Abstract
Purpose:
We evaluated the correlation of postoperative clinical outcomes and radiologic findings using computed tomography and simple X-ray in intra-articular calcaneal fractures.
Materials and Methods:
The current study is based on 41 feet, 38 patients with displaced intra-articular fracture who underwent surgical treatment with at least one year of follow-up. Evaluation of clinical outcome included American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) ankle-hindfoot score, visual analogue scale (VAS) score, and subjective satisfaction. A simple X-ray was used in evaluation of preoperative and postoperative Gissane angle, BÖhler angle, and calcaneal fracture width. Computed tomography scan was performed for evaluation of preoperative and postoperative articular step-off and articular gap in all cases. Finally, we evaluated the correlation of the postoperative clinical outcomes and radiologic findings based on the measurement.
Results:
The average postoperative AOFAS score and VAS score was 84.1±8.5 and 2.2±2.2. Subjective satisfaction was excellent in 15 cases, good in 19 cases, and fair in seven cases. The average BÖhler angle was restored from 11.1° to 24.7° (p<0.05), Gissane angle was changed from 121.0° to 119.0° (p>0.05), and the average width was restored from 45.8 to 35.0 mm (p<0.05). The average articular step-off and gap were decreased from 6.3 to 2.0 mm and from 11.1 to 4.6 mm, respectively (p<0.05). No significant correlations were observed between the clinical outcome and Gissane angle, BÖhler angle, and width, and there was no significant correlation between the clinical outcome and Sanders classification. However, postoperative articular step-off showed correlation with VAS and AOFAS score and articular gap showed correlation with VAS score.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Cave EF. Fracture of the os calcis--the problem in general. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1963. 30:64–6.
2.Ebraheim NA., Elgafy H., Sabry FF., Tao S. Calcaneus fractures with subluxation of the posterior facet. A surgical indication. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000. 377:210–6.
3.Hildebrand KA., Buckley RE., Mohtadi NG., Faris P. Functional outcome measures after displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996. 78:119–23.

4.Sanders R. Displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000. 82:225–50.

5.Magnan B., Bortolazzi R., Marangon A., Marino M., Dall’Oca C., Bartolozzi P. External fixation for displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneum. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006. 88:1474–9.

6.Kurozumi T., Jinno Y., Sato T., Inoue H., Aitani T., Okuda K. Open reduction for intra-articular calcaneal fractures: evaluation using computed tomography. Foot Ankle Int. 2003. 24:942–8.

7.Parmar HV., Triffitt PD., Gregg PJ. Intra-articular fractures of the calcaneum treated operatively or conservatively. A prospective study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993. 75:932–7.

8.Chung HJ., Ahn JK., Bae SY., Jung H. Operative treatment of in-traarticular calcaneal fractures using extensile lateral approach. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2009. 13:60–7.
9.Sanders R., Fortin P., DiPasquale T., Walling A. Operative treatment in 120 displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Results using a prognostic computed tomography scan classification. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993. 290:87–95.
10.Chapman MW. Calcaneus fractures. Chapman MW, editor. editor.Chapman’s orthopaedic surgery. 3rd ed.Philadelphia: Lippin-cott Williams & Wilkins;2001. p. 2966–79.
11.Essex-Lopresti P. The mechanism, reduction technique, and results in fractures of the os calcis. Br J Surg. 1952. 39:395–419.

12.Carr JB., Hamilton JJ., Bear LS. Experimental intra-articular calcaneal fractures: anatomic basis for a new classification. Foot Ankle. 1989. 10:81–7.

13.Maxfield JE., McDermott FJ. Experiences with the Palmer open reduction of fractures of the calcaneus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1955. 37:99–106.

14.Buckley RE., Meek RN. Comparison of open versus closed reduction of intraarticular calcaneal fractures: a matched cohort in workmen. J Orthop Trauma. 1992. 6:216–22.

15.Giachino AA., Uhthoff HK. Intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989. 71:784–7.

16.Kundel K., Funk E., Brutscher M., Bickel R. Calcaneal fractures: operative versus nonoperative treatment. J Trauma. 1996. 41:839–45.
17.Song KS., Kang CH., Min BW., Sohn GJ. Preoperative and postoperative evaluation of intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus based on computed tomography scanning. J Orthop Trauma. 1997. 11:435–40.

18.Kim CW., Chung MY., Jung KT., Bae EH., Park SH., Park HK, et al. Comparison of the conservative and operative treatment of the intraarticular calcaneal fractures. J Korean Soc Fract. 1999. 12:335–43.

