Abstract
Multidetector CT (MDCT) is widely used in the clinical field and becoming the new standard in radiological diagnosis. In contrast to cardiovascular, thoracic and abdominal imaging, the role of MDCT is not yet clearly documented in neuroradiology. However, the application of MDCT in stroke, head and neck trauma, spinal diseases and tumor staging of head and neck cancer is actively performed in many institutions, and the results are promising. The shorter scan time, higher resolution, and less radiation dose enable higher and safer CT diagnosis in various neurological diseases. Due to thin slicing and isotropic multiplanar reconstruction (MPR), scanning in one axis is enough to get multiplanar images allowing for a more accurate diagnosis. Further clinical applications and research will be mandatory to prove the clinical utility of MDCT in the field of neuroimaging.
Figures and Tables
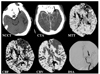 | Figure 1CBF: cerebral blood flow, CBV: cerebral blood volume, MTT: meat transit time
A 66-year-old male with the complaint of right side hemiparesis. Non-contrast CT (NCCT) shows hyperdense thrombus at the left middle cerebral artery (MCA) (black arrow). CT angiography (CTA) reveals occlusion of left MCA and perfusion CT shows decreased CBF, CBV and delayed MTT at the affected territory. Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) during emergency thrombolysis demonstrates occlusion of left MCA (black arrow)
|
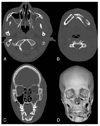 | Figure 2A 22-year-old male with facial trauma
(A), (B) Axial CT with bone setting shows multiple fractures at left facial bones and mandible
(C) Coronal reconstruction from axial images demonstrates precise locations of multiple fractures
(D) Three dimensional reconstruction image shows detailed configuration of fracture lines
|
References
1. Astrup J, Siesjo BK, Symon L. Thresholds in cerebral ischemia-the ischemic penumbra. Stroke. 1981. 12:723–725.

2. Adams HP Jr, Adams RJ, Brott T, del Zoppo GJ, Furlan A, Goldstein LB, Grubb RL, Higashida R, Kidwell C, Kwiatkowski TG, Marler JR, Hademenos GJ. Guidelines for the early management of patients with ischemic stroke: A scientific statement from the Stroke Council of the American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2003. 34:1056–1083.

3. von Kummer R, Bourquain H, Bastianello S, Bozzao L, Manelfe C, Meier D, Hacke W. Early prediction of irreversible brain damage after ischemic stroke at CT. Radiology. 2001. 219:95–100.

4. Pexman JH, Barber PA, Hill MD, Sevick RJ, Demchuk AM, Buchan AM. Use of the Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) for assessing CT scans in patients with acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001. 22:1534–1542.
5. Nabavi DG, Cenic A, Craen RA, Gelb AW, Bennett JD, Kozak R, Lee TY. CT assessment of cerebral perfusion: experimental validation and initial clinical experience. Radiology. 1999. 213:141–149.

6. Schaefer PW, Roccatagliata L, Ledezma C, Hoh B, Schwamm LH, Koroshetz W, Gonzalez RG, Lev MH. First pass quantitative CT perfusion identifies thresholds for salvageable penumbra in acute stroke patients treated with intra-arterial therapy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006. 27:20–25.
7. Wintermark M, Flanders AE, Velthuis B, Meuli R, van Leeuwen M, Goldsher D, Pineda C, Serena J, van der Schaaf I, Waaijer A, Anderson J, Nesbit G, Gabriely I, Medina V, Quiles A, Pohlman S, Quist M, Schnyder P, Bogousslavsky J, Dillon WP, Pedraza S. Perfusion-CT assessment of infarct core and penumbra: receiver operating characteristic curve analysis in 130 patients suspected of acute hemispheric stroke. Stroke. 2006. 37:979–985.

8. Wildermuth S, Knauth M, Brandt T, Winter R, Sartor K, Hacke W. Role of CT angiography in patient selection for thrombolytic therapy in acute hemispheric stroke. Stroke. 1998. 29:935–938.

9. Sims JR, Rordorf G, Smith EE, Koroshitz WJ, Lev MH, Buonanno F, Schwamm LH. Arterial occlusion revealed by CT angiography predicts NIH stroke score and acute outcomes after IV tPA treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005. 26:246–251.
10. Sylaja PN, Dzialowski I, Krol A, Roy J, Federico P, Demchuk AM. Role of CT angiography in thrombolysis decision-making for patients with presumed seizure at stroke onset. Stroke. 2006. 37:915–917.

11. Philipp MO, Funovics MA, Mann FA, Herneth AM, Fuchsjaeger MH, Grabenwoeger F, Lechner G, Metz VM. Four-channel multidetector CT in facial fractures: do we need 2 × 0.5 mm collimation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003. 180:1707–1713.

12. Ahvenjarvi L, Mattila L, Ojala R, Tervonen O. Value of multidetector computed tomography in assessing blunt multitrauma patients. Acta Radiol. 2005. 46:177–183.

13. Chan PN, Antonio GE, Griffith JF, Yu KW, Rainer TH, Ahuja AT. Computed tomography for cervical spine trauma. The impact of MDCT on fracture detection and dose deposition. Emerg Radiol. 2005. 11:286–290.

14. Geijer M, El-Khoury GY. MDCT in the evaluation of skeletal trauma: principles, protocols and clinical applications. Emerg Radiol. 2006. 13:7–18.

15. Boll DT, Bulow H, Blackham KA, Aschoff AJ, Schmitz BL. MDCT angiography of the spinal vasculature and the artery of Adamkiewicz. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006. 187:1054–1060.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download