Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study is to analyze the measurement differences of simple radiographs according to radiation projection angle using a phantom and to propose methods for objective analysis of simple radiographs.
Materials and Methods
We took simple radiographs with different projection angles using a C-arm image intensifier and measured five parameters of the foot on the simple radiographic images. Five parameters include lateral tibiocalcaneal angle, lateral talocalcaneal angle, naviculocuboid overlap, lateral talo-first metatarsal angle, and lateral calcaneo-first metatarsal angle. Intraobserver and interobserver reliability were verified, and then intraclass correlations of parameters were analyzed.
Results
Radiographic parameters of the foot showed high intraobserver and interobserver reliability. Lateral tibiocalcaneal angle has a strong negative linear relationship with rotation and a moderate negative linear relationship with tilt. Lateral talocalcaneal angle has a moderate positive linear relationship with rotation and a strong positive linear relationship with tilt. Naviculocuboid overlap has a strong positive linear relationship with rotation and a moderate positive linear relationship with tilt. Lateral talo-first metatarsal angle does not have a linear relationship with rotation and a moderate negative linear relationship with tilt. Lateral calcaneo-first metatarsal angle has a moderate positive linear relationship with rotation and tilt.
Go to : 
References
1. Rankine JJ, Nicholas CM, Wells G, Barron DA. The diagnostic accuracy of radiographs in Lisfranc injury and the potential value of a craniocaudal projection. AJR Am J Roentgenol1. 2012; 198:W365–9.

2. Barg A, Amendola RL, Henninger HB, Kapron AL, Saltzman CL, Anderson AE. Influence of ankle position and radiographic projection angle on measurement of supramalleolar alignment on the anteroposterior and hindfoot alignment views. Foot Ankle Int. 2015; 36:1352–61.

