Abstract
Abnormal posture of the head and neck can happen to anybody from neonates to adults, which requires appropriate interventions according to etiologies. Congenital muscular torticollis is the most common cause of abnormal posture of the head and neck in infancy, where early intervention as soon as possible is critical for better therapeutic outcome. Childhood laterocollis is heterogeneous condition, which needs etiological diagnosis for the proper management. Cervical dystonia is the most common form of focal dystonia and an overview on clinical presentations and therapeutic options including chemodenervation with botulinum toxin injection was provided. Abnormal posture of the head and neck of acute onset could be a sign of serious conditions and needs differential diagnosis.
Go to : 
References
1. Cheng JC, Metreweli C, Chen TM, Tang S. Correlation of ultrasonographic imaging of congenital muscular torticollis with clinical assessment in infants. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2000; 26:1237–1241.

2. Cheng JC, Tang SP, Chen TM, Wong MW, Wong EM. The clinical presentation and outcome of treatment of congenital muscular torticollis in infants-a study of 1,086 cases. J Pediatr Surg. 2000; 35:1091–1096.

3. Chen MM, Chang HC, Hsieh CF, Yen MF, Chen TH. Predictive model for congenital muscular torticollis: analysis of 1021 infants with sonography. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005; 86:2199–2203.

4. Dudkiewicz I, Ganel A, Blankstein A. Congenital muscular torticollis in infants: ultrasound-assisted diagnosis and evaluation. J Pediatr Orthop. 2005; 25:812–814.

5. Sonmez K, Turkyilmaz Z, Demirogullari B, Ozen IO, Karabulut R, Bagbanci B, Basaklar AC, Kale N. Congenital muscular torticollis in children. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2005; 67:344–347.
6. Do TT. Congenital muscular torticollis: current concepts and review of treatment. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2006; 18:26–29.
7. Tatli B, Aydinli N, Caliskan M, Ozmen M, Bilir F, Acar G. Congenital muscular torticollis: evaluation and classification. Pediatr Neurol. 2006; 34:41–44.
8. Cheng JC, Au AW. Infantile torticollis: a review of 624 cases. J Pediatr Orthop. 1994; 14:802–808.
9. Cheng JC, Tang SP, Chen TM. Sternocleidomastoid pseudotumor and congenital muscular torticollis in infants: a prospective study of 510 cases. J Pediatr. 1999; 134:712–716.

10. Friedman M, LoSavio P, Ibrahim H. Superior laryngeal nerve identification and preservation in thyroidectomy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002; 128:296–303.

11. Kiray A, Naderi S, Ergur I, Korman E. Surgical anatomy of the internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. Eur Spine J. 2006; 15:1320–1325.

12. Reynolds SM, Mackenzie AJ, Spina D, Page CP. The pharmacology of cough. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2004; 25:569–576.

13. Thompson F, McManus S, Colville J. Familial congenital muscular torticollis: case report and review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986. 193–196.
14. Davids JR, Wenger DR, Mubarak SJ. Congenital muscular torticollis: sequela of intrauterine or perinatal compartment syndrome. J Pediatr Orthop. 1993; 13:141–147.
15. Yu CC, Wong FH, Lo LJ, Chen YR. Craniofacial deformity in patients with uncorrected congenital muscular torticollis: an assessment from three-dimensional computed tomography imaging. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004; 113:24–33.

16. Park MC, Song HS, Kim CS, Yim SY, Park DH, Pae NS, Lee IJ. Treatment of congenital muscular torticollis with unipolar release. J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009; 35:38–45.
17. Oleszek JL, Chang N, Apkon SD, Wilson PE. Botulinum toxin type a in the treatment of children with congenital muscular torticollis. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2005; 84:813–816.

18. Collins A, Jankovic J. Botulinum toxin injection for congenital muscular torticollis presenting in children and adults. Neurology. 2006; 67:1083–1085.

19. Singh A, Wacogne I. What is the role of helmet therapy in positional plagiocephaly? Arch Dis Child. 2008; 93:807–809.

20. Lee RP, Teichgraeber JF, Baumgartner JE, Waller AL, English JD, Lasky RE, Miller CC, Gateno J, Xia JJ. Long-term treatment effectiveness of molding helmet therapy in the correction of posterior deformational plagiocephaly: a five-year follow-up. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2008; 45:240–245.

21. Raman S, Takhtani D, Wallace EC. Congenital torticollis caused by unilateral absence of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Pediatr Radiol. 2009; 39:77–79.

22. Williams CR, O'Flynn E, Clarke NM, Morris RJ. Torticollis secondary to ocular pathology. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996; 78:620–624.

23. Madigan WP, Zein WM. Recent developments in the field of superior oblique palsies. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2008; 19:379–383.

