Abstract
We experienced a patient in whom rupture of the peroneus longus tendon occurred after ostectomy of the peroneus tubercle of the calcaneus. Acute rupture of the peroneus tendon can be managed by end-to-end anastomosis, while neglected cases can be treated by tenodesis, tendon transfer, or tendon graft. In the current patient, the tendon ends were mildly retracted, yielding a small gap. We successfully repaired the retracted tendon ends after lengthening by Z-plasty.
Go to : 
References
1. Arbab D, Tingart M, Frank D, Abbara-Czardybon M, Waizy H, Wingenfeld C. Treatment of isolated peroneus longus tears and a review of the literature. Foot Ankle Spec. 2014; 7:113–8.

2. Ng VY, Hothem E, Calhoun J. Radiologic case study. Peroneus longus rupture. Orthopedics. 2010; 33(701):778–9.
3. Dombek MF, Lamm BM, Saltrick K, Mendicino RW, Catanzariti AR. Peroneal tendon tears: a retrospective review. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2003; 42:250–8.

5. Redfern D, Myerson M. The management of concomitant tears of the peroneus longus and brevis tendons. Foot Ankle Int. 2004; 25:695–707.

6. Krause JO, Brodsky JW. Peroneus brevis tendon tears: pathophysiology, surgical reconstruction, and clinical results. Foot Ankle Int. 1998; 19:271–9.

Go to : 
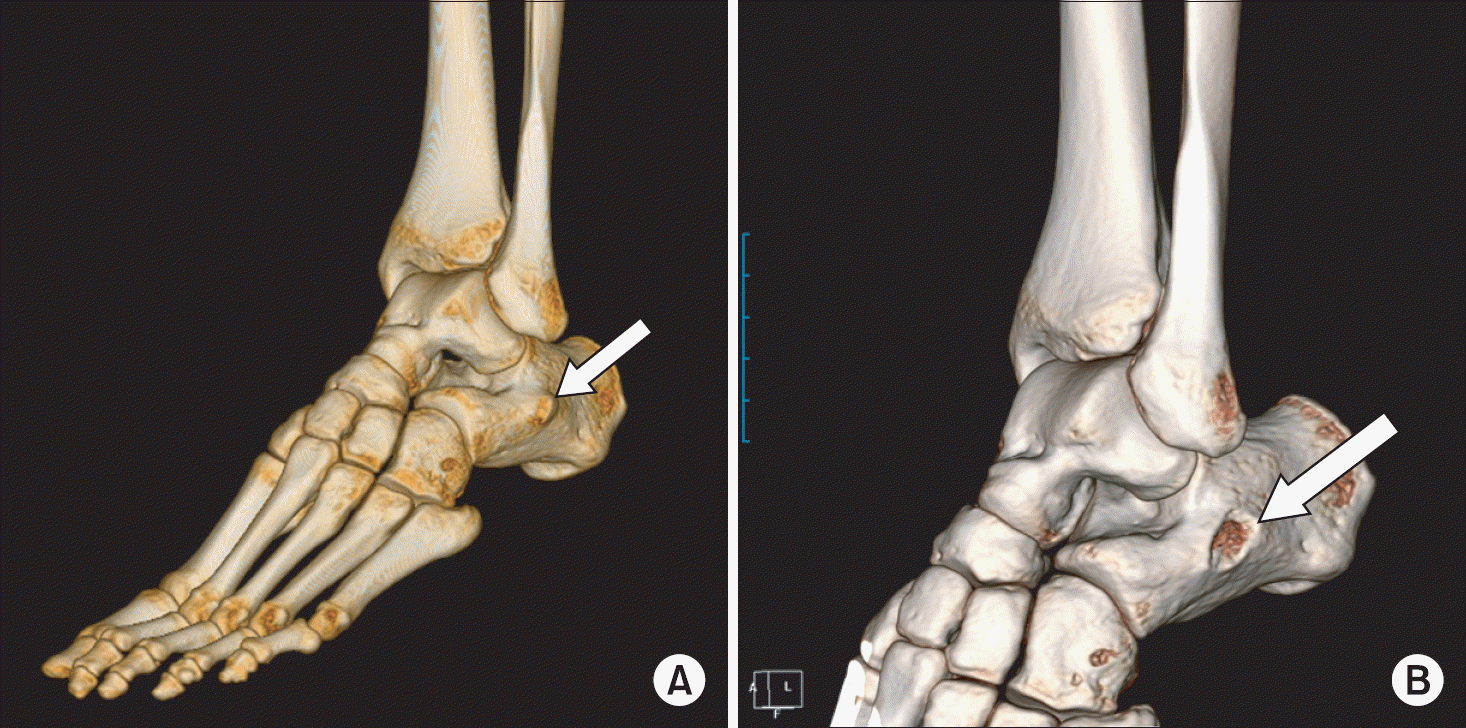 | Figure 1.(A) Peroneus tubercle (white arrow) was seen in the three-dimensional reconstructed images of computed tomography performed before ostectomy of peroneus tubercle of calcaneus. (B) Irregular surface of peroneus tubercle stump (white arrow) was shown in the three-dimensional reconstructed images of computed tomography performed after ostectomy. |