3. Saltzman CL, Brandser EA, Berbaum KS, DeGnore L, Holmes JR, Katcherian DA, et al. Reliability of standard foot radiographic measurements. Foot Ankle Int. 1994; 15:661–5.

4. Noh KC, Shim JS, Kim SJ, Park SJ, Sung KS. Variability of radiographic measurements of bowleg deformity in children: a new method for metaphyseal diaphyseal angle (MDA). J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2003; 38:179–82.

5. Thomas JL, Kunkel MW, Lopez R, Sparks D. Radiographic values of the adult foot in a standardized population. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2006; 45:3–12.

6. Steel MW 3rd, Johnson KA, DeWitz MA, Ilstrup DM. Radiographic measurements of the normal adult foot. Foot Ankle. 1980; 1:151–8.

7. Lee DY, Seo SG, Kim EJ, Kim SJ, Lee KM, Farber DC, et al. Correlation between static radiographic measurements and intersegmental angular measurements during gait using a multisegment foot model. Foot Ankle Int. 2015; 36:1–10.

Go to : 
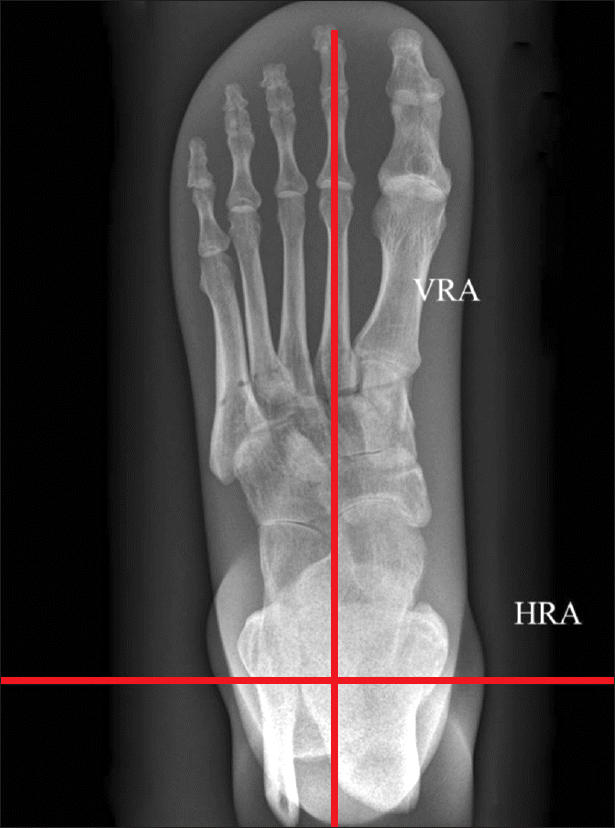 | Figure 1.We defined the second metatarsal longitudinal axis as the vertical reference axis (VRA), and the horizontal line perpendicular to the vertical reference axis passing the center of ankle joint as the horizontal reference axis (HRA). |
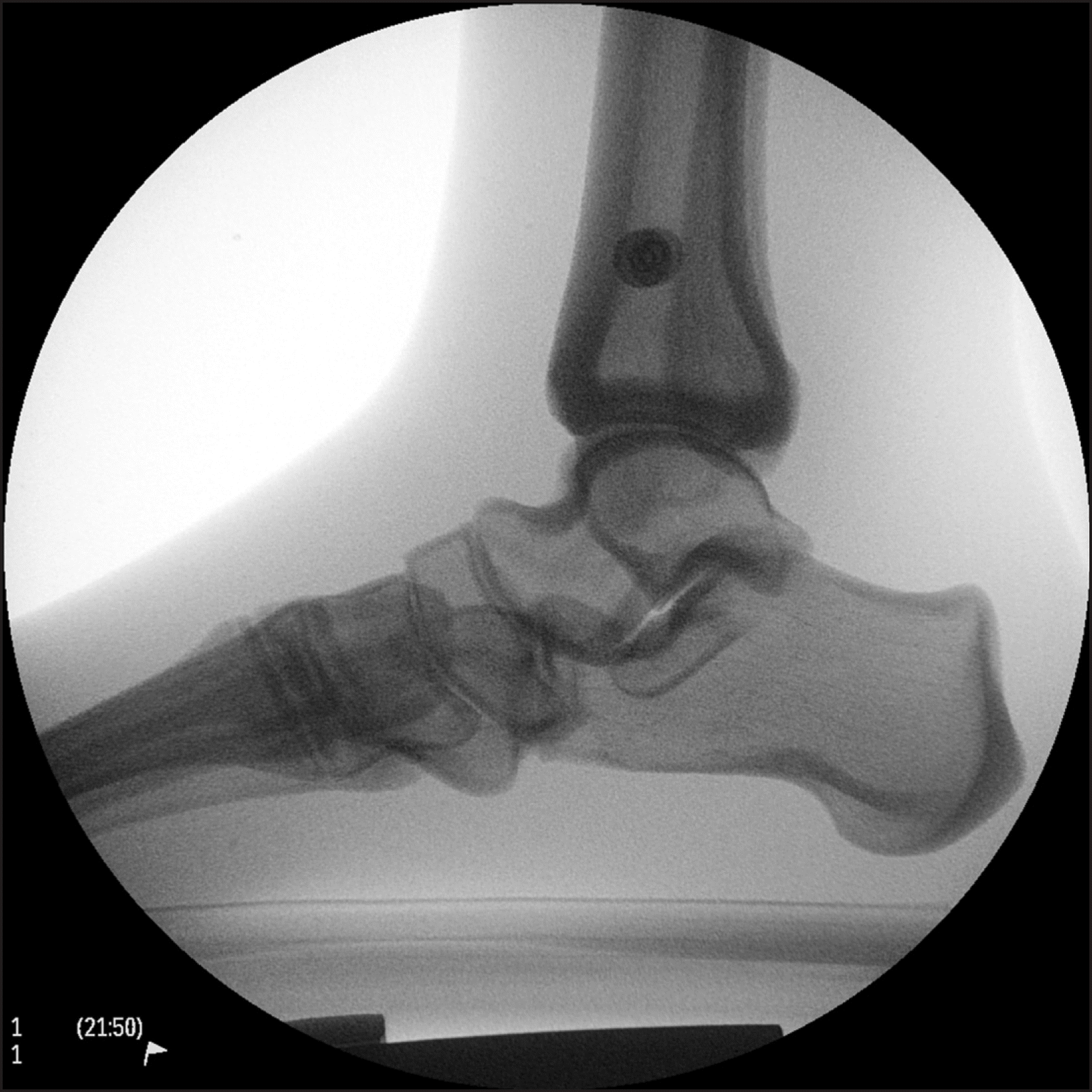 | Figure 2.Both markers on phantom foot should overlap for the radiation projection to be parallel to the horizontal reference axis. |
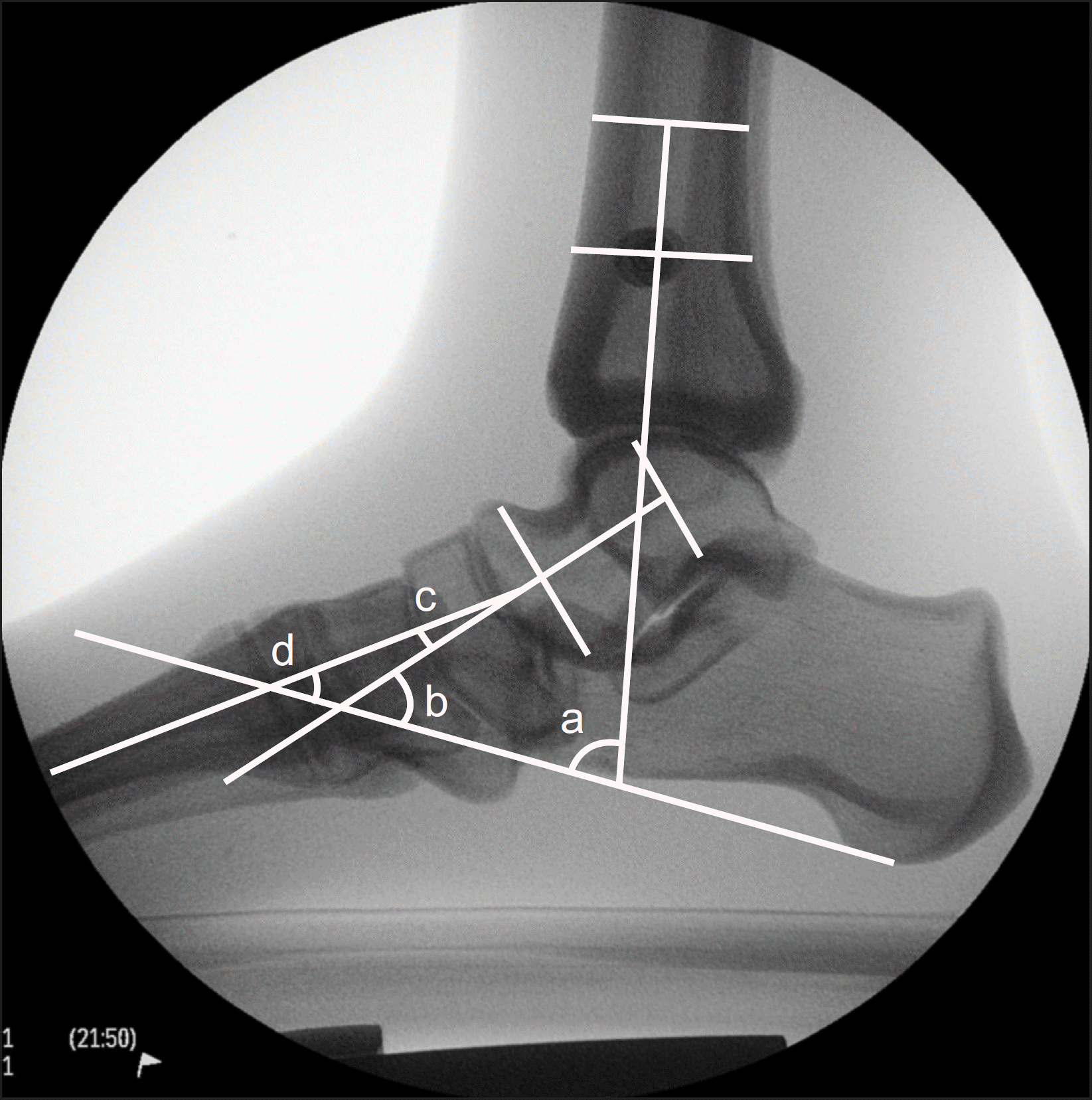 | Figure 3.Angles were measured on plain lateral radiograph. a: Lateral tibiocalcaneal angle was measured to evaluate hindfoot alignment. b: Lateral talocalcaneal angle was measured to evaluate hindfoot alignment. c: Lateral talo-first metatarsal angle was measured to evaluate flatfoot deformity. d: Lateral calcaneo-first metatarsal angle was measured to evaluate cavus deformity. |
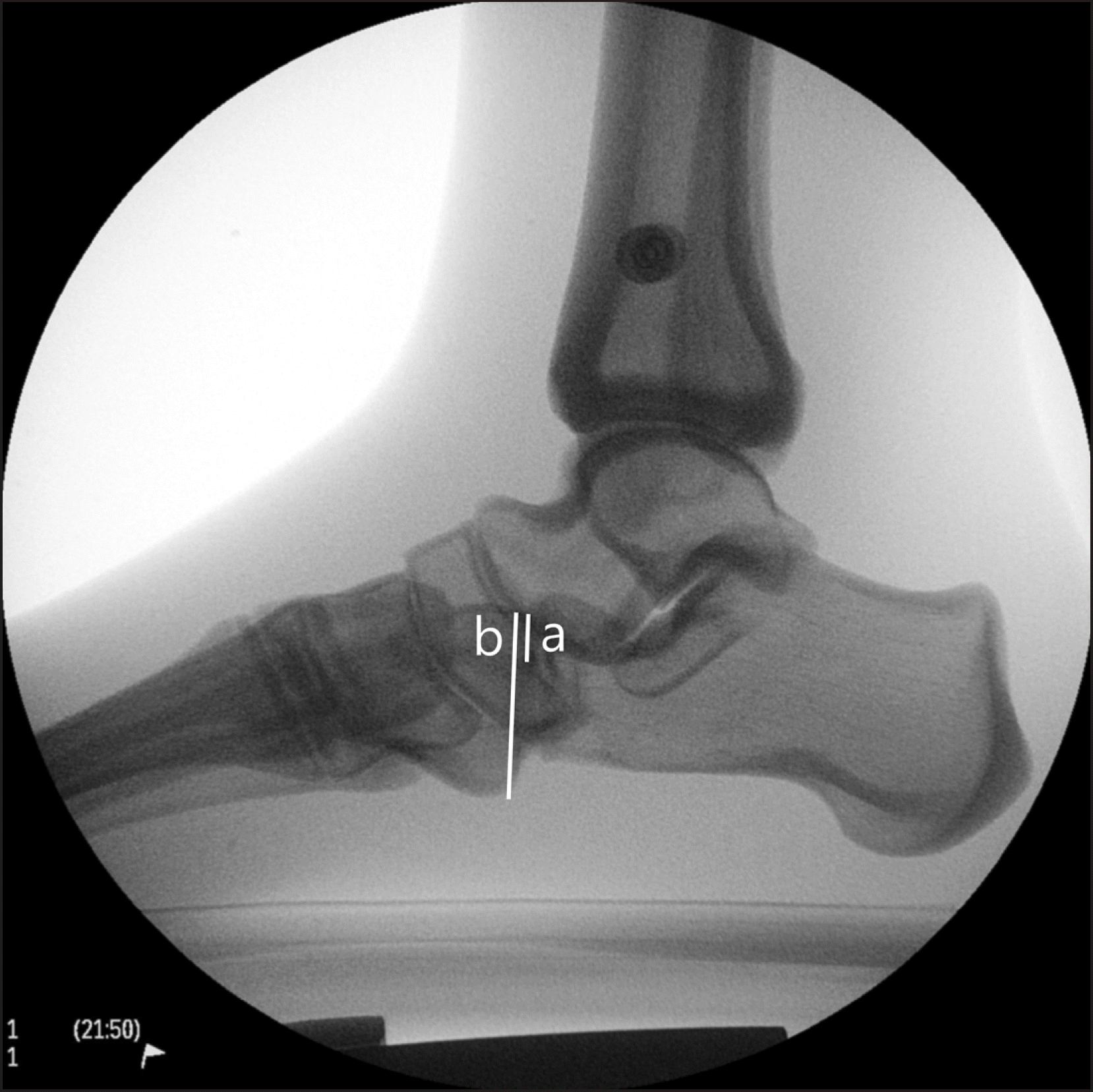