24. Quartarone A, Rizzo V, Morgante F. Clinical features of dystonia: a pathophysiological revisitation. Curr Opin Neurol. 2008; 21:484–490.

25. Benecke R, Dressler D. Botulinum toxin treatment of axial and cervical dystonia. Disabil Rehabil. 2007; 29:1769–1777.

26. Stacy M. Epidemiology, clinical presentation, and diagnosis of cervical dystonia. Neurol Clin. 2008; 26(Suppl 1):23–42.
27. Jankovic J, Tsui J, Bergeron C. Prevalence of cervical dystonia and spasmodic torticollis in the United States general population. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2007; 13:411–416.

28. Lee CS, Lee CS, Chung SJ, Chung SJ, Im JH, Im JH, Lee MC, Lee MC, Yoo HW, Yoo HW. The DYT1 Gene Mutation in Primary Torsion Dystonia without Familial Background. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2003; 21:169–173.
29. Nishiyama N, Yukishita S, Hagiwara H, Kakimoto S, Nomura Y, Segawa M. Gene mutation in hereditary progressive dystonia with marked diurnal fluctuation (HPD), strictly defined dopa-responsive dystonia. Brain Dev. 2000; 22(Suppl 1):S102–106.

30. Adam OR, Jankovic J. Treatment of dystonia. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2007; 13(Suppl 3):S362–368.

32. Ranoux D. Cervical dystonia. In: Ranoux D, Gury C, eds. Practical handbook on botulinum toxin. Marseile, France: 33. Agrawal A, Cincu R, Joharapurkar SR, Bhake A, Hiwale KM. Hemorrhage in brain stem cavernoma presenting with torticollis. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2009; 45:49–52.
34. Hicazi A, Acaroglu E, Alanay A, Yazici M, Surat A. Atlantoaxial rotatory fixation-subluxation revisited: a computed tomographic analysis of acute torticollis in pediatric patients. Spine. 2002; 27:2771–2775.
35. Maigne JY, Mutschler C, Doursounian L. Acute torticollis in an adolescent: case report and MRI study. Spine. 2003; 28:E13–15.
36. Simsek S, Yigitkanli K, Kazanci A, Belen D, Bavbek M. Medically treated paravertebral Brucella abscess presenting with acute torticollis: case report. Surg Neurol. 2007; 67:207–210.

37. Sankar J, Srinivasan A, Ramakrishnan V, Balasubramaniam C. An Unusual Cause of Acute Torticollis. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2009.

