Abstract
Otitis media (OM) is one of the most common pediatric infectious diseases. The burden of OM is known in many countries, but data for Korea has not been collected. The primary objective of this study was to evaluate the disease burden of OM in both children and adults. The Health Insurance Review and Assessment database study was analyzed to estimate the clinical and economic burden of OM and acute OM (AOM) for 2004. OM was defined as all cases coded H65, H66, or H67 and AOM cases coded H65, H65.0, H65.1, H65.9, H66, H66.4 or H66.9. For AOM, repeated visits within 30 days were considered to be one episode. Age specific incidence, and direct and indirect costs were estimated. A survey on pediatricians and otolaryngologists who most frequently diagnosed OM was carried out. The objective was to evaluate the accuracy of the claims made for OM and to examine the diagnosis and treatments of OM. A total of 5,964,587 claims for OM and 2,924,532 AOM episodes were reported. The incidence of outpatients presenting AOM was 60.9/1,000. The incidence of AOM was highest in children aged 1 year (736.9/1,000). The overall hospitalization rate due to AOM was 2.8/10,000, with a peak of 29.4/10,000 (1 year). The total cost incurred by AOM in Korea was estimated to be around 606.3 billion Korean won (KRW; 1,000 KRW is approximately US$1.00). The total cost of admissions was approximately 22.9 billion KRW, and the average cost of admission per person was about 1,690,000 KRW in a year. The cost of outpatient visits was 583.4 billion KRW, and 199,000 KRW per person. According to a survey of pediatricians and otolaryngologists on the accuracy of the OM diagnostic code, treatment, and prescription habits, the first-line diagnosis of AOM seemed to be fairly accurate. OM, including AOM, causes a considerable clinical and economic burden in Korea.
Otitis media (OM) is inflammation of the middle ear. It is not only a common disorder that occurs in children after respiratory infection, but also the most frequent disease requiring antibiotics and surgery [1-4]. OM can be divided into suppurative and non-suppurative OM. Suppurative OM occurs as acute OM (AOM) while non-suppurative OM occurs as OM with effusion (OME) which is caused by the accumulation of effusion fluid in the middle ear cavity. AOM and OME regress spontaneously in most cases, and in general complete clinical recovery occurs within one to two weeks in 70% of pediatric patients [5]. However, AOM also recurs frequently. It has been reported that 50% to 65% of pediatric patients three to five years of age had three or more recurrent episodes and that in pediatric patients 24 months of age or younger the recurrence rate of OME was 50% [6].
OM occurs most frequently in infants or young children. Approximately two-thirds of children experience one episode of AOM by the time they reach two years of age and 50% at least twice, but the incidence falls dramatically after six years of age [1]. According to other reports on the incidence of OM, over 80% of children experience OM at least once before they reach three, with an average of 1.9 times a year between six and eleven months of age and an average of 1.7 times a year between twelve and twenty three months of age and an average of 1.1 times a year between twenty three and twenty six months of age [5]. OM has a high frequency of outpatient visits and antibiotic prescribing rate. It may be accompanied by sequelae, such as chronic OM, hearing difficulty and can negatively impact the quality of life thus increasing the burden of disease [7]. In the US, the annual cost of OM is estimated to be three to five billion dollars [8], but if we take the indirect cost incurred by the families of pediatric patients, such as lost productivity, into account, the actual burden would be heavier [7].
OM is a common disease in Korea, but data on the burden of disease, such as the incidence, prevalence, and cost are limited. This lack of data greatly limits evaluations of related policies and vaccines. The objective of this study is to estimate the incidence of OM and burden of disease in Korea. The study was conducted in two ways: one was by analyzing the health insurance data and the other was by carrying out a survey on doctors. The health insurance data include most of the national medical insurance claims data, however, it has always been a problem how well the classification of diseases in the claims would match the actual diagnosis, in particular with infectious diseases. This study aims also to explore the accuracy of health insurance data of OM indirectly, based on the survey on doctors.
