Abstract
The shortage of donor organs is one of the major barriers of transplantation worldwide. After the success of the direct exchange donor (swap) program in Korea since 1991, a swap-around program has been developed. Recently, a web-based (computerized) algorithm to facilitate donor kidney exchange was devised and tested in multi-center settings. An excellent long-term outcome was achieved by using the donor exchange program as an option to reduce the donor organ shortage. Herein, we discussed on the current status of the exchange donor renal transplantation in Korea, a couple of problems we have had, and future directions we have to head and make better to improve organ donation activities.
Figures and Tables
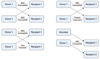 | Figure 1Sample model of exchange living-unrelated donor program: direct swap. Cited from Huh, et al.(6). |
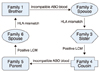 | Figure 2Sample model of exchange living-unrelated donor relay program: swap-around. Cited from Huh, et al.(6). |
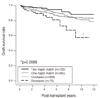 | Figure 3Graft survival rates by types of kidney donors. Patient numbers at risk are depicted. Cited from Huh, et al.(6). |
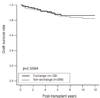 | Figure 4Graft survival rates of exchange versus non-exchange living-unrelated donor kidney transplantation. Patient numbers at risk are depicted. Cited from Huh, et al.(6). |
Table 1
Number of patients on waiting list and number of patient with successful transplantation: Data from KONOS 2006 annual report (2).

References
1. Kim SI, Kwon KH, Huh KH, Lee JH, Kim YS, Park K. Experience with cyclosporine in adult living donor kidney transplantation: from 1984 to 2002 at Yonsei University. Transplant Proc. 2004. 36:186S–192S.

2. 2006 Annual Report. Korean Network for Organ Sharing (KONOS) web data. Accessed June 2008. Available at:
http://www.konos.go.kr.
3. Rapaport FT. The case for a living emotionally related international kidney donor exchange registry. Transplant Proc. 1986. 18:5–9.
4. Kwak JY, Kwon OJ, Lee KS, Kang CM, Park HY, Kim JH. Exchange-donor program in renal transplantation: a single-center experience. Transplant Proc. 1999. 31:344–345.

5. Park K, Moon JI, Kim SI, Kim YS. Exchange donor program in kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 1999. 67:336–338.
6. Huh KH, Kim MS, Ju MK, Chang HK, Ahn HJ, Lee SH, Lee JH, Kim SI, Kim YS, Park K. Exchange living-donor kidney transplantation: Merits and limitations. Transplantation. 2008. 86:(In press).

7. Schweitzer EJ, Wilson JS, Fernandez-Vina M, Fox M, Gutierrez M, Wiland A, Hunter J, Farney A, Philosophe B, Colonna J, Jarrell BE, Bartlett ST. A high panel-reactive antibody rescue protocol for cross-match-positive live donor kidney transplants. Transplantation. 2000. 70:1531–1536.

8. Montgomery RA, Zachary AA, Racusen LC, Leffell MS, King KE, Burdick J, Maley WR, Ratner LE. Plasmapheresis and intravenous immune globulin provides effective rescue therapy for refractory humoral rejection and allows kidneys to be successfully transplanted into cross-match-positive recipients. Transplantation. 2000. 70:887–895.

9. Glotz D, Antoine C, Julia P, Suberbielle-Boissel C, Boudjeltia S, Fraoui R, Hacen C, Duboust A, Bariety J. Desensitization and subsequent kidney transplantation of patients using intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIg). Am J Transplant. 2002. 2:758–760.

10. Gloor JM, Lager DJ, Moore SB, Pineda AA, Fidler ME, Larson TS, Grande JP, Schwab TR, Griffin MD, Prieto M, Nyberg SL, Velosa JA, Textor SC, Platt JL, Stegall MD. ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation using both A2 and non-A2 living donors. Transplantation. 2003. 75:971–977.

11. Tanabe K, Tokumoto T, Ishida H, Ishikawa N, Miyamoto N, Kondo T, Shimmura H, Setoguchi K, Toma H. Excellent outcome of ABO-incompatible living kidney transplantation under pretransplantation immunosuppression with tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil, and steroid. Transplant Proc. 2004. 36:2175–2177.

12. Ross LF, Rubin DT, Siegler M, Josephson MA, Thistlethwaite JR Jr, Woodle ES. Ethics of a paired-kidney-exchange program. N Engl J Med. 1997. 336:1752–1755.

13. Kaplan I, Houp JA, Montgomery RA, Leffell MS, Hart JM, Zachary AA. A computer match program for paired and unconventional kidney exchanges. Am J Transplant. 2005. 5:2306–2308.

14. Saidman SL, Roth AE, Sonmez T, Unver MU, Delmonico FL. Increasing the opportunity of live kidney donation by matching for two - and three-way exchanges. Transplantation. 2006. 81:773–782.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download