Abstract
Chronic extensor hallucis longus tendon ruptures are very rare, and may lead to hallux dysfunction. To the best of our knowledge, reconstruction of a chronic extensor hallucis longus rupture using interposed scar tissue has not been previously reported. Our results show that direct repair method using interposed scar tissue for chronic extensor hallucis longus rupture can successfully restore function of the hallux and provide good satisfaction in carefully selected patients.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Berens TA. Autogenous graft repair of an extensor hallucis longus laceration. J Foot Surg. 1990. 29:179–82.
2.Mulcahy DM., Dolan AM., Stephens MM. Spontaneous rupture of extensor hallucis longus tendon. Foot Ankle Int. 1996. 17:162–3.

3.Mann RA. Miscellaneous afflictions of the foot. Mann RA, editor. editor.Surgery of the foot. 5th ed.St. Louis: Mosby;1986. p.2556.
4.Park HG., Lee BK., Sim JA. Autogenous graft repair using semitendinous tendon for a chronic multifocal rupture of the extensor hallucis longus tendon: a case report. Foot Ankle Int. 2003. 24:506–8.

5.Yasuda T., Kinoshita M., Okuda R. Reconstruction of chronic achilles tendon rupture with the use of interposed tissue between the stumps. Am J Sports Med. 2007. 35:582–8.

6.Lee KB., Park YH., Yoon TR., Chung JY. Reconstruction of neglected Achilles tendon rupture using the flexor hallucis tendon. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2009. 17:316–20.

7.Cho HJ., Yeo JH., Lee KB. Reconstruction of chronic achilles tendon rupture using interposed scar tissue (a report of two cases). J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2013. 17:316–20.
8.Noonan KJ., Saltzman CL., Dietz FR. Open physeal fractures of the distal phalanx of the great toe. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994. 76:122–5.

