Abstract
The majority of hypertensive patients do not achieve target blood pressure for a variety of reasons, including insufficient medication, drug resistance, and noncompliance. There remains a significant need to develop new agents to better control hypertension. Nebivolol is a third-generation β-adrenergic receptor blocker which is very highly cardioselective and has direct vasodilator properties via stimulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity. Aliskiren is the first orally active inhibitor of renin as an antihypertensive agent. It is associated with dose-related falls in blood pressure comparable to other major classes of antihypertensive drugs with a placebo level of side effects. Endothelin is a powerful vasoconstrictor peptide. An endothelin-receptor antagonist such as bosentan significantly lowered blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension. Vasopeptidase inhibitors inhibit neutral endopeptidase and angiotensin converting enzymes, but side-effects such as angio-oedema and cough remain to be overcome. AngQb vaccine in hypertensive patients showed a marked reduction in early morning blood pressure without serious adverse events.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
The renin_angiotensin system and the sites of inhibition by renin-inhibitors, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs),angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), aldosterone-receptor blockers, and neutral endopeptidase (NEP) inhibitors. This figure was adapted from the reference 7.
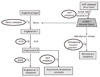
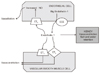
Figure 2
The opposing effects of endothelin on endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells are shown and are mediated by differential response to endothelin-receptor (ETA and ETB) stimulations. Endothelin-converting enzyme (ECE) is found on endothelial cells and is responsible for conversion of big endothelin-1 to endothelin-1, the predominant form of endothelin. This figure was adapted from the reference 7.
References
1. Munzel T, Gori T. Nebivolol: the somewhat-different beta adrenergicreceptor blocker. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009. 54:1491–1499.
2. Manrique C, Giles TD, Ferdinand KC, Sowers JR. Realities of newer beta-blockers for the management of hypertension. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2009. 11:369–375.
3. Van Nueten L, Taylor FR, Robertson JI. Nebivolol vs atenolol and placebo in essential hypertension: a double-blind randomized trial. J Hum Hypertens. 1998. 12:135–140.

4. Czuriga I, Riecansky I, Bodnar J, Fulop T, Kruzsicz V, Kristof E, Edes I. For The NEBIS Investigators; NEBIS Investigators Group Comparison of the new cardioselective beta-blocker nebivolol with bisoprolol in hypertension: the Nebivolol, Bisoprolol Multicenter Study (NEBIS). Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2003. 17:257–263.
5. Van Nueten L, Schelling A, Vertommen C, Dupont AG, Robertson JI. Nebivolol vs enalapril in the treatment of essential hypertension: a double-blind randomized trial. J Hum Hypertens. 1997. 11:813–819.

6. Van Bortel LM, Bulpitt CJ, Fici F. Quality of life and antihypertensive effect with nebivolol and losartan. Am J Hypertens. 2005. 18:1060–1066.

7. Wu KC, Gerstenblith S. Update on Newer Antihypertensive Medicines and Interventions. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2010. 05. 1–11.
8. Rongen GA, Lenders JW, Smits P, Thien T. Clinical pharmacokinetics and efficacy of renin inhibitors. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1995. 29:6–14.

11. Parving HH, Persson F, Lewis JB, Lewis EJ, Hollenberg NK. AVOID Study Investigators. Aliskiren combined with losartan in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2008. 358:2433–2446.

12. Yanagisawa M, Kurihara H, Kimura S, Tomobe Y, Kobayashi M, Mitsui Y, Yazaki Y, Goto K, Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988. 332:411–415.

13. Krum H, Viskoper RJ, Lacourciere Y, Budde M, Charlon V. Bosentan Hypertension Investigators. The effect of an endothelin-receptor antagonist, bosentan, on blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1998. 338:784–790.

14. Anand I, McMurray J, Cohn JN, Konstam MA, Notter T, Quitzau K, Ruschitzka F, Luscher TF. Long-term effect of darusentan on left-ventricular remodelling and clinical outcomes in the endothelin A receptor antagonist trial in heart failure (EARTH): randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2004. 364:347–354.

15. Kirchengast M, Luz M. Endothelin receptor antagonists-Clinical realities and future directions. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2005. 45:182–191.
16. Daull P, Jeng AY, Battistini B. Towards triple vasopeptidase inhibitors for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2007. 50:247–256.

17. Rouleau JL, Pfeffer MA, Stewart DJ. Comparison of vasopeptidase inhibitor omapatrilat, and lisinopril on exercise tolerance and morbidity in patients with heart failure. Lancet. 2000. 356:615–620.

18. Azizi M, Bissery A, Peyrad S. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the vasopeptidase inhibitor AVE7688 in humans. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006. 79:49–61.

19. Drospirenone in HRT? Drug Ther Bull. 2009. 47:41–44.
20. Krattenmacher R. Drospirenone: pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of a unique progestogen. Contraception. 2000. 62:29–38.

21. White WB, Pitt B, Preston RA, Hanes V. Antihypertensive effects of drospirenone with 17beta-estradiol, a novel hormone treatment in postmenopausal women with stage 1 hypertension. Circulation. 2005. 112:1979–1984.

22. Perreault S, Lamarre D, Blais L, Dragomir A, Berbiche D, Lalonde L, Laurier C, St-Maurice F, Collin J. Persistence with treatment in newly treated middle-aged patients with essential hypertension. Ann Pharmacother. 2005. 39:1401–1408.

23. Tissot AC, Maurer P, Nussberger J, Sabat R, Pfister T, Ignatenko S, Volk HD, Stocker H, Müllter P, Jennings GT, Wagner F, Bachmann MF. Effect of immunization against angiotensin II with CYT006-AngQb on ambulatory blood pressure: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase IIa study. Lancet. 2008. 371:821–827.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download