Abstract
Several advances in premature and neonatal care, such as, development in new drugs and equipments, and improvement of medical skills, have also undoubtedly contributed to the reductions in morbidity and mortality of premature infants during last several decades in Korea. This review was conducted for focusing the development of new medical drug therapy and its clinical application and outcomes for preterm. The details of the artificial pulmonary surfactant replacement therapy for respiratory distress syndrome, indomethacin for patent ductus arteriosus, inhaled nitric oxide therapy for persistent pulmonary hypertension, total parenteral nutrition, and drugs for neonatal resuscitation program were reviewed in this paper.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
Changes in respiratory distress syndrome mortality rates over the past 17years among those that received pulmonary surfactant replacement therapy in Korea. Mortality rates were found to have reduced dramatically, that is, from 40%, 30%, 18.7%, to 14.3% in Groups I (1990/1), II (1996), III (2002), and IV (2007), respectively.

Figure 2
Changes of mortality in 5-yr interval of low birth weight infant (LBWI) and very low birth weight infant (VLBWI) in Korea. (A) first half of the decade, (B) second half of the decade.
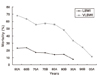
Figure 3
Trends in the survival rates for very low birth weight infants (VLBWI) and extremely low birth weight infants (ELBWI) in Korea. (A) first half of the decade, (B) second half of the decade.

Table 1
Preparations of artificial pulmonary surfactant clinically available in Korea

*Lipid extracts of bovine lung mince+DPPC, PG, PA (containing surfactant proteins-B and -C)
**Mixture of phospholipid (not contained surfactant proteins-B and-C)
***Chloroform/methanol extracts of porcine lung mince, purified by liquid gel electrophoresis (also containing surfactant proteins-B and-C).
References
1. Bae CW. The changes in the birth and mortality rates of newborn in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2006. 49:975–978.

2. Manual of neonatal intensive care. 2008. 2nd ed. The Korean Society of Neonatology.
3. Bae CW, Han WH. Surfactant therapy for neonatal respiratory distress syndrome: A review of Korean experiences over 17 years. Korean J Med Sci. 2009. (in press).





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download