Go to : 
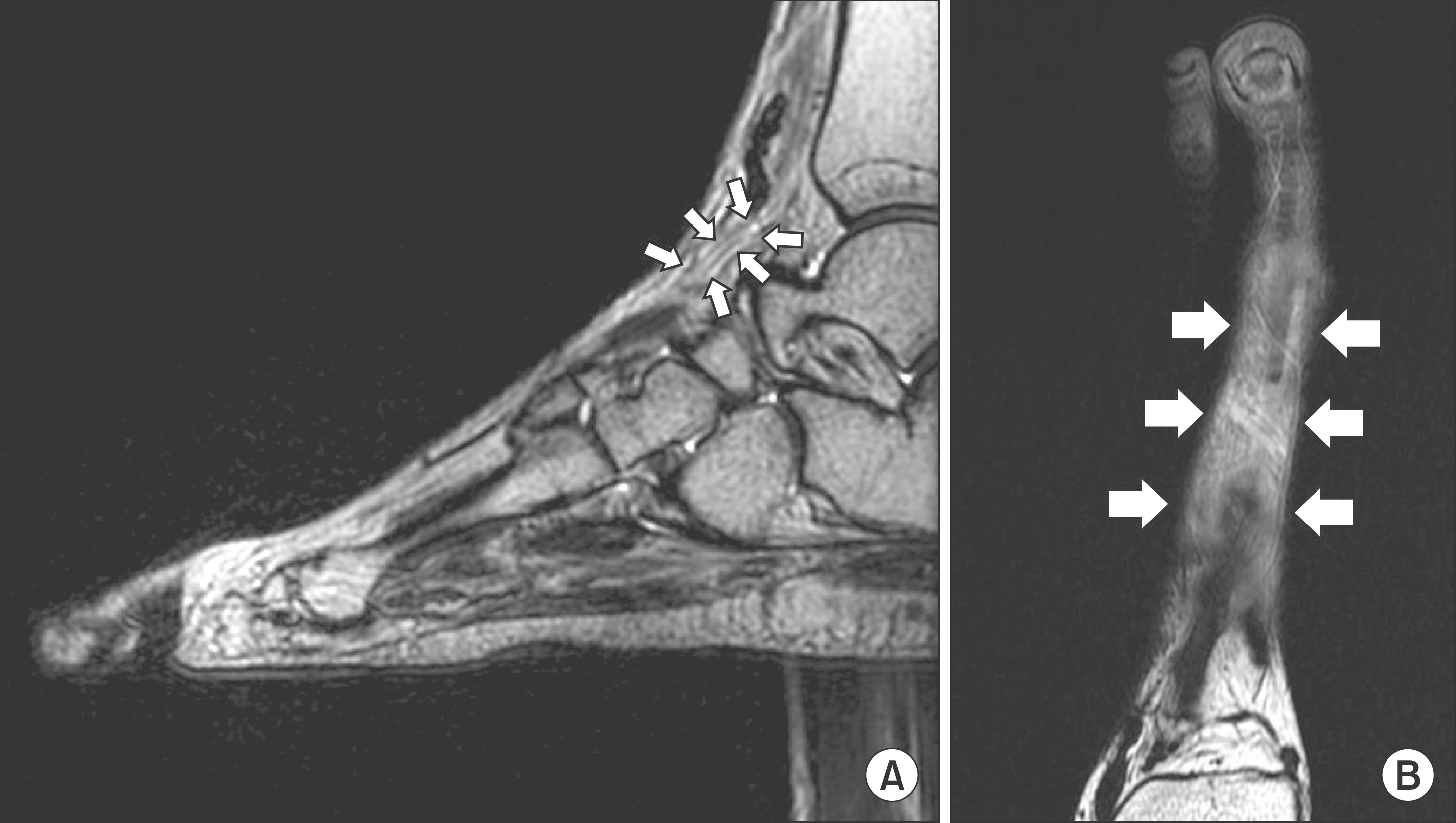 | Figure 2.T2-weighted magnetic resonance imagings show extensor hallucis longus with diffuse intratendinous heterogenous-signal change (arrows) on sagittal (A) and axial view (B). |
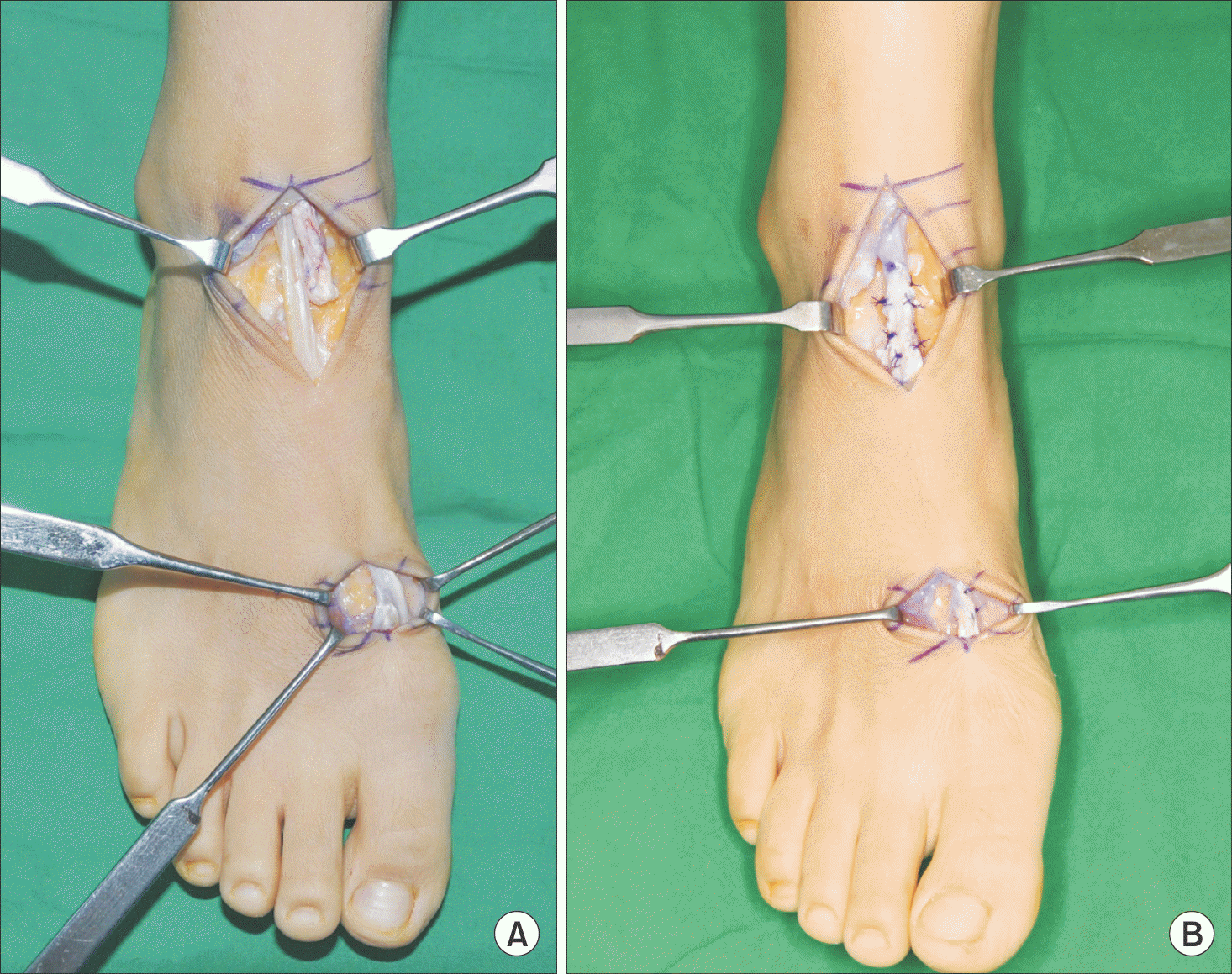 | Figure 3.Intraoperative photo shows gap between the tendon stumps filled with thick connectivce tissue (A), direct repair incorporating scar tissue interposed between the tendon stumps (B). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download