19.Kim KS., Choi YS., Han SC., Shon KS. Operative treatment of displaced intraarticular fractures of the calcaneus. J Korean Soc Fract. 1998. 11:894–9.

20.Roh JY., Bae SY., Kim SD. Computed tomographic classification and operative treatment of intraarticular calcaneal fractures. J Korean Foot Surg Soc. 2002. 6:149–55.
21.Segal D., Marsh JL., Leiter B. Clinical application of computerized axial tomography (CAT) scanning of calcaneus fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985. 199:114–23.

22.Dooley P., Buckley R., Tough S., McCormack B., Pate G., Leighton R, et al. Bilateral calcaneal fractures: operative versus nonoperative treatment. Foot Ankle Int. 2004. 25:47–52.

23.Buckley R., Tough S., McCormack R., Pate G., Leighton R., Petrie D, et al. Operative compared with nonoperative treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a prospective, randomized, controlled multicenter trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002. 84:1733–44.
24.Crosby LA., Fitzgibbons T. Computerized tomography scanning of acute intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. A new classification system. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990. 72:852–9.

25.Crosby LA., Fitzgibbons TC. Open reduction and internal fixation of type II intra-articular calcaneus fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 1996. 17:253–8.

26.Basile A. Subjective results after surgical treatment for displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2012. 51:182–6.

27.Guyer BH., Levinsohn EM., Fredrickson BE., Bailey GL., Formikell M. Computed tomography of calcaneal fractures: anatomy, pathology, dosimetry, and clinical relevance. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1985. 145:911–9.

28.Paley D., Hall H. Intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. A critical analysis of results and prognostic factors. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993. 75:342–54.