Go to : 
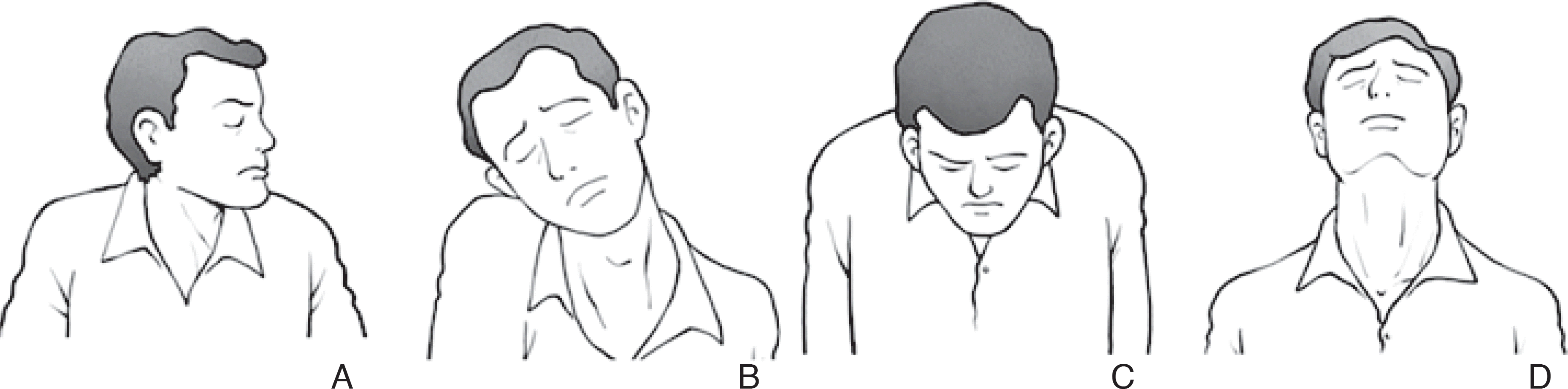 | Figure 1.Abnormal posture of the head and neck. (A) Left torticollis, (B) Right laterocollis, (C) Anterocollis, (D) Retrocollis. |
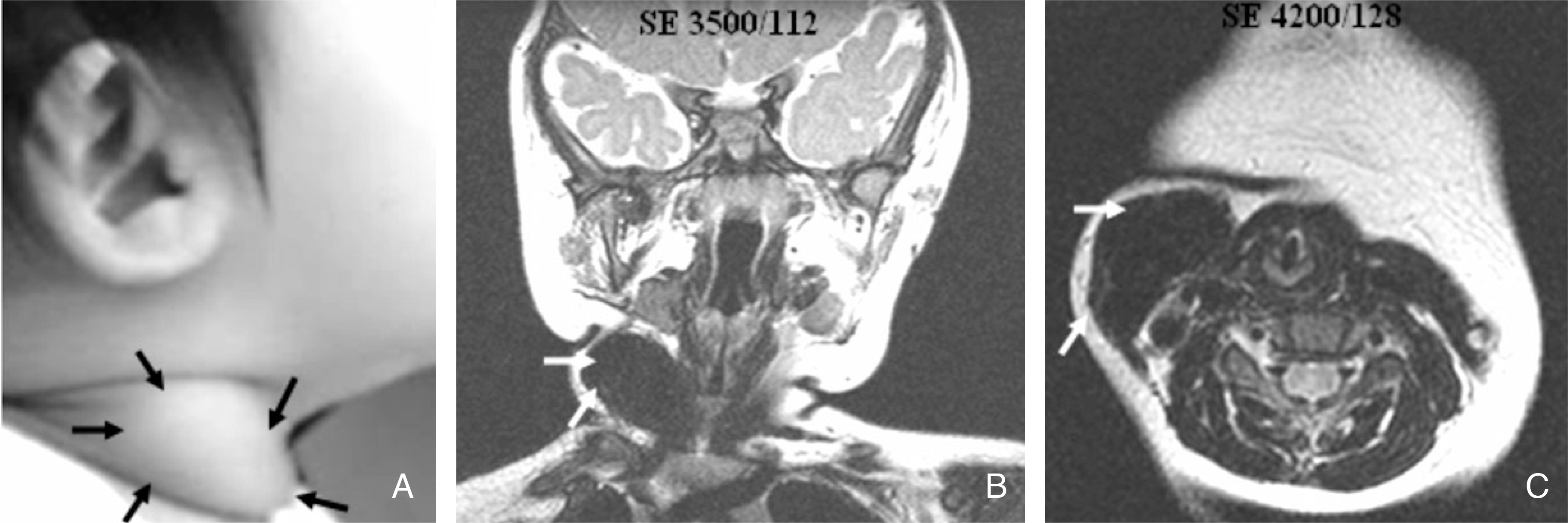 | Figure 2.A 10 month-old girl who has right congenital muscular torticollis. (A) Unilateral palpable neck mass of muscle-consistency on right sternocleidomastoid muscle. (B) and (C) Neck MRI findings showing large mass of right sternocleidomastoid muscle. |
