Abstract
Drug development is a lengthy, expensive, and complex process, and clinical development is the longest and the most expensive stage of drug development. To obtain market authorization of a new drug, applicants must prove the effectiveness and the safety of a drug through clinical trials. Korea has the same requirements for new drug approval as in developed countries and bridging data are required for approval of a new drug that was developed in another country. Clinical evaluation in humans consists of 3 phases, from phase 1 to phase 3, and the failure rates remain high while the clinical trial cost increases rapidly. Not only pharmaceutical sponsors but also patients and physicians want new, innovative medicines faster, simultaneously with improved productivity of drug development. With strong competition and market forces, the pressure to accelerate drug development and to predict the efficacy and safety profile of a drug candidate at an earlier stage is increasing. To improve the productivity of new drug development, modern principles of pharmaceutical sciences, clinical pharmacology, and information technology are being researched and employed by both health authorities and sponsors. Many global pharmaceutical companies are also pursuing geographical expansion strategies to enroll subjects faster among more diverse ethnic groups. To deliver innovative medicines to patients in a faster and more cost-effective ways, close and continuous collaboration among sponsors, academia, and health authorities is essential.
Figures and Tables
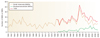
Figure 1
Timeline of approvals of new molecular entities (nMEs) and new bilolgical entities (nBEs) by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) between 1950 and 2008[17].
References
1. Understanding clinical trials. ClinicalTrials.gov. Available from:
http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/info/understand#Q01.
2. About Clinical Trials. National Institute of Health. Available from:
http://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/clinicalresearch/aboutclinicaltrials.cfm.
3. Sahoo A. The Future of R&D Outsourcing. 2010. Business Insights.
4. Fletcher AJ, Edwards LD, Fox AW, Stonier P. Chapter 10, Phase I: The first opportunity for extrapolation from Animal data to human exposure. Principles and practice of Pharmaceutical Medicine. c2002. West Sussex (UK): John Wiley&Sons, Ltd;95–114.
5. Paul SM, Mytelka DS, Dunwiddie CT, Persinger CC, Munos BH, Lindborg SR, Schacht SL. How to improve R&D productivity: the pharmaceutical industrys grand challenge. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010. 9:203–214.

6. Guideline for Investigational New Drug application 2008. Korea Food&Drug Administration.
7. Kayser O, Müller RH. Chapter 11, Drug approval in the European Union and the United States. Pharmaceutical Biotechnology Drug Discovery and Clinical Applications. c2004. 2nd ed. Weinheim (Germany): Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH&Co. KGaA;201–210.
8. Dickson M, Gagnon P. Key factors in the rising cost of new drug discovery and development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004. 3:417–429.

9. Lacasse FX, Larouche R, Tanguay M. Early phases in drug development. GOR. 2005. 7:69–73.
10. Guideline for evaluation of bridging data 2008. Korea Food&Drug Administration.
11. Wax PM. Elixirs, diluents, and the passage of the 1938 Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act. Ann Intern Med. 1995. 122:456–461.

12. Philipson TJ, Sun E. Is the Food and Drug Administration safe and effective? J Econ Persp. 2008. 22:85–102.

13. Katzung BG. Chapter 5, Development & regulation of drugs. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology. c2009. 11th ed. New York (US): The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc;67–76.
14. Kishore R, Tabor E. Overview of the FDA Amendment Act of 2007: Its effect on the drug development landscape. Drug Inf J. 2009. 44:469–475.

15. DiMasi JA, Hansen RW, Grabowski HG. The price of innovation: new estimates of drug development costs. J Health Econ. 2003. 22:151–185.

16. DiMasi JA, Hansen RW, Grabowski HG, Lasagna L. Cost of innovation in the pharmaceutical industry. J Health Econ. 1991. 10:107–142.

17. Munos B. Lessons from 60 years of pharmaceutical innovation. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009. 8:959–968.

18. Innovation or Stagnation: Challenge and Opportunity on the Critical Path to New Medical Product. US Food and Drug Administration. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/ScienceResearch/SpecialTopics/CriticalPathInitiative/CriticalPathOpportunitiesReports/ucm077262.htm.
19. Microdosing (Phase 0 Trials), Adaptive trials, phase IV trials and information technology set to revolutionize new drug development. Rx to OTC. Available from: http://rxtootc.com/a163693-microdosing-phase-trials-adaptive-trials-.cfm.
20. Press release. Korea National Enterprise for Clinical Trials. 2010. 02. 17.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download