Abstract
Scabies is one of the most common world-wide arthropod-born diseases in both humans and animals caused by the "itch" mite Sarcoptes scabiei. The incidence of scabies has shown a tendency to increase for the last several years in Korea. The previous peak incidence in Korea was between the early 1970s and early 1980s. A substantial part of the cyclic resurgence of scabies has been considered the result of inexperience and indifference of medical doctors toward the disease. The recent resurgence is presumed to be derived from not only indifference of the doctors but also an increase in elderly patients admitted to nursing homes and eldercare hospitals. Scraping using mineral oil for scabies patients is a very simple and effective method for definite diagnosis. A new diagnostic method using a dermoscope is also effective, especially for very young patients. Lindane and crotamiton are two available antiscabietic preparations in Korea. Crotamiton is less effective, while infants and pregnant women should not use lindane. In conclusion, medical personnel should be alert coping with the resurgence of scabies, and it is strongly suggested that other antiscabietic drugs such as permethrin, ivermectin, etc. should be made available for resistant patients in the near future in the Republic of Korea.
Figures and Tables
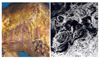
 | Figure 1Dorsal surface of female Sarcoptes scabiei showing names of the characteristic morphological features. |
 | Figure 2Ventral surface of male Sarcoptes scabiei showing church bell-shaped male genitalia between 4th legs. |
 | Figure 3Dorsal surface of Saroptes canis without bare area (A) and Sarcoptes scabiei with bare area (B). |
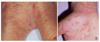
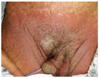 | Figure 8Crusted scabies showing hyperkeratotic patches on the glans penis and pubic area in a 71-year-old man. |
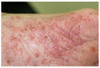
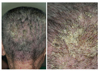 | Figure 9Crusted scabies showing seborrheic dermatitis-like yellowish hyperkeratotic patches on the scalp in a 86-year-old man admitted in an eldercare hospital (courtesy of Professor Moo Kyu Suh, Dongguk University). |
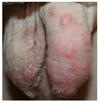
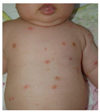 | Figure 10Nodular scabies in a 9-month-old boy (courtesy of Professor Moon Bum Kim, Pusan National University). |
References
1. Ramos-e-Silva M. Giovan Cosimo Bonomo (1663-1696): discoverer of the etiology of scabies. Int J Dermatol. 1998. 37:625–630.

2. Lee WK, Cho BK. Taxonomical approach to scabies mites of human and animals and their prevalence in Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 1995. 33:85–94.

3. Hengge UR, Currie BJ, Jager G, Lupi O, Schwartz RA. Scabies: a ubiquitous neglected skin disease. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006. 6:769–779.

4. Yang YS, Lew BL, Sim WY. Clinical study of 27 cases with scabies. Korean J Dermatol. 2008. 46:1603–1608.
5. Ki MR, Moon HJ, Cho H. Outbreak of scabies at geriatric long-term care facilities in Korea. Korean J Epidemiol. 2006. 28:100–111.