 | Figure 3.Children who have left congenital muscular torticollis which have thick and short left sternocleidomastoid muscle, ending up with right torticollis and left laterocollis. |
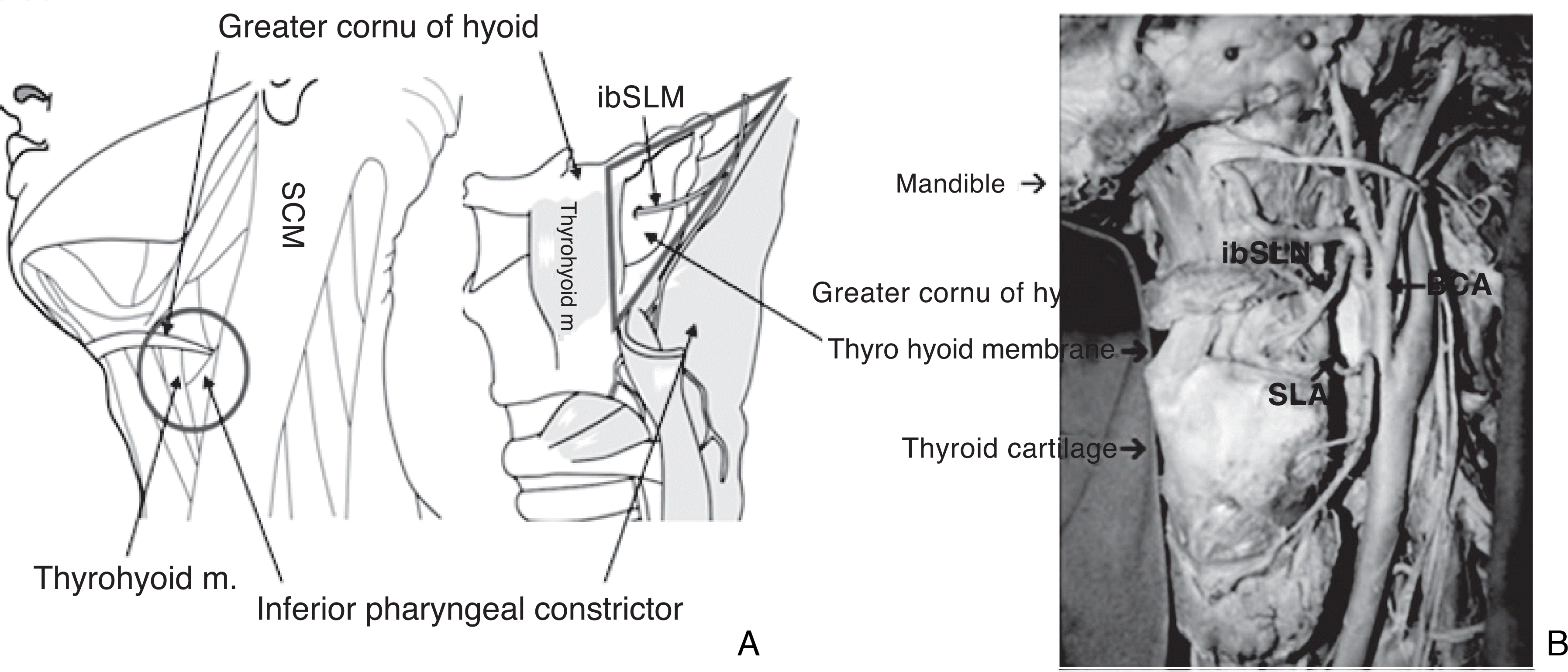 | Figure 4.(A) Relations between the sternocleidomastoid muscle (SCM) and the internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve (ibSLN). (B) Relations between the ibSLN and the