Abstract
The asbestos textile industry is characterized by the highest asbestos ambient air concentration of those workers who have suffered from high incidence of lung cancer, malignant mesothelioma, and other asbestos related diseases (ARDs). Also, asbestos dust occurred in a factory can be disseminated into the environmental air around the factory, which can cause ARDs among residents of the factory. High lung cancer and malignant mesothelioma mortality rates among asbestos textile workers were established, and increase of ARDs among residents around the factory has been reported. A large number of environmentally exposed residents as well as severity of health problems among asbestos textile workers would cause huge social problems. The high exposure group needs to be monitored for early detection and management. In addition, a nationwide mandatory malignant mesothelioma registration system to identify exposure sources and high risk groups might help to predict and manage ARDs.
Figures and Tables
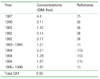
Figure 1
Distribution of malignant mesothelioma cases around asbestos textile factories in Busan during 1997 and 2006.

References
1. Choi J, Paek D, Paik D. The production, the use, the number of workers and exposure level of asbestos in Korea. Korean Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1998. 8:242–253.
2. Ahn YS, Kang SK. Asbestos-related occupational cancers compensated under the Industrial Accident Compensation Insurance in Korea. Ind Health. 2009. 47:113–122.

3. Choi Y. Dangerous Trades Case report of International trades of Asbestos Industry in Asia. International Symposium on Removal & Transfer of Asbestos in Asia. 2008. 223–246.
4. Kim K. Research on the realities of the workers who retired from asbestos textile factory. Korea Occupational Safety & Health Agency. 2008.
5. Ministry of Labor's National Labor Science Research Center. Research on the Public Sanitation Realities of the Workers Handling Asbestos. 1987.
6. Paik N, Lee Y. Characterization of Worker Exposure to Airborne Asbestos in Asbestos Industry. Korean Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1991. 1:144–153.
7. Park D, Paik N. Worker Exposure to Asbestos Fibers in Asbestos Slate Manufacturing and Asbestos Textile Industries. Korean J Env Hlth Soc. 1988. 14:13–27.
8. Oh S, Shin Y, Park D, Park D, Chung K. A Study on Worker Exposure Level and Variation to Asbestos in Some Asbestos in Some Asbestos Industries. Korean Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1993. 3:100–109.
9. Yun I, Park C, Lee W, Lim Y, Kim K. Epidemiological Survey on Environment and Health Status in Asbestos Factories. Korean J Occup Med. 1993. 5:137–151.

10. Paek D, Paik N, Choi J, Son M, Im J, Lee W, Moon Y, Park J, Choi B. Prevalence of Asbestosis in Asbestos Industry. Korean J Occup Med. 1995. 7:46–57.
11. Park J, Yoon C, Paik N. A study on Exposure Among Asbestos Textile Workers and Estimation of their Historical Exposures. Korean Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1995. 5:16–39.
12. U.S Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). http://www.epa.gov/NCEA/iris/subst/0371.htm.
13. Pira E, Pelucchi C, Buffoni L, Palmas A, Turbiglio M, Negri E, Piolatto PG, La Vecchia C. Cancer mortality in a cohort of asbestos textile workers. Br J Cancer. 2005. 92:580–586.

14. Hein MJ, Stayner LT, Lehman E, Dement JM. Follow-up study of chrysotile textile workers: cohort mortality and exposure-response. Occup Environ Med. 2007. 64:616–625.

15. Richardson DB. Lung cancer in chrysotile asbestos worker: analyses based on the two-stage clonal expansion model. Springer Science. Business Media. 2009.
16. Paek D, Paik N, Choi J, Son M. Prevalence of Asbestos in Korean Asbestos Industry. Korean J Occup Med. 1995. 7:46–57.
17. Kim J, Jang T, Lee D, Choi J, Park M, Chung M, Jang T, Choi H, Moon I, Kang S. A case of diffuse malignant pleural Mesothelioma with Occupational asbostos exposure. Korean J Int Med. 1995. 48:526–530.
18. Asbestos suit: U.S.A cases. www.lawtimes.co.kr/LawSeries/SeriesPS/SeriesPSContents.aspx?serial=605&Key=us.
19. Kurumatani N, Kumagai S. Mapping the risk of mesothelioma due to neighborhood asbestos exposure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008. 178:624–629.

20. Kang D. Estimation of past asbestos exposure-Indonesian field study. 2008. In : Kor Soc Occup Environ Med 41th Conference; Busan. 167–168.
21. Marfels H, Spurny K, Boose C, Schoermann J, Opiela H, Althaus W, Weiss G. Measurements of fibrous dusts in ambient air of the Federal Republic of Germany I, Measurements in the vicinity of an industrial source. StaubReinhalt Luft. 1984. 44:259–263.
22. Marfels H, Spurny K, Boose C, Schoermann J, Opiela H, Althaus W, Weiss G. Measurements of fibrous dusts in ambient air of the Federal Republic of Germany II, Measurements on a busy crossing of a large town. Staub-Reinhalt Luft. 1984. 44:410–414.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download