6. Walton SF, Holt DC, Currie BJ, Kemp DJ. Scabies: new future for a neglected disease. Adv Parasitol. 2004. 57:309–376.

7. Cho BK, Lee WK. Mite and tick related dermatoses. 2004. Seoul: Seo Heung.
8. The Korean Society of Systemic Zoology. List of animals in Korea: excluding insects. 1997. Seoul: Academy Pub. Co..
9. Lee KH, Cho BK. Features and morphologic differences between 2 strains of Sarcoptes scabiei from a Norwegian scabies patient and a scabietic dog. Korean J Dermatol. 2003. 41:708–715.
11. Heilesen B. Studies on Acarus scabiei and scabies. Acta Derm Venereol. 1946. 26:Suppl 14. 1–370.
12. Chosidow O. Clinical practices: scabies. N Engl J Med. 2006. 354:1718–1727.
13. Alexander J. Arthropods and human skin. 1984. New York: Springer-Verlag.
14. Cho BK, Lee JB, Kim CW, Houh W. Clinical study of scabies and itch mite. Korean J Dermatol. 1975. 13:95–101.
15. Chang KH, Lee WH, Chun SI, Koh CJ. The clinical study of scabietic patients. Korean J Dermatol. 1983. 21:23–27.
16. Lee BJ, Suh KS, Chung SL, Kim KH. Trends in scabies for 12 years. Korean J Dermatol. 1981. 19:391–395.
17. Haag ML, Brozena SJ, Fenske NA. Attack of the scabies: what to do when an outbreak occurs. Geriatrics. 1993. 48:45–46. 51–53.
18. Chung KH, Lee MJ, Jun JB. Tinea unguium hidden by Norwegian scabies. Korean J Med Mycol. 2009. 14:194–198.
19. Kang GS, Hwang SM, Suh MK. Seborrheic dermatitis-like Norwegian scabies on a patient living in an eldercare hospital. Korean J Dermatol. 2009. 47:1182–1185.
20. Kim KW, Oh YJ, Cho BK, Houh W, Kim JA, Lee YS. Norwegian scabies: dissemination of mites by medical instruments. Ann Dermatol. 1990. 2:50–54.
21. Lee E, Oh ST, Park HJ, Lee JY, Cho BK. A case of Norwegian scabies outbreak. Korean J Dermatol. 2007. 45:724–727.
22. Seo PS, Kim SJ, Yoon NH, Park SD. A case of Norwegian scabies in a patient with Down's syndrome. Korean J Dermatol. 2005. 43:701–703.
23. Park KD, Jung HD, Lee WJ, Na GY, Lee SJ, Kim DW. A case of Norwegian scabies in a patient with pemphigus foliaceus. Korean J Dermatol. 2006. 44:1345–1348.
24. Kim SH, Jeon YS, Sim HJ, Jang MS, Suh KS, Kim ST. A case of generalized nodular scabies. Korean J Dermatol. 2004. 42:116–118.
25. Kim SH, Ko HC, Kim SJ, Kim MB, Oh CK, Kwon KS. Four cases of infantile nodular scabies: the usefulness of dermoscopy for in vivo detection of scabies. Korean J Dermatol. 2008. 46:86–89.
26. Yi JY, Park CW, Cho BK, Houh W. A case of scabies incognito. Korean J Dermatol. 1986. 24:518–522.
27. Jo I, Key CJ, Koh CJ, Cho BK. Two cases of unusual scabies. Korean J Dermatol. 1979. 17:131–137.
28. Hong JK, Jang IG, Cho BK, Lee WK. A clinical and histopathological study of experimental canine scabies. Ann Dermatol. 1998. 10:238–246.

29. Kang SB, Lee JY, Cho BK, Houh W. A case of human infestation of canine scabies. Korean J Dermatol. 1988. 26:570–574.
30. Chun BM, Park JH, Her Y, Kim CW, Kim SS. A case of human infestation of canine scabies. Korean J Dermatol. 2009. 47:104–107.
31. Muller G, Jacobs PH, Moore NE. Scraping for human scabies: a better method for positive preparations. Arch Dermatol. 1973. 107:70.

32. Houh W, Yoon JM. Scabies: scraping results using mineral oil. Korean J Dermatol. 1974. 12:21–26.
33. Argenziano G, Fabbrocini G, Delfino M. Epiluminescence microscopy: a new approach to in vivo detection of Sarcoptes scabiei. Arch Dermatol. 1997. 133:751–753.

34. Estes SA, Estes J. Therapy of scabies: nursing homes, hospitals, and the homeless. Semin Dermatol. 1993. 12:26–33.
35. Jin SP, Choi JE, Won CH, Cho S. Scabies in a 2-month-old Infant successfully treated with lindane. Ann Dermatol. 2009. 21:200–202.

36. Lee WH, Kim YK, Tak MJ, Lee JB. Crotamiton resistant scabies. Korean J Dermatol. 1980. 18:207–211.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download