other anatomic structures. ECA external carotid artery, SLA superior laryngeal artery Adapted from Kiray A, Naderi S, Ergur?, Korman E. Surgical anatomy of the internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. Eur Spine J 2006; 15: 1320–1325 with kind permission of Springer Science + Business Media. |
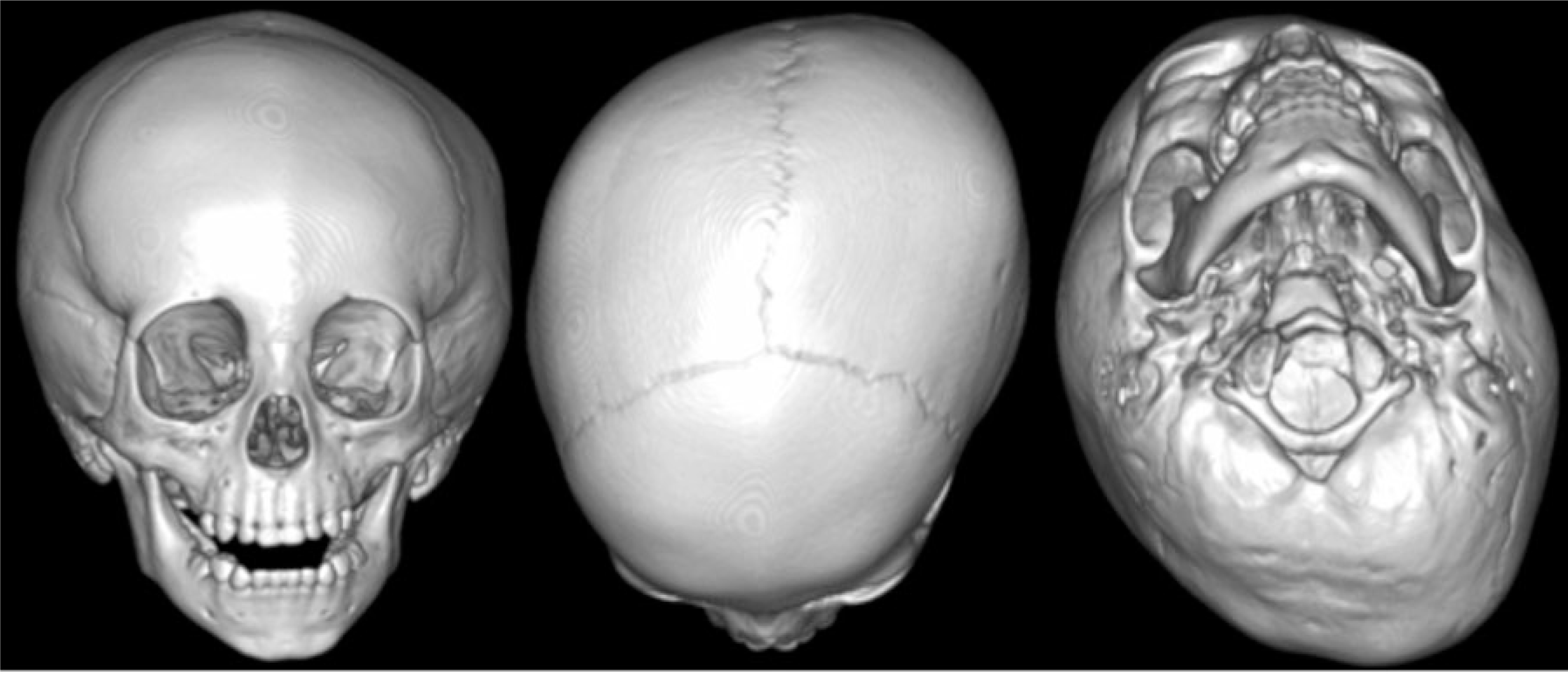 | Figure 5.Three-dimensional CT showing left plagiocephaly associated with left congenital muscular torticollis. |