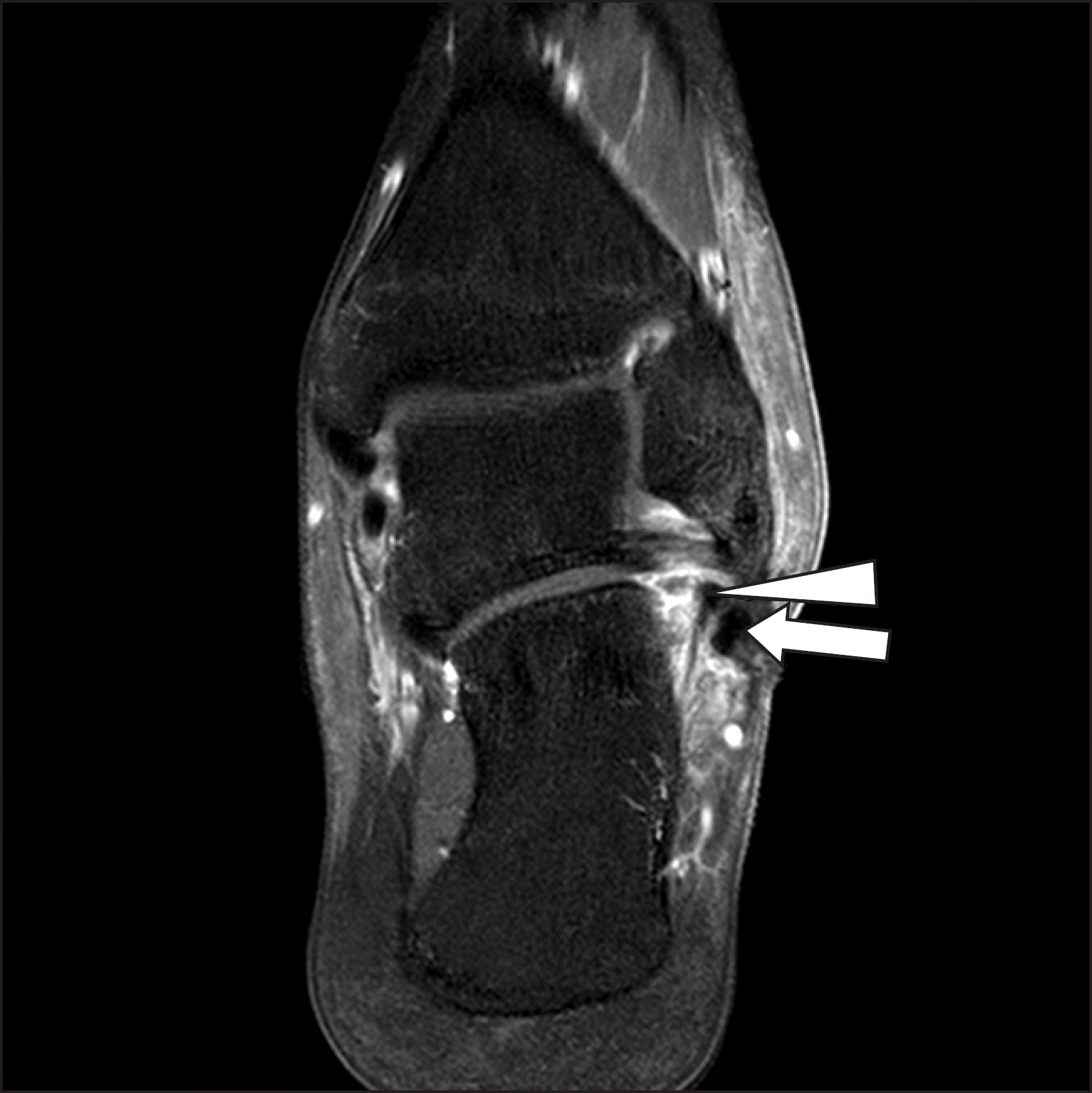
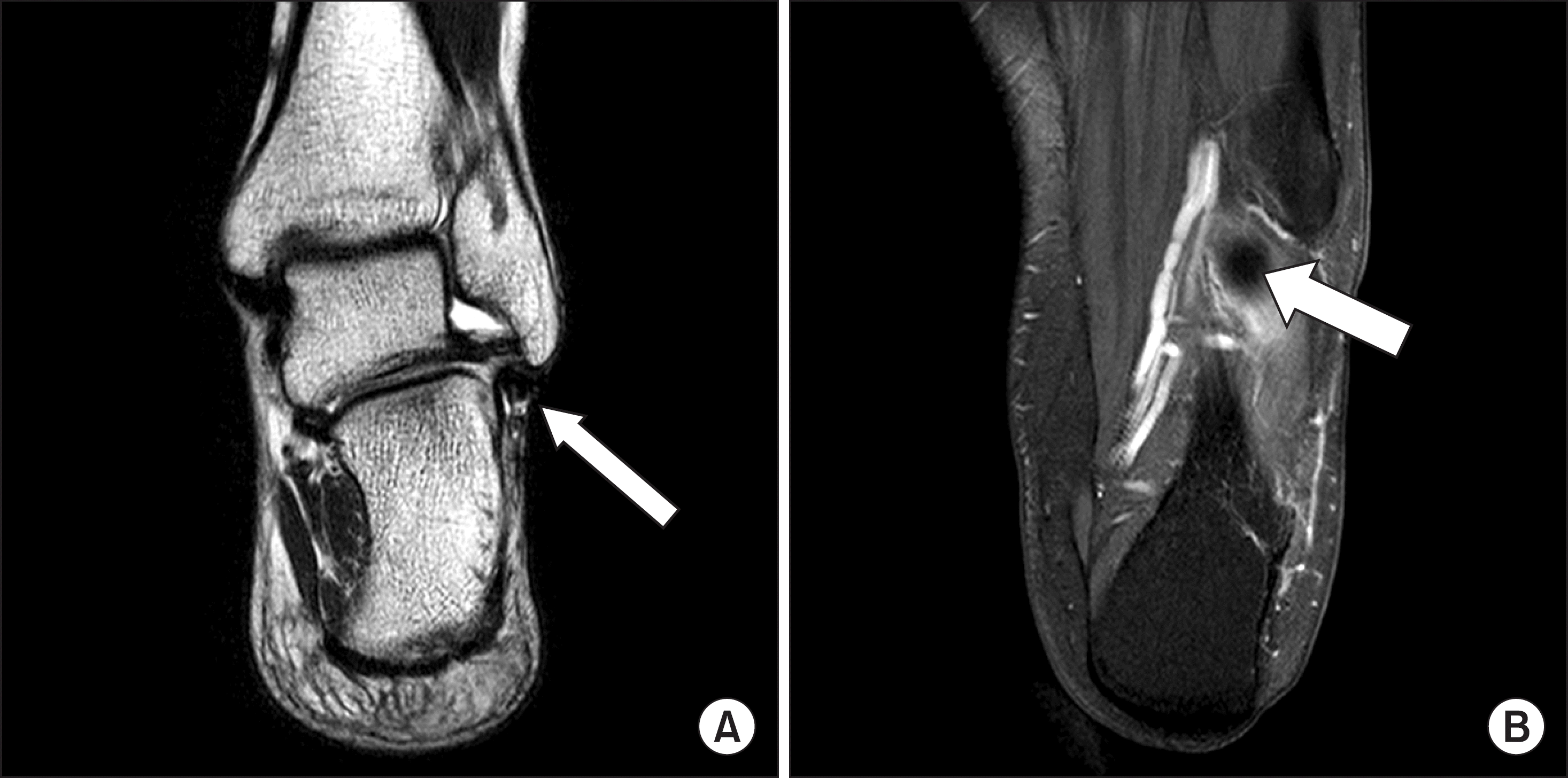 | Figure 2.(A) Peroneus brevis tendon (white arrow) was found intact, but the continuity of peroneus longus tendon was not shown below the peroneus brevis tendon. (B) Distal stump of the ruptured peroneus longus tendon (white arrow) was found at the undersurface of the cuboid. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


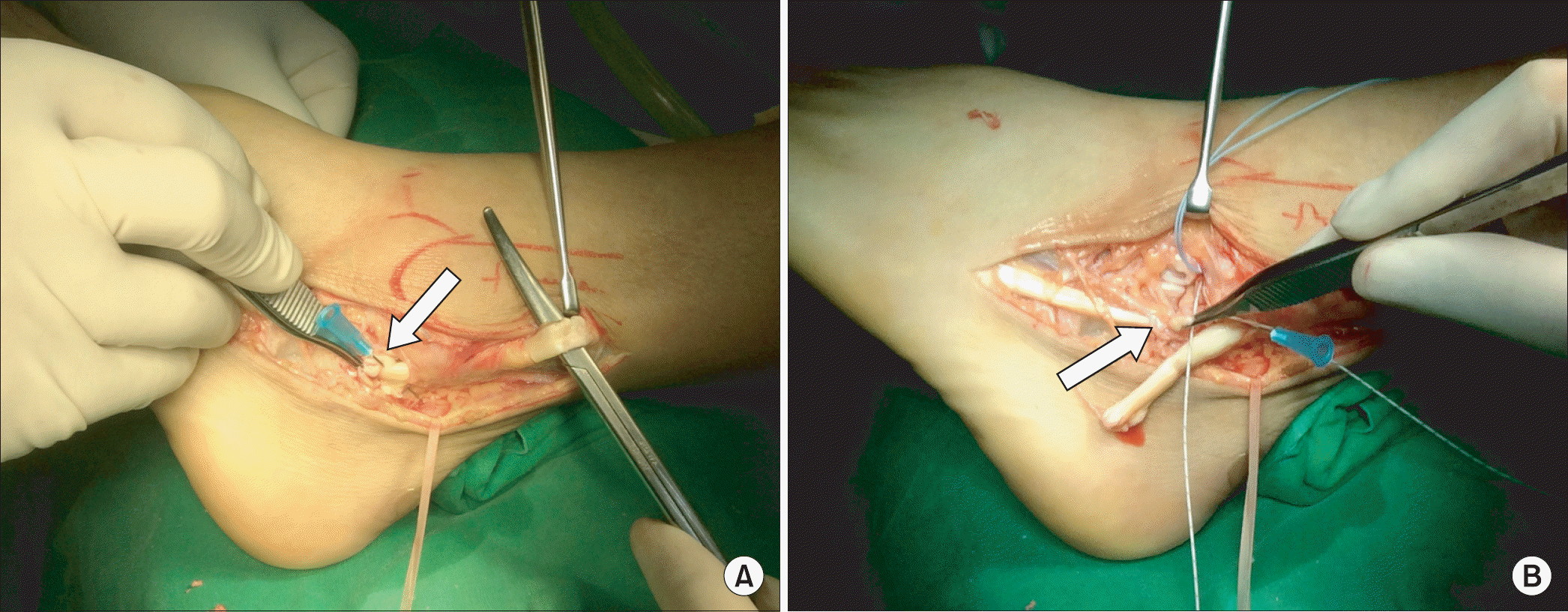
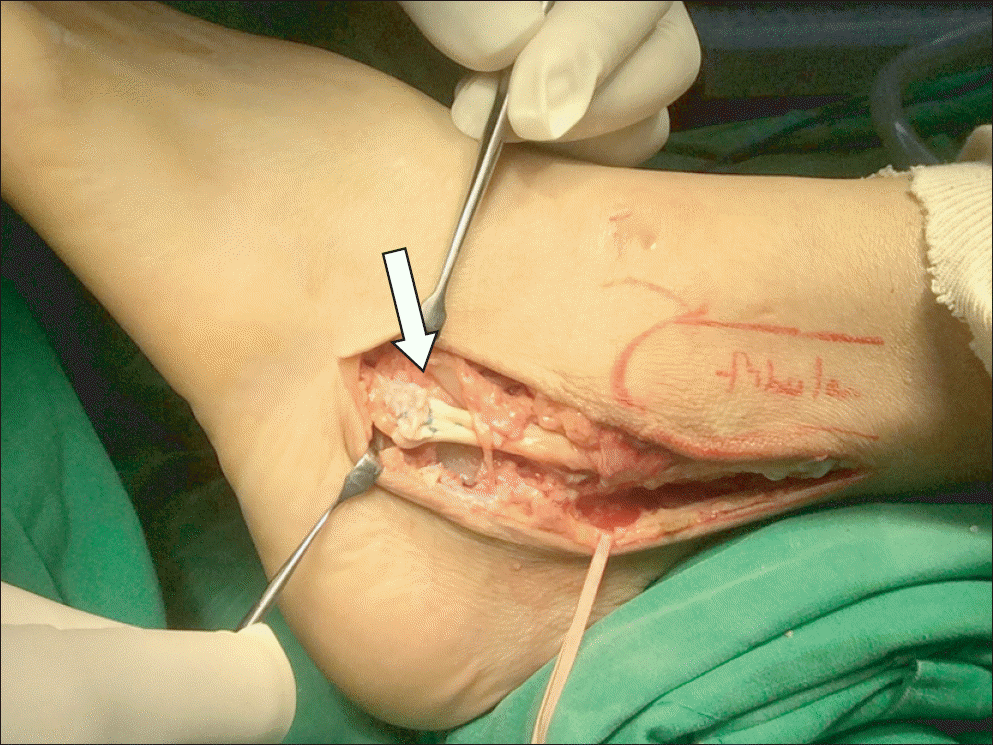
 XML Download
XML Download