Abstract
Currently, the drug pricing and reimbursement schemes in the Korean Medical Insurance System are based on a purchasing price reimbursement system. Since the pharmaceutical pricing is not stable and is continuously increasing, a need has developed for an analysis of the reason for the increase in pharmaceutical pricing and appropriate management measures. Consequently, a policy for the optimization of pharmaceutical expenditures in the Korean National Health Insurance (KNHI) System was introduced in 2006. In this policy, conversion to positive list system, price-volume agreements, and intensification of postmanagement of drug costs were newly introduced. In Korea, there are difficulties in smooth decisionmaking between the insured and the pharmaceutical companies in the process of determining the reimbursed price. When a proper agreement on the drug price is not made, the expenses of drug could incentive rapidly. This study was focused on the process of change in the policy of drug pricing and reimbursement in KNHI system to analyze its significance and study appropriate measures for drug reimbursement decision-making. The data for this study was collected mainly from announcement data of international and domestic agencies, related groups, and experts, along with data on the current situation regarding purchase of drugs, yearly status data, and statistical data for drugs. In Korea, the positive list system for the insured decides whether or not the national insurance will provide reimburse. Thus, it affects the demand determination through a large impact on the burden on the patients themselves. Principly the price of drug determined by the patient as a direct demander. The KNHI could be a agency for patient. The KNHI should find-out the proper purchasing method. Thus, this study proposes principles for drug pricing and reimbursement by inducing price competition according to market principles in Korea's health insurance determination.
Figures and Tables
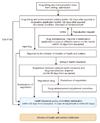
Figure 5
New drug insurance acceptance procedure by the Health Insurance Drug Reimbursement Committee.
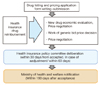
Table 2
Statistics relevant to OECD drug cost (1998-2003) [9]
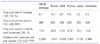
a)Health care cost: medical service&medical insurance, administration cost of public health and other funds of treatment prevention care (disease) health promotion program, rehabilitation (disability), hospice.
b)Medicine care cost: treatment, non-treatment medicine, vaccine, vitamin, mineral, oral contraceptive pill and Chinese medicine.
References
1. Yang MS. A study on the legislation of fee schedules and the process of updating in the korean health insurance program [dissertation]. 1993. Gyeongsan: Kyungsan Univ.
2. Jeong HS, Lee EK, Kim EJ, Ryu GC, Song YM. Impact of the purchasing price reimbursement system for insurance drugs upon the health insurer's financial situation. Korean J Health Policy Adm. 2005. 15:40–59.

3. Yoo SH. A study on necessity of merger&acquisition in medicine wholesaler industry [dissertation]. 2004. Seoul: Chung-Ang Univ.
4. Ministry of Health and Welfare. Health welfare family. white paper. 2008. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare.
5. Yoon HS. A study on the drug pricing system in health insurance. 2008. Seoul: KDI.
6. Bae SJ, Lim GH, Choi SE, Bae EY. A Study on resonable drug pricing system in health insurance. 2009. Seoul: Health Insurance Review&Assessment Service.
7. Choi YJ, Choi SE. A study on drug reimbursement in health insurance system. 2009. Seoul: Health Insurance Review&Assessment Service.
8. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. OECD health data 2009: statistics and indicator. 2009. Paris: OECD.
9. Ministry of Health and Welfare. Drug cost containment in health insurance. 2006. Seoul: Ministry of Health and Welfare.
10. Bae EY, Kim JH, Choi SE. Development of economic evaluation drug reimbursement system of health insurance. 2005. Seoul: Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service.
11. National Health Insurance Cooperation. Korea's insurance medical price system and the management methods. 2009. Seoul: National Health Insurance Cooperation.
12. Health Insurance Review&Assessment Service [Internet]. 2010. cited 2010 Sep 20. Seoul: Health Insurance Review&Assessment Service;Available from: http://www.hira.or.kr.
13. LFN Pharmaceutical Benefits Board. The Swedish pharmaceutical reimbursement system. 2007. Solna, Sweden: LFN.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print








 XML Download
XML Download