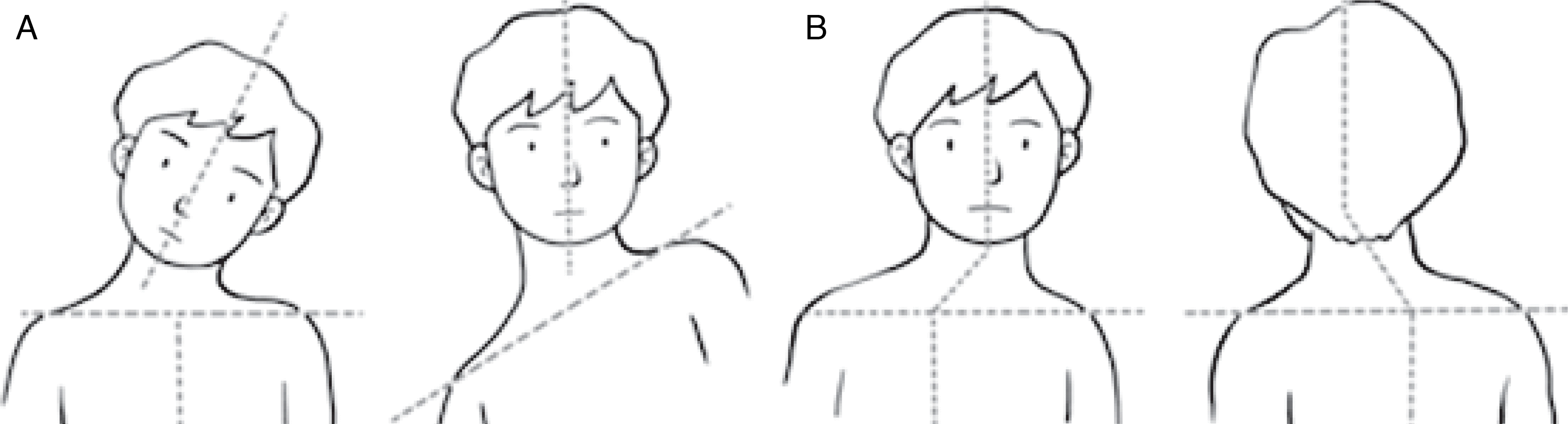 | Figure 6.A diagram showing spontaneous compensation for torticollis by (A) elevation of the shoulder on the affected side or by (B) production of cervical scoliosis with two curves. |
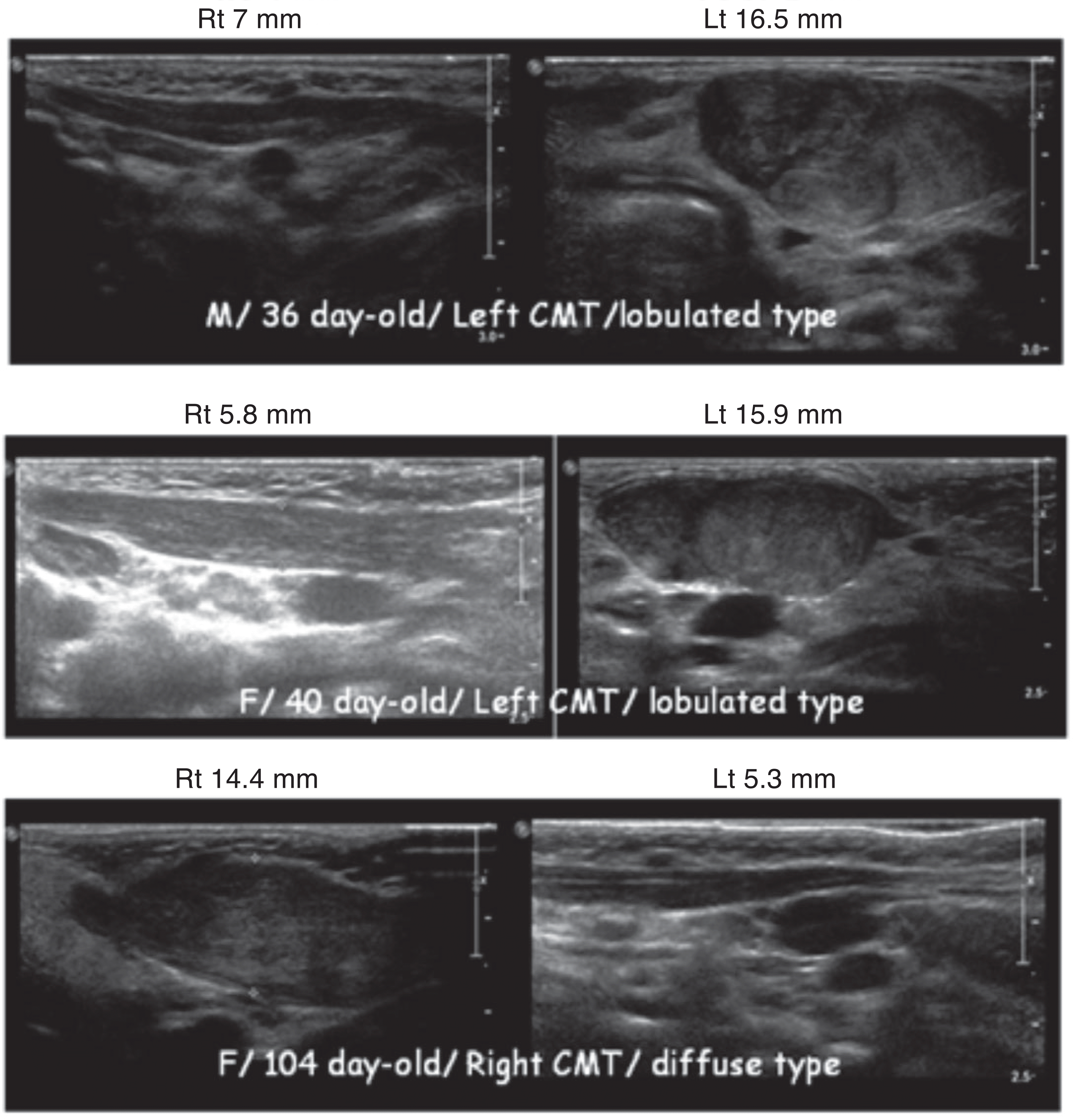 | Figure 7.The ultrasonographic findings of the sternocleidomastoid muscle for the children who had congenital muscular torticollis (CMT). |
