.
13. Giannini BS, Ceccarelli F, Benedetti MG, Catani F, Faldini C. Surgical treatment of flexible flatfoot in children a four-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001; 83(Suppl 2 Pt 2):73–9.
14. Maxwell J, Nakra A, Ashley C. Use of the Maxwell-Brancheau arthroereisis implant for the correction of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. Tech Orthop. 2000; 15:183–96.

15. Arangio GA, Reinert KL, Salathe EP. A biomechanical model of the effect of subtalar arthroereisis on the adult flexible flat foot1 Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2004; 19:847–52.
16. Roth S, Sestan B, Tudor A, Ostojic Z, Sasso A, Durbesic A. Minimally invasive calcaneo-stop method for idiopathic, flexible pes planovalgus in children. Foot Ankle Int. 2007; 28:991–5.

17. Pisani G. About the pathogenesis of the so-called adult acquired pes planus. Foot Ankle Surg. 2010; 16:1–2.

18. Akiyama K, Takakura Y, Tomita Y, Sugimoto K, Tanaka Y, Tamai S. Neurohistology of the sinus tarsi and sinus tarsi syndrome. J Orthop Sci. 1999; 4:299–303.

19. Moraleda L, Mubarak SJ. Flexible flatfoot: differences in the relative alignment of each segment of the foot between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients. J Pediatr Orthop. 2011; 31:421–8.
20. Carranza A, Gimeno V, Gomez J, Gutierrez M. Giannini's prosthesis in the treatment of juvenile flatfoot1 J Foot Ankle Surg. 2000; 6:11–7.
Figure 1.
(A) Preoperative weightbearing anteroposterior radiograph of 11-year-old boy shows abnormal talonavicular coverage angle of 28o. (B) Preoperative weightbearing lateral radiograph shows decreased lateral talo-first metatarsal angle of ―26o. (C) Preoperative Saltzman's alignment view shows heel alignment angle of valgus 25o.
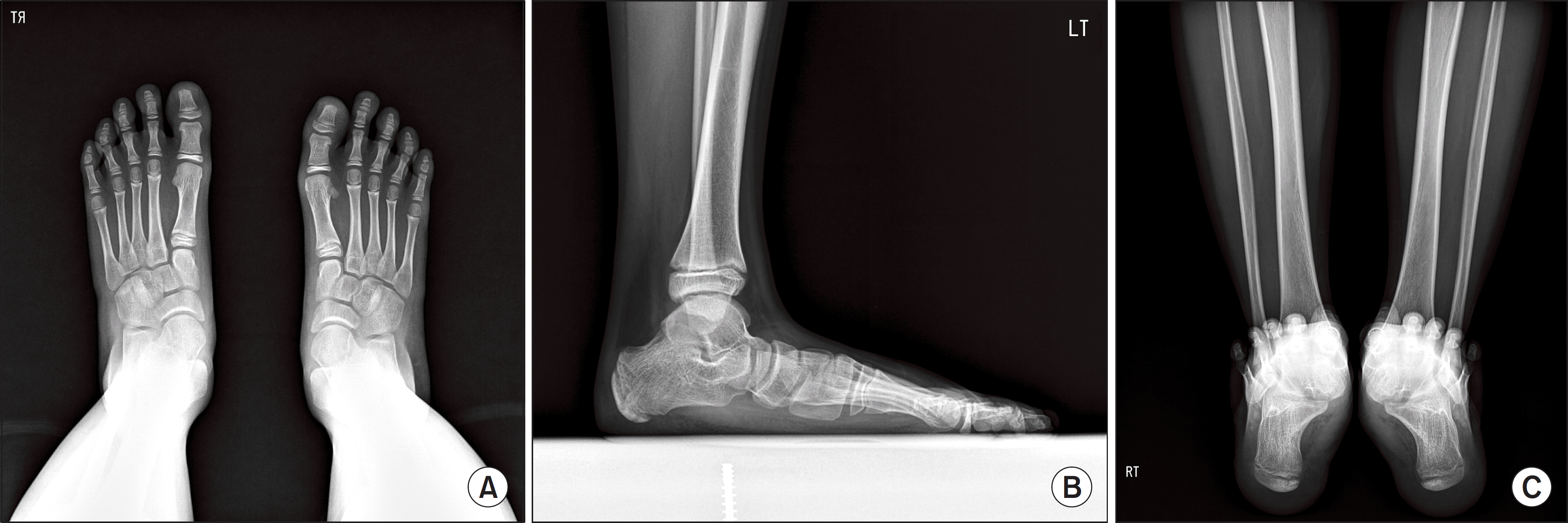
Figure 2.
Calcaneo-stop procedure was performed and postoperative radiograph was taken at 2-year follow-up. (A) weightbearing anteroposterior radiograph shows normal talonavicular coverage angle of 7o. (B) weightbearing lateral radiograph shows improved lateral talo-first metatarsal angle of 1o. (C) Saltzman's alignment view shows heel alignment angle of valgus 4o.
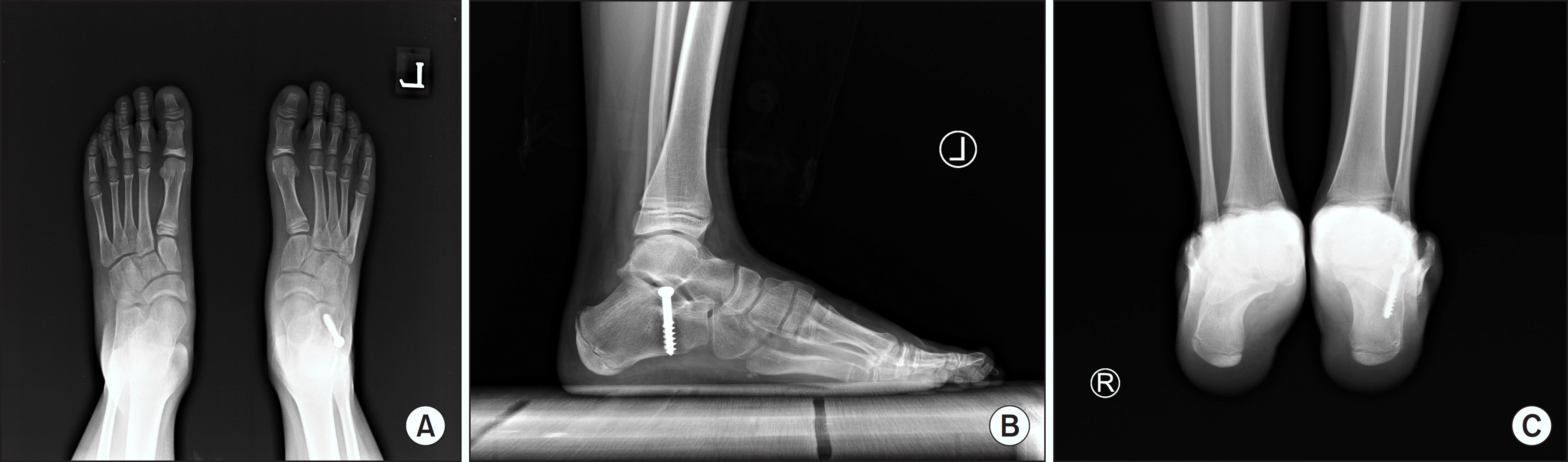
Table 1.
Radiographic and Clinical Results of Children with Calcaneo-Stop Procedure




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download