We assessed and analyzed National Health Insurance Review and Assessment (HIRA) database of 2004. Korea has unique universal national medical insurance system, so all insured medical services and expenditures in Korea must be reported to HIRA in order to be reimbursed. HIRA database is representative of the disease and health care of Korean population and is the most frequently used database for disease burden studies in Korea. OM was defined as cases claimed for H65 (nonsuppurative OM), H66 (suppurative and unspecified OM), H67 (OM in disease classified elsewhere) codes. AOM was defined as cases claimed for H65 (nonsuppurative OM), H65.0 (acute serous OM), H65.1 (other acute nonsuppurative OM), H65.9 (nonsuppurative OM unspecified). H66 (suppurative and unspecified OM), H66.0 (acute suppurative OM), H66.4 (suppurative OM specified H66.9 OM unspecified). All persons registered in the national health insurance system from January 01, 2004 to December 31, 2004 were considered as population at risk for OM. Repeated visits of the same cases within one months after 1st visit of any medical facilities due to AOM were considered one episode [9]. Age-specific incidence rate was defined as the total number of new episodes per 1,000 populations by age.
The financial burden of OM was also estimated by calculating the direct and indirect cost due to OM related outpatient visits and hospitalizations. Direct cost is cost for hospitalization and visiting outpatient clinic to manage the disease. Includes medical cost (both covered by health insurance and private expense), pharmaceutical cost, transportation cost and nursing fee.
Direct cost and cost of work loss were defined as below.
i: age (0,1,2…n)
α: percentage of hospitalization fee not covered by national health insurance
β: percentage of outpatient fee not covered by national health insurance
Ei: hospitalization cost
OEi: outpatient cost
Oi: duration (days) of outpatient visit
M: average round trip transportation fee
Ni: duration (days) of hospitalization
I: average daily nursing fee
i: age (0,1,2...n)
j: sex (1,2)
Nij: duration (days) of hospitalization
δ: the proportion rate of outpatient vs. hospitalization
Oij: duration (days) of outpatient visit
pij: rate of participation in financial activity
eij: employment rate
yij: average daily income
Non-productive days for inpatient was calculated as number of days hospitalized and for outpatient number of outpatient visits multiplied by 1/3. This was in reference to previous study hypothesizing that a doctor's productivity for one inpatient equals three outpatient visits [10,11]. We assumed that cost of loss of productivity did not apply to pediatric patients between 0 and 19 years of age and elderly patients 65 years of age or older. However, by hypothesizing that their families (guardians) in these age groups are females (1 to 19 years of age: mothers, 65 years of age: daughters and daughter-in-laws), and their age is placed between 30 and 49 years of age, we estimated the cost of lost productivity, by applying the average hourly and daily wage of the females in this age group [11]. The economic activity participation rate and employment rate by age group were referenced from the Ministry of Labour's 2004 data. Any loss incurred due to premature death was not included in the indirect cost. The estimated cost was viewed from sociological perspective. All used variables and data sources are presented in Table 1.
The survey on pediatricians and otolaryngologists was conducted between 21 June 2010 and 31 July 2010 by mail. The questions included individual characteristics such as specialty and experiences, diagnostic method of AOM, differentiation between acute suppurative and non-suppurative otitis media (OME), and classification of AOM used for health insurance claims. Such questions were prepared to indirectly evaluate the significance of differences between the classification of AOM used in health insurances and the patients actually diagnosed with OM. Apart from questions, information regarding the incidence of invasive treatments (myringectomy, v-tube insertion), duration of antibiotic use, and also pneumococcal vaccination were included in the survey, since a pneumococcal vaccine can prevent OM caused by certain types of Streptococcus pneumoniae.
To analyze the incidence of AOM, basic descriptive epidemiological analysis and frequency analysis were used. To obtain the total cost for all patients and by age groups, the direct cost and indirect cost incurred by inpatients and outpatients were calculated per person by age groups, and then multiplied by the numbers of outpatients and inpatients. In an item analysis, basic frequency analysis and chi-square test were used for discrete variables between pediatricians and otolaryngologists. The significance test was carried out by choosing a significance level of 0.05. Necessary data has been retrieved from the health insurance data for the statistical analysis by applying SAS ver. 9.2 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and SPSS ver. 12.0 (SPSS Inc.) for the item analysis.
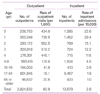
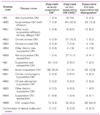
A total of 5,964,587 claims for OM and 2,924,532 AOM episodes were reported. Incidence of outpatients presenting AOM was 60.9/1,000 (Table 2). The incidence of AOM was highest in children aged 1 year (736.9/1,000), followed by 552.5 (2 years), 518.2 (3 years), 445.1 (4 years), and 434.8 (0 year). The overall hospitalization rate due to AOM was 2.8/10,000, with a peak of 29.4/10,000 (1 year), followed by 22.6 (<1 year) 15.1 (2 years), 12.2 (3 years), 11.5 (4 years), and 4.5 (5 to 9 years).