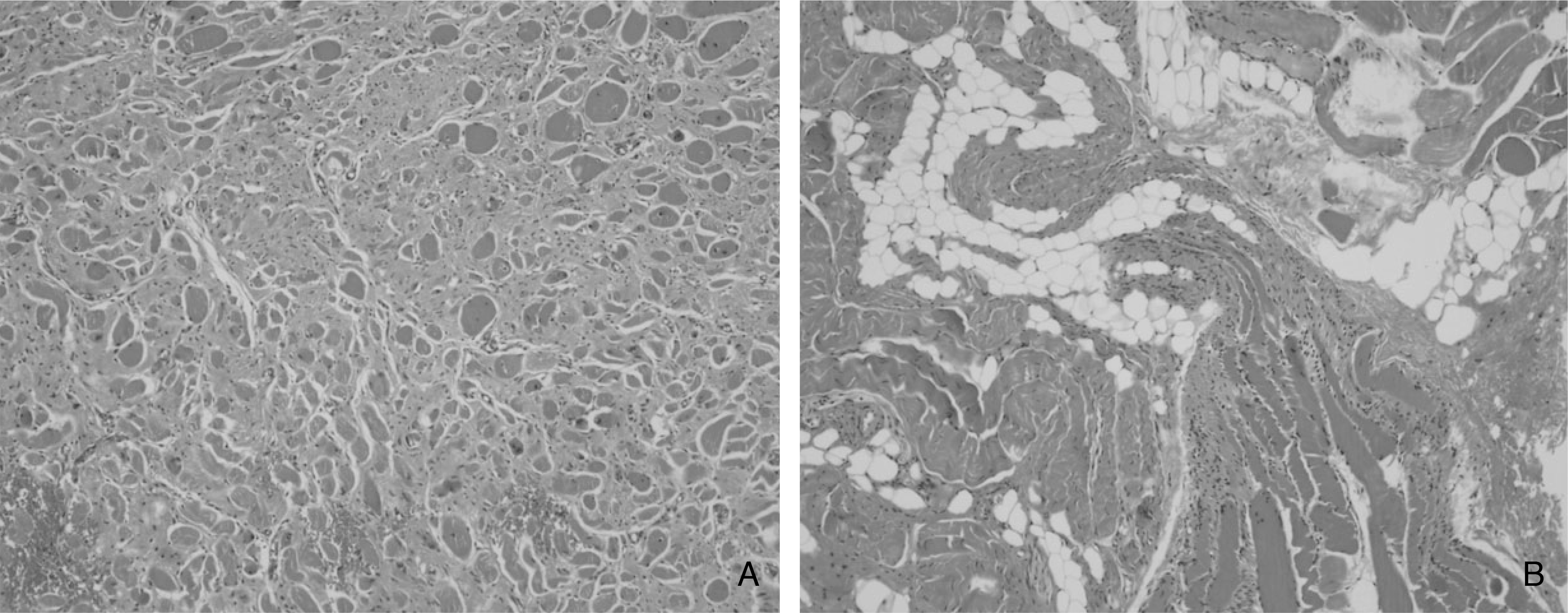 | Figure 8.Histologic findings of the sternocleidomastoid muscle with congenital muscular torticollis. (A) Diffuse fibroblastic proliferation with fibrosis and accompanying atrophic muscle fibers. H&E;x100. (B) Irregular arrangement of fibrous trabeculae, mature adipose cells and muscle fibers. H&E;x100. |
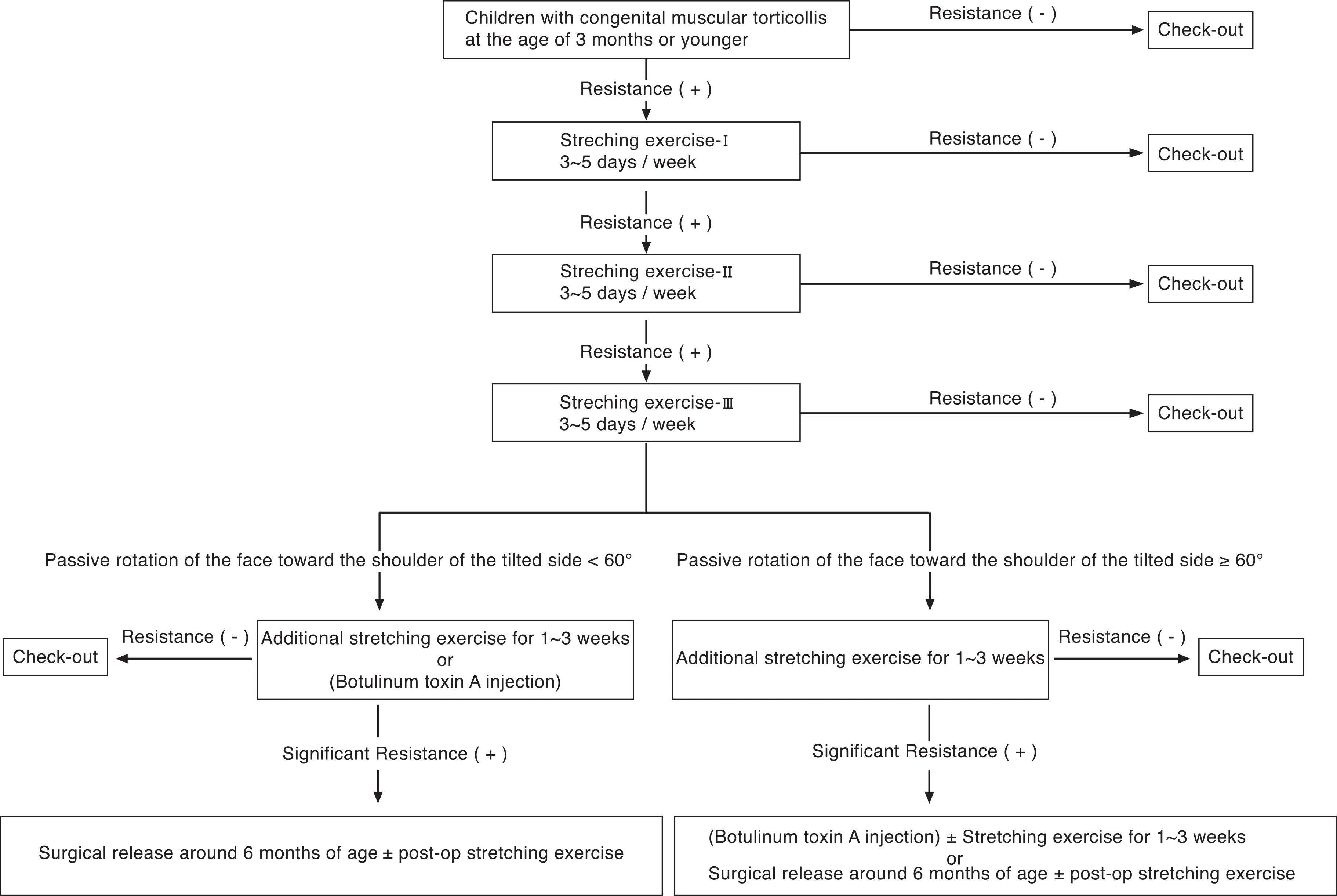 | Figure 9.Ajou therapeutic protocol for children with congenital muscular torticollis at the age of 3 months or younger. |