Go to : 
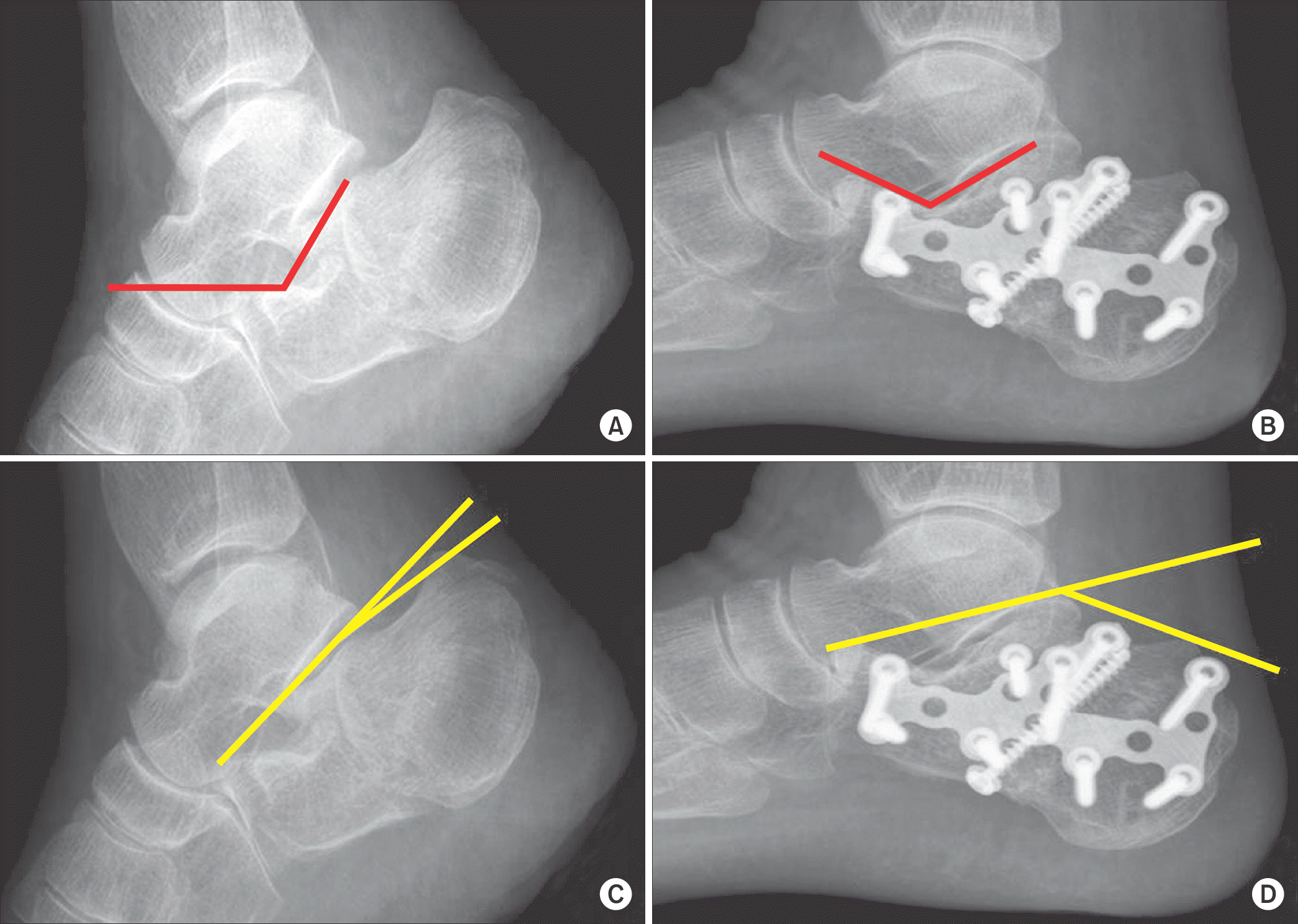 | Figure 1.The radiographs show preoperative Gissane angle (A), postoperative Gissane angle (B), preoperative Böhler angle (C), and postoperative Böhler angle (D). |
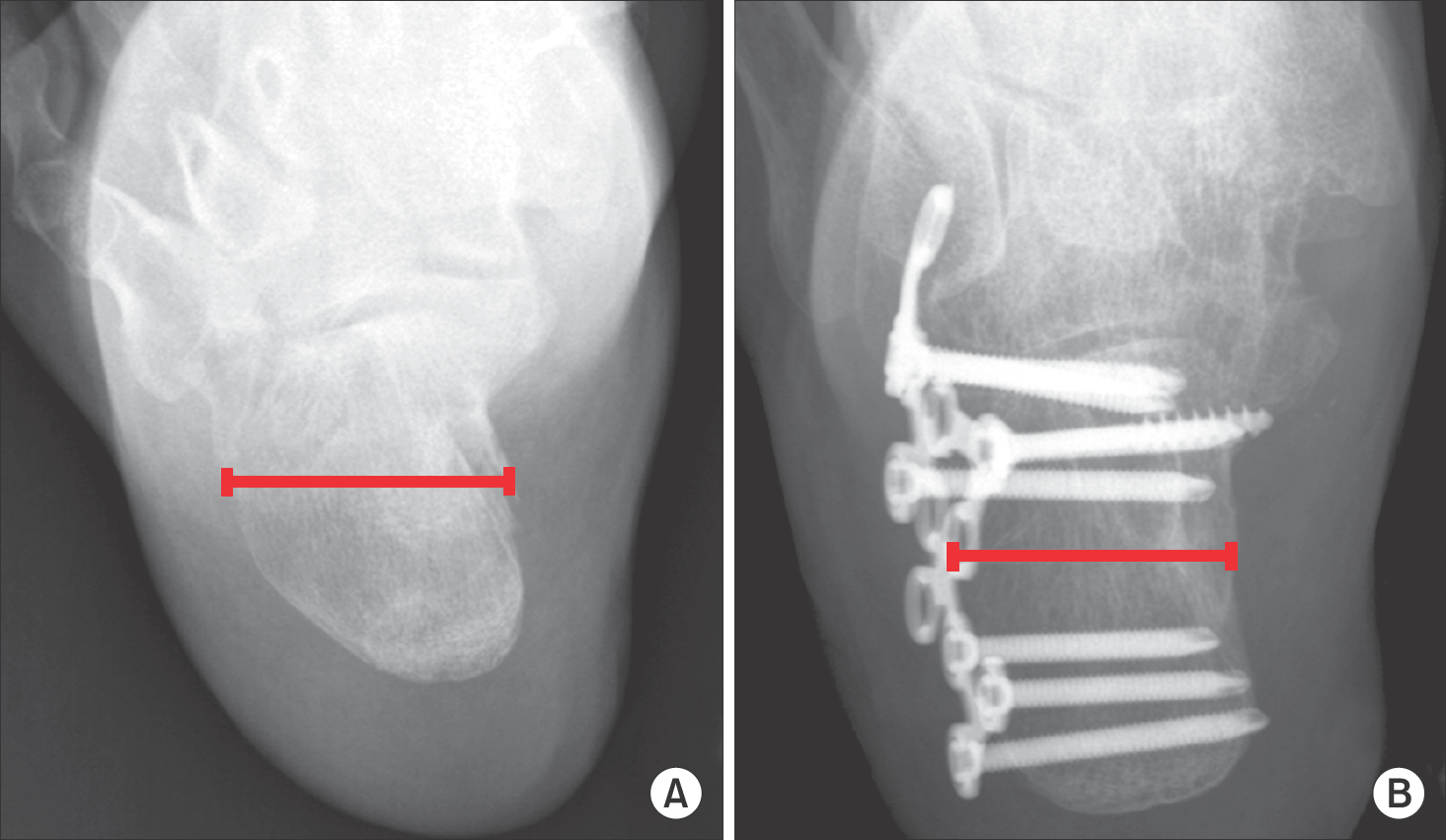 | Figure 2.Preoperative (A) and postoperative (B) axial radiographs show fracture width. Fracture width is measured as the widest part of calcaneus. |
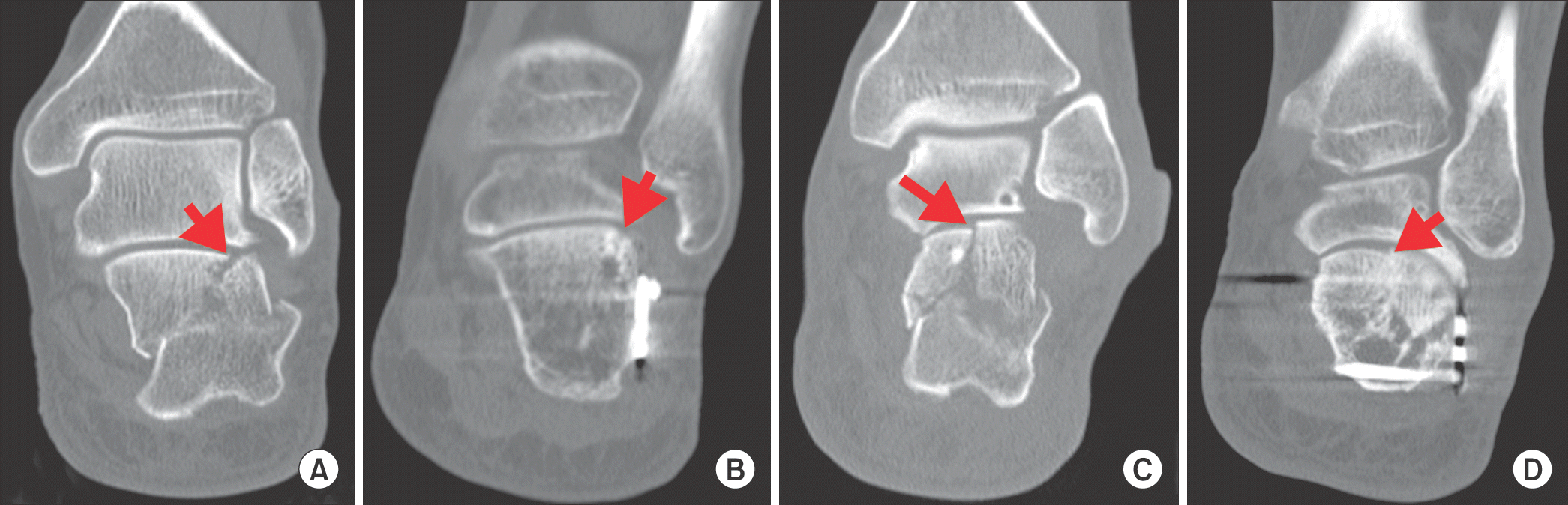 | Figure 3.Computed tomographic images show preoperative articular gap (A, arrow), postoperative articular gap (B, arrow), preoperative articular step-off (C, arrow), and postoperative articular step-off (D, arrow) in the intra-articular calcaneal fracture. |
Table 1.
Correlation Analysis of Postoperative Articular Step-off and Articular Gap with Clinical Outcomes
| Group | Foot | VAS score | AOFAS score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Step-off ≥2 mm | 22 | 3.0±2.4 | 81.1±9.6 |
| <2 mm | 19 | 1.3±1.7 | 87.1±6.2 |
| Gap ≥2 mm | 33 | 2.4±2.2 | 82.7±8.7 |
| <2 mm | 8 | 1.50±2.1 | 88.7±6.9 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download