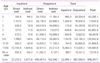
The total cost incurred by AOM in Korea was estimated to be around 606.3 billion Korean won (KRW) (Table 3). The total cost of admissions was approximately 22.9 billion KRW, and the average cost of admission per person was about 1,690,000 KRW in a year. The cost of outpatient visits was 583.4 billion KRW, and 199,000 KRW per person. By age group, the highest number of outpatient visits was observed in patients 1 year of age (77.3 billion). The cost of patients between 0 year of age and 4 years of age was 244.6 billion KRW, which takes up 40.3% of the total cost.
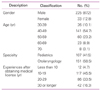
Out of 700 survey subjects, 259 people responded to the survey (37.0%), and among them a total of 258 responders (36.9%) were chosen for an analysis excluding one insincere responder. 107 of them were pediatricians and 151 were otolaryngologists. Out of 258 responders, 87.2% were male and 54.7% were in their 40's (Table 4).
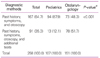
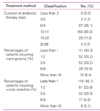
In the diagnosis of pediatric patients 5 years of age and younger with AOM, none of the doctors diagnosed their patients by using only past history and symptoms without otoscopy, 64.7% used past history, symptoms and otoscopy, and 35.3% used additional diagnostic methods (Table 5). Otolaryngologists (85.7%) used more additional tests than pediatricians. In other words, Korean pediatricians and otolaryngologists at least use otoscopy in establishing the diagnosis, and do not rely only on symptoms. In many cases OM is not accompanied by specific symptoms, such as otalgia or otorrhea. Thus the responders were asked whether or not they perform otoscopy when their patients did not present any specific symptoms of OM. The proportion of doctors who performed otoscopy in patients who made visits due to symptoms, such as cold symptoms and fever, without otalgia or otorrhea was high. The proportion of doctors who said they perform otoscopy in over 90% of cases was 73.3% in pediatric patients 0 year of age, 75.6% between 1 and 5 years of age, 67.0% in 5 years of age and older. Since the figure is fairly high, we believe that OM without ear symptoms is being diagnosed most of the cases.
To check the codes that are actually used in insurance claims, we requested them to confirm the codes they use when they diagnose their patients by distinguishing acute suppurative OM and non-suppurative otitis media (OME), and when they do not distinguish between suppurative and non-suppurative OM (Table 6). The most commonly used code for acute suppurative OM was H66.0 (65.6%), 11.6% used incomplete code H66, unspecified suppurative OM (H66.4) and unspecified OM (H66.9) was used in 8.6 and 5.3% of cases, respectively. Among non-suppurative OM claims, acute serious OM (H65.0) was the most frequent (42.8%), and chronic serious OM (H65.2) was the second highest (15.2%). In conclusion, 71% of pediatricians and otolaryngologists distinguish, diagnose and claim for suppurative and non-suppurative OM separately, and in most cases they made claims according to the diagnosed disease. However, 29% answered that they mostly do not distinguish suppurative and non-suppurative OM, and in such cases they usually made claims as unspecified OM (44.0%), while some used chronic serious OM and chronic suppurative OM (13% each) for claims.
When patients with AOM needed antibiotic prescriptions, the most common length of antibiotic treatment was ten to fourteen days (60.3%), followed by six to nine days (26.1%) (Table 7). The weighted average duration of antibiotic treatment was 11.4 days and none were prescribed for duration of less than three days or over thirty days. Although most of the responders (43.3%) responded that less than one percent of patients required myringotomy another 16.3 percent answered that over six percent of patients needed myringotomy, and the weighted average was 2.7 percent. Most responders (46.1%) said the rate of patients who required v-tube insertion was less than one percent, and the weighted average was 2.2 percent.
It is well established in other countries that AOM is particularly common in children and the burden of disease is high. The causative organisms of AOM are diverse, but bacteria such as S. pneumoniae (30% to 50%), Hemophilus influenza (20% to 30%), Moraxella catarrhalis (1% to 5%), and Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas aureginosa are known as causative organisms [1]. Because of the structure of a child's middle ear and the various causative organisms including viruses, OM not only occurs frequently in children but also recurs commonly and in some cases it may become chronic or develop complications. Although antibiotics has significantly reduced the frequency of complications associated with suppurative OM various complications may occure including persistent OM with effusion (10% to 25%), hearing difficulty, perforation of tympanic membrane, chronic OM and mastoiditis, cholesteatoma, labyrinthitis, petrositis, tympanosclerosis, facial nerve palsy, meningitis and even brain abscess [1]. Although it is widely regarded that OM is very common and incurs a heavy burden on patients, it was difficult to find relevant studies in Korea. Because epidemiologic studies that prospectively assess incidence and prevalence of OM are lacking, and there are limitations in using health insurance data as secondary data. The question was, how well the OM patients who made claims would correspond to their actual diagnosis.