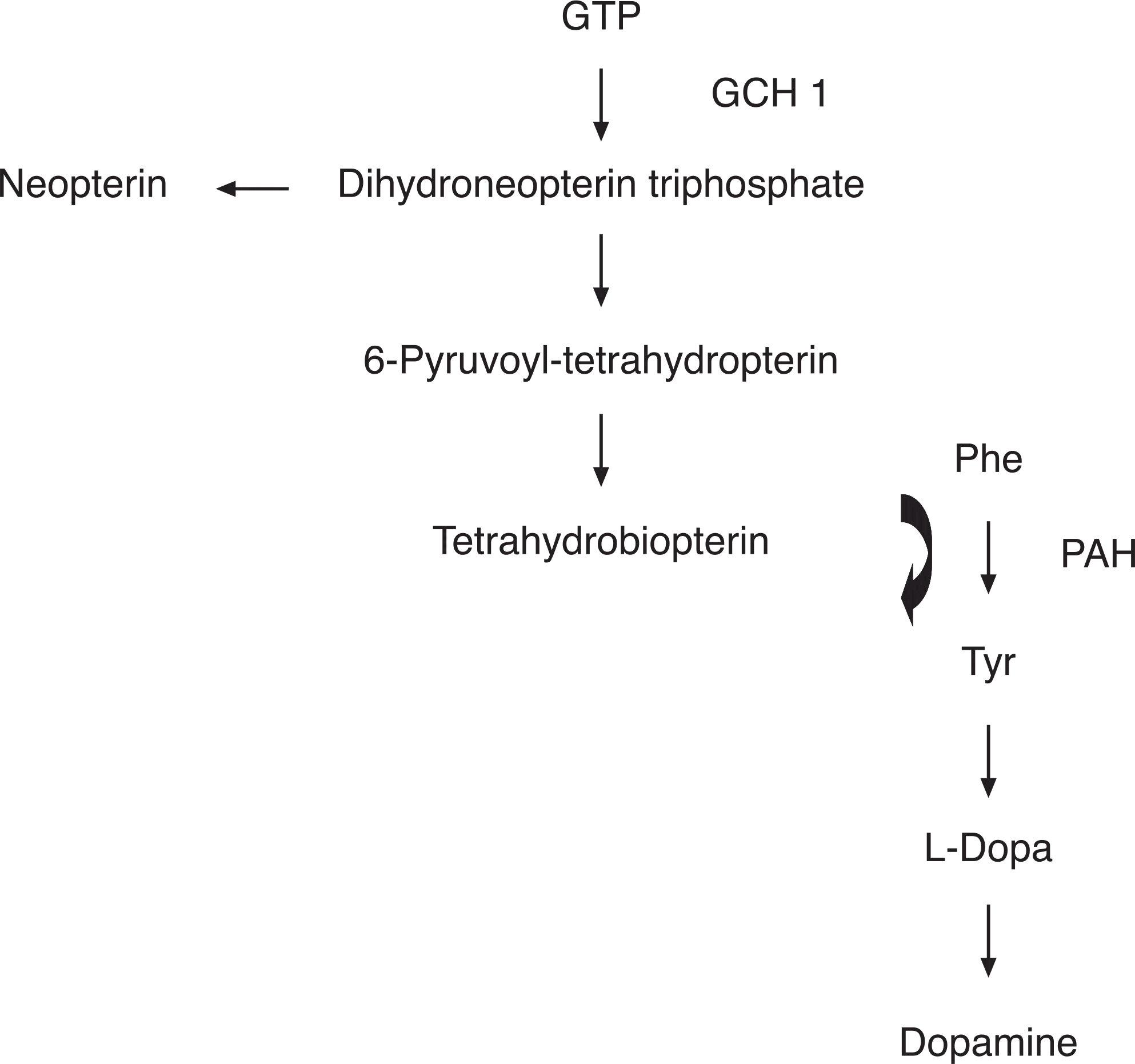 | Figure 12.The biosynthetic pathway of tetrahydrobiopterin and dopa from guanosine triphosphate (GTP). GCH 1:GTP cyclohydrolase I, Phe: phenylalanine, Try: tyrosine. |
Table 1.
Doses and muscles to inject as first line therapy, as well as maximum does, depending on the type of cervical dystonia




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download