Abstract
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Electrocardiogram of sheep inoculated with crude Ts venom. II derivation, 50 mm/sec, with 10 mm/mV sensibility. (A) QR complex (red circle). (B) QS complex (red circle). (C) qR complex (red circle).

Fig. 2
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) characterization of the anti-Ts venom sheep antibodies, per group. Reactivity of sheep sera immunized with either PBS (G1, white bars), crude Ts venom (G2, black bars) or glutaraldehyde detoxified Ts venom (G3, grey bars). Serum from each animal was pooled by group and used at different dilutions (1/100; 1/500; 1/1,000; 1/5,000; 1/10,000 and 1/50,000). Plates were coated with 100 µL of Ts crude venom (10 µg/mL). Three independent experiments were conducted and plotted values are the means ± SEM of triplicates (error bars).
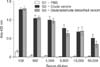
Fig. 3
ELISA characterization of the anti-Ts venom sheep antibodies, per animal. Reactivity of individual sheep serum. In G1, animals 1, 2, 3 and 4 were immunized with PBS (A). In G2, animals 5, 6, 7 and 8 were immunized with crude Ts venom (B). In G3, animals 9, 10, 11 and 12 were immunized with glutaraldehyde detoxified Ts venom (C). Serum from each animal was used at different dilutions (1/100; 1/500; 1/1,000; 1/5,000; 1/10,000 and 1/50,000). Plates were coated with 100 µL of Ts crude venom (10 µg/mL). Values are means of duplicates from two independent experiments. Anti-Ts sheep serum that was previously produced by the injection of eight doses of 500 µg of Ts venom and emulsified in Freund's adjuvant was used as a positive control (C+).
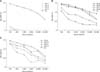
Fig. 4
Western blotting characterization of individual sheep sera. A total of 20 µg Ts venom were subjected to 18% sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and then transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. The membrane was then analysed against each individual serum at 1/1,000 dilution, and revealed with 3,3′-diaminobenzidine/chloronaphthol. P, molecular weight marker; Lanes 1–4, serum from animals immunized with PBS (G1); Lanes 5–8, serum from animals immunized with crude Ts venom (G2); Lanes 9–12, serum from animals immunized with glutaraldehyde-detoxified Ts venom (G3); Lane C+, anti-Ts sheep serum which was previously produced by the injection of eight doses of 500 µg of Ts venom emulsified in Freund's adjuvant.

Table 1
Serum neutralization in mice challenged with Tityus serrulatus venom (TsV)

Groups 1 to 14 received amounts corresponding to 2 LD50 of TsV that had been preincubated for 1 h at 37℃ with individual sheep serum (groups 1 to 12), PBS (group 13, negative control) or commercial anti-venom (group 14, positive control). Group 15 received only 200 µL of pooled sheep sera to verify any adverse events.
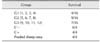
Table 4
Survival rates for in vitro neutralization assay
Measurement of survival rates after challenge with amounts corresponding to 2 LD50 of Ts crude venom pre-incubated with 200 µL of serum from each individual animal immunized with either PBS (G1, animals 1, 2, 3, and 4), crude Ts venom (G2, animals 5, 6, 7, and 8) or glutaraldehyde-detoxified Ts venom (G3, animals 9, 10, 11, and 12). As a negative control (C−), venom was preincubated with 200 µL of PBS, while as a positive control (C+), venom was preincubated with commercial horse anti-Ts. To detect possible adverse effects, one group was injected with only 200 µL of a pool of all sheep sera and no venom.
Table 5
Survival following in vivo neutralization by individual serum

Measurement of survival rates after challenge with amounts corresponding to 2 LD50 of Ts crude venom pre-incubated with 200 µL of serum from each individual animal. Sheep number 5, 6, 7 and 8 were immunized with Ts crude venom (G2) and sheep number 9, 10, 11 and 2 were immunized with glutaraldehyde-detoxified Ts venom (G3).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download