The incidence of AOM varies greatly depending on assessment methods or countries. This study found that the number of outpatient visits made annually due to AOM per person was 0.74 times for patients 1 year of age, 0.55 for patients 2 years of age, and an average of 0.53 for patients between 0 and 4 years of age. According to a British study that surveyed children between 1 and 4 years of age in 2003 [18], the number of visits per person was around 0.4 times, while a study by Eskola et al. [19] that surveyed children 2 years of age and younger in 2003 noted that the annual incidence of AOM was 1.24. Meanwhile, a prospective study pointed to a higher incidence, for instance, according to a prospective study in children in Boston stated that children aged 0 year had 1.2 episodes, 1 year 1.1, 2 years 0.7, and 3 years 0.8 [7], and in another study conducted in the US [20], children aged between 3 and 42 months who visited medical institutions due to AOM had 1.8 episodes. A prospective observational study carried out in the US [21] reported that children aged between 6 and 11 months, 12 and 23 months, and 24 and 35 months had 1.9, 1.7 and 1.1 episodes of OM in a year, respectively. Since AOM occurs multiple times in children who cannot express their symptoms, the reported incidence may vary greatly, depending on the interests of their parents and the use of medical institutions.
In using the Korean health insurance data, what worried us at first was that the incidence of OM might be exaggeratedly high, because doctors can use OM for the classification of disease to justify prescriptions of antibiotics. Such cases may exist in reality, and even if we say that asymptomatic infections take up about fifty percent, the estimated incidence in Korean health insurance data is still lower than that in other countries. Furthermore, based on the survey, we found out that in many cases doctors confirm OM via otoscopy in patients who made visits due to acute respiratory infections. We believe that many cases of OM without its symptoms are included in the health insurance data. Such facts can ground the assumption that the incidence of AOM stated in the Korean health insurance data is not too exaggerated as we feared at first.
There are several limitations in making a direct comparison of the cost of disease between countries, because the definition of each cost included in the cost of disease, level of healthcare cost, level of incomes, and changes in monetary values vary every year in different countries. This study found that the cost of admissions due to OM was 1,690,000 KRW (1,530 US dollar [USD]) in 2004 per person, the cost of outpatient visits was about 199,000 KRW (181 USD) per person. In a study carried out by directly observing patients for three months in the US in 1999 suggested that the cost per person was 1,330 USD (95% confidence interval, 1,008.8 to 1652.4) [22]. Considering that most of patients are outpatients and the data is not observational data for whole year, the cost is extremely high compared to the cost in Korea. Likewise, the cost of disease, which was estimated to be approximately 606.3 billion KRW (551.2 million USD), cannot be compared directed with that of other countries. According to a study conducted in Canada in 1999 [23], which reflected direct and indirect cost of OM by age groups in the data on cost of disease, the cost of OM was 611.0 million USD in 1994, and 70.1 percent (428.4 million USD) of this amount were incurred by children aged under 14 years old. The present study also argued that the cost incurred by children between 0 and 9 years of age is 428.6 billion KRW, which corresponds to about 70.7 percent of the total cost, and although the ratio was similar across all age groups, we need to consider the following facts, there is a ten year difference between the years assessed; and differences in national incomes.
We believe that at least the first-line diagnosis of AOM is pretty accurate, since almost all doctors used otoscopy for their diagnosis, based on the survey conducted in this study. In particular, we acknowledge that the classifications of diseases used for health insurance claims do match well with the diagnosis, and at least confirmed that chronic OM and AOM have few classification errors. However, when detailed terms such as suppurative OM and non-suppurative OM were categorized, according to the classification of disease for insurance claims, some inaccuracies were found. Taking such facts into account, this study used the code for AOM to minimize errors.
This study was carried out in order to estimate the burden of AOM in Korea. We indirectly examined the accuracy of AOM presented in the health insurance claims data referred to in this study, by comparing the survey result of doctors and conditions in other countries. However, one limitation of this study is that the accuracy has not been examined directly. In addition, to grasp more accurate incidences and characteristics of AOM, a prospective community study is required.
