The defense mechanisms of vertebrates are generally divided into two types, the innate and acquired immune responses. Acquired immune responses involve the production of specific immunoglobulins (Igs) by the host following antigen stimulation [19]. The Igs produced protect the host by removing the pathogen or preventing it from spreading into the blood or organs. Mammals possess five classes of Ig heavy chains: IgM, IgG, IgA, IgE, and IgD [19]. Fish, on the other hand, have been reported to have four Ig heavy chain isotypes at the genomic level, namely IgM, IgD, IgZ, and IgT [16]. Of these four Igs, only IgM has a function that has been demonstrated in the immune responses of fish [7,19]. In addition, although fish and mammalian IgMs share some structural similarities, the teleost IgM is characterized by its major polymeric form, the tetramer (~800 kDa) [7].
The black rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli Higendorf) belongs to the family Scorpaenidae, and is an important mariculture fish in Korea. In 2002, the annual production of black rockfish in Korea was 16,548 metric ton (2002 Statistics, Ministry of Maritime Affairs & Fisheries, Korea). In spite of the importance of this fish species, there have been very few studies about humoral immune response in these fish. The lack of knowledge in this area has resulted in heavy economic losses in the fish farming industry due to various infectious diseases such as lymphocystis, streptococcosis and vibriosis [8,13,17]. In an effort to better understand the humoral immune response of black rockfish, the present study was performed to produce monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) against serum Ig of this species.
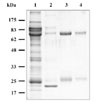
Affinity columns bound with specific ligands, such as protein A, mannan binding protein (MBP) and IgG, have been widely used for purifying IgM from fish sera due to their methodological simplicity and specificity for IgM [1,4,11,12]. In the present study, three different affinity columns were able to successfully purify Ig-like proteins from the sera of black rockfish. The concentrations of purified Ig-like proteins were as follows: immunoaffinity columns, 0.7 ± 0.1 mg/ml; MBP affinity columns, 0.9 ± 0.1 mg/ml; and protein A affinity columns 1.2 ± 0.08 mg/ml. Furthermore, the protein A-purified Ig-like proteins eluted in a single peak at 0.46M NaCl using anion-exchange column chromatography (data not shown).
SDS-PAGE analysis under reducing conditions previously revealed that teleost IgM was comprised of a 70-81 kDa heavy chain and a 22-32 kDa light chain [1,4,11,12]. Consistent with these findings, all of the Ig-like proteins purified in the present study consisted of two bands at approximately 70 and 25 kDa (Fig. 1). Therefore, the 70 kDa band was regarded as the heavy chain and that of 25 kDa was thought to be the light chain. However, additional bands at 97 and 23 kDa were seen in the SDS-PAGE profile for the Ig-like protein purified from the MBP affinity column. Similar findings were also observed in the SDS-PAGE analysis of Igs purified from barramundi sera using MBP [4]. As in the previous study, we also could not explain whether these bands were non-specific or some type of contamination that resulted from using the MBP affinity column [4].
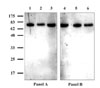
MAbs against black rockfish serum Ig were produced from mice immunized with the Ig-like protein purified from the protein A affinity column, as previously described [9]. ELISA screening, followed by SDS-PAGE immunoblot assays, allowed selection of 21 MAb clones. Of the MAbs, 19 clones (R7B4-8, R7B4-9, etc) were specific for the heavy chain and 2 clones (R11H4-1, R9C7-6) were specific for the light chain in immunoblot assays with rockfish Ig purified with protein A (data not shown). All MAbs produced belonged to the IgG2, IgG1 or IgM isotype classes based on assays to assign type.
The MAbs raised against protein A-purified Ig possessed similar reactivity to all of the Igs purified from the three affinity columns (Fig. 2). Various groups have reported IgM subvariants in assorted fish such as Atlantic salmon [6], giant grouper [3], rainbow trout [5], channel catfish [10], carp [15], and olive flounder [2]. The heavy chains of each of these IgM types are reported to differ with respect to pI, molecular weight (MW), and antigenicities. However, based on the current results of SDS-PAGE, anion exchange column chromatography, and immunoblot assays with MAbs, the Ig of black rockfish is thought to exist as a single isotype within the serum.
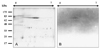
Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) immunoblot assays were applied to identify the Ig heavy chain from whole serum of black rockfish. The resulting 2-DE immunoblot profile showed that MAbs for Ig heavy chain reacted with spots that were distributed in a horizontal, chain-like pattern over the pI range between 4.8 and 5.6 with a MW of 70 kDa (Fig. 3). Previous 2-DE experiments have shown that the spots corresponding to the heavy chain of human IgM were found within a pI range of 5.6 to 6.4 at a MW of 80-82 kDa [18]. The pI ranges and MW of the heavy chain of IgM differed slightly in the emerald rockcod (Trematomus bernacchii; pI range 4.0-6.0, MW 78 kDa) [14], rainbow trout (pI 4.8-6.0, MW 76 kDa) and Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus; pI 5.0-6.5, MW 76 kDa) [6], whereas the light chain spots in all three fish species were broadly distributed across a pI range of 4 to 7 [6,14,18]. Therefore, the heavy chain of black rockfish Ig is thought to be similar characteristics with those of other Igs in terms of pI and MW [6,14,18]. In summary, we purified Igs from black rockfish using protein A, MBP, and goat IgG affinity columns. Black rockfish Ig is believed to exist as a single isotype within serum based on anion-exchange column chromatography, SDS-PAGE, and immunoblot assays using MAbs. In addition, the produced MAbs could identify Ig heavy chain on 2-DE immunoblot profiles from whole serum. These MAbs may prove useful in studying the humoral immune response in black rockfish against pathogens, and in developing diagnostic markers and vaccines for maricultural use.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download