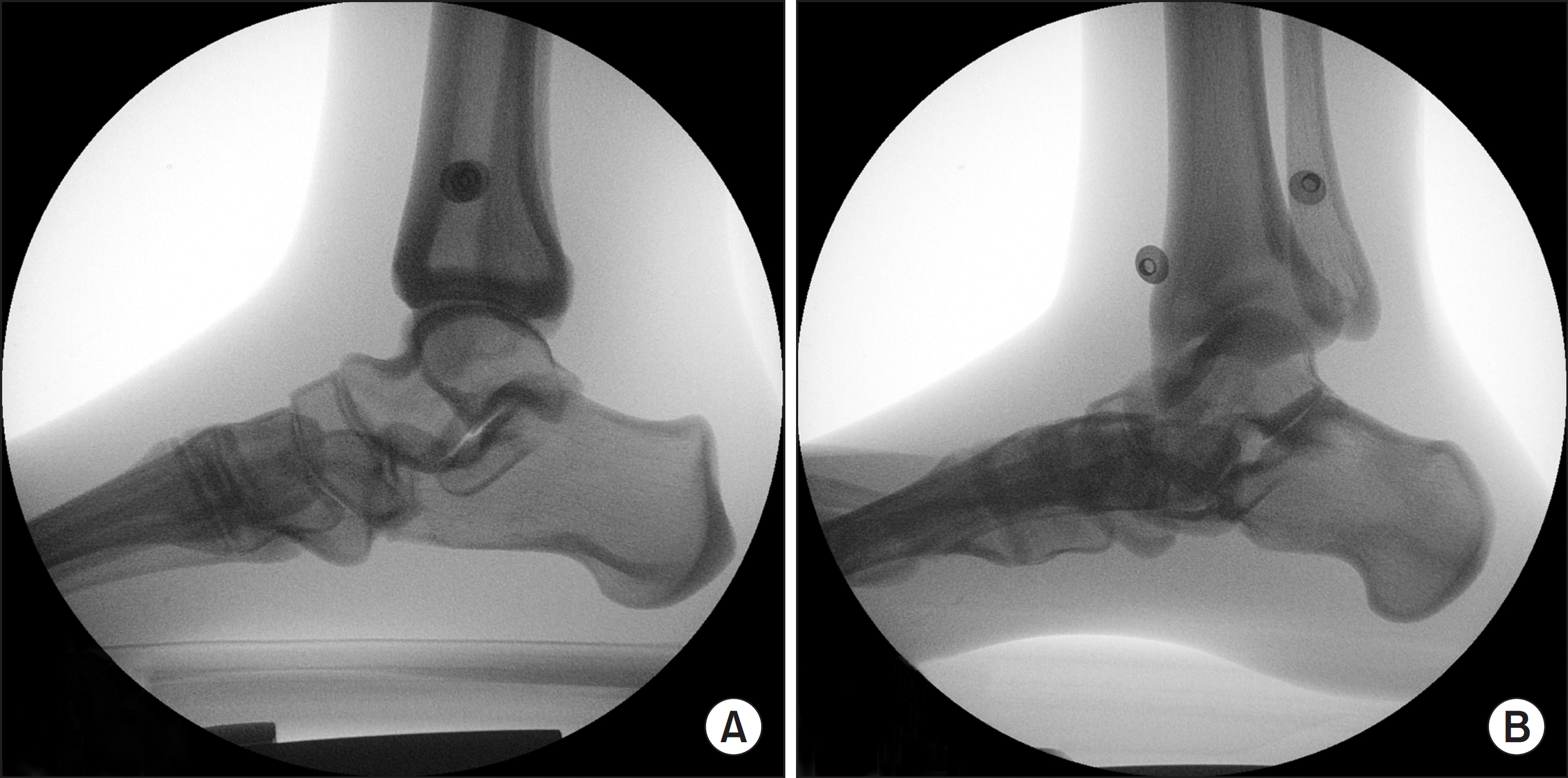 | Figure 5.(A) Two markers on phantom foot overlap with radiation projection with 0o rotation and 0o tilt. (B) Two markers on phantom foot and alignment were twisted with radiation projection with 30o external rotation and 15o medial tilt. |
Table 1.
Intraobserver Reliability (Intraclass Correlation Coefficient)
Table 2.
Interobserver Reliability (Intraclass Correlation Coefficient)
Table 3.
Comparison of Normal Values and Measurement Values
| Radiographic parameter | Normal value* | Measurement value |
|---|---|---|
| Lateral tibiocalcaneal angle (o) | N/A | 76.95 |
| Lateral talocalcaneal angle (o) | 46.5±5.45 | 47.33 |
| Naviculocuboid overlap | N/A | 0.21 |
| Lateral talo-first metatarsal angle (Meary angle) (o) | ―2.5±4.6 | ―6.67 |
| Lateral calcaneo-first metatarsal angle (Hibbs angle) (o) | 44.0±4.5 | 41.16 |
Table 4.
Changes according to Radiation Projection Angle
Table 5.
Correlation between Radiographic Parameters and Radiation Projection Angle




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download