Figures and Tables
Acknowledgement
The authors wish to thank Dr. Young Kyu Shin, Myoungmoon Pediatric Clinic, Dr. Kwon Oh Hwi, Yonsei ENT Clinic and Professor Park Hun Yi, Ajou University Hospital for very helpful comments and discussions.
This study was supported by grant from GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA, and partly supported by grant of the Transgovernmental Enterprise for Pandemic Influenza in Korea, which part of Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project by Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant no. 2010-E-13).
References
1. Ahn HS. Hong CE, editor. Respiratory disorders. Pediatrics. 2005. 8th ed. Seoul: Daehan Textbook Publishing;653–681.
2. Freid VM, Makuc DM, Rooks RN. Ambulatory health care visits by children: principal diagnosis and place of visit. Vital Health Stat 13. 1998. (137):1–23.
3. Leibovitz E. Acute otitis media in pediatric medicine: current issues in epidemiology, diagnosis, and management. Paediatr Drugs. 2003. 5:Suppl 1. 1–12.
4. Pennie RA. Prospective study of antibiotic prescribing for children. Can Fam Physician. 1998. 44:1850–1856.
5. Rosenfeld RM, Kay D. Rosenfeld RM, Bluestone CD, editors. Natural history of untreated otitis media. Evidence-based otitis media. 2003. 2nd ed. Hamilton: BC Decker;180–198.

6. Teele DW, Klein JO, Rosner B. Epidemiology of otitis media during the first seven years of life in children in greater Boston: a prospective, cohort study. J Infect Dis. 1989. 160:83–94.

8. Schwartz SR, Gates GA. Rosenfeld RM, Bluestone CD, editors. Economic costs. Evidence-based otitis media. 2003. 2nd ed. Hamilton: BC Decker;333–341.
9. Prymula R, Peeters P, Chrobok V, Kriz P, Novakova E, Kaliskova E, Kohl I, Lommel P, Poolman J, Prieels JP, Schuerman L. Pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides conjugated to protein D for prevention of acute otitis media caused by both Streptococcus pneumoniae and non-typable Haemophilus influenzae: a randomised double-blind efficacy study. Lancet. 2006. 367:740–748.

10. Park CS, Kang HY, Kwon I, Kang DR, Jung HY. Cost-of-illness study of asthma in Korea: estimated from the Korea National Health insurance claims database. J Prev Med Public Health. 2006. 39:397–403.
11. Jung YH, Ko S. The socioeconomic cost of diseases in Korea. J Prev Med Public Health. 2006. 39:499–504.
12. National Health Insurance Corporation. 2004 National health insurance statistical yearbook. 2005. Seoul: National Health Insurance Corporation.
13. National Health Insurance Corporation. A case study for insured patient's out-of-pocket medical service fees' 2004 [Internet]. 2005. cited 2013 Jan 4. Seoul: National Health Insurance Corporation;Available from: http://www.nhic.or.kr.
14. Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs. 2004 National health and nutrition survey. 2005. Seoul: Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs.
15. Hanna care. Fee for care [Internet]. cited 2013 Jan 4. Seoul: Hanna care;Available from: http://hcare.or.kr/htm/sub03_02.html.
16. Ministry of Labor. 2004 Survey report on wage structure. 2004. Gwacheon: Ministry of Labor.
17. Korean Statistical Information Service. 2004 Demographic data [Internet]. cited 2013 Jan 4. Dajeon: Statistics Korea;Available from: http://kosis.kr/abroad/abroad_01List.jsp?parentId=A.
18. Melegaro A, Edmunds WJ, Pebody R, Miller E, George R. The current burden of pneumococcal disease in England and Wales. J Infect. 2006. 52:37–48.

19. Eskola J, Kilpi T, Palmu A, Jokinen J, Haapakoski J, Herva E, Takala A, Kayhty H, Karma P, Kohberger R, Siber G, Makela PH. Finnish Otitis Media Study Group. Efficacy of a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine against acute otitis media. N Engl J Med. 2001. 344:403–409.

20. Fireman B, Black SB, Shinefield HR, Lee J, Lewis E, Ray P. Impact of the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on otitis media. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003. 22:10–16.

21. Chonmaitree T, Revai K, Grady JJ, Clos A, Patel JA, Nair S, Fan J, Henrickson KJ. Viral upper respiratory tract infection and otitis media complication in young children. Clin Infect Dis. 2008. 46:815–823.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download