Abstract
Backgrounds/Aims
We compared the efficacy and safety of a hepatectomy, combined with intraoperative radiofrequency ablation to those of wider extent hepatectomy, alone, in patients with multiple hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs).
Methods
Between January 2004 and December 2013, 78 patients with multiple HCCs underwent surgery. 25 patients were treated by hepatectomy, combined with intraoperative radiofrequency ablation (RFA) (group A), and 53 underwent hepatectomy only (group B). We retrospectively analyzed medical records to compare the clinical features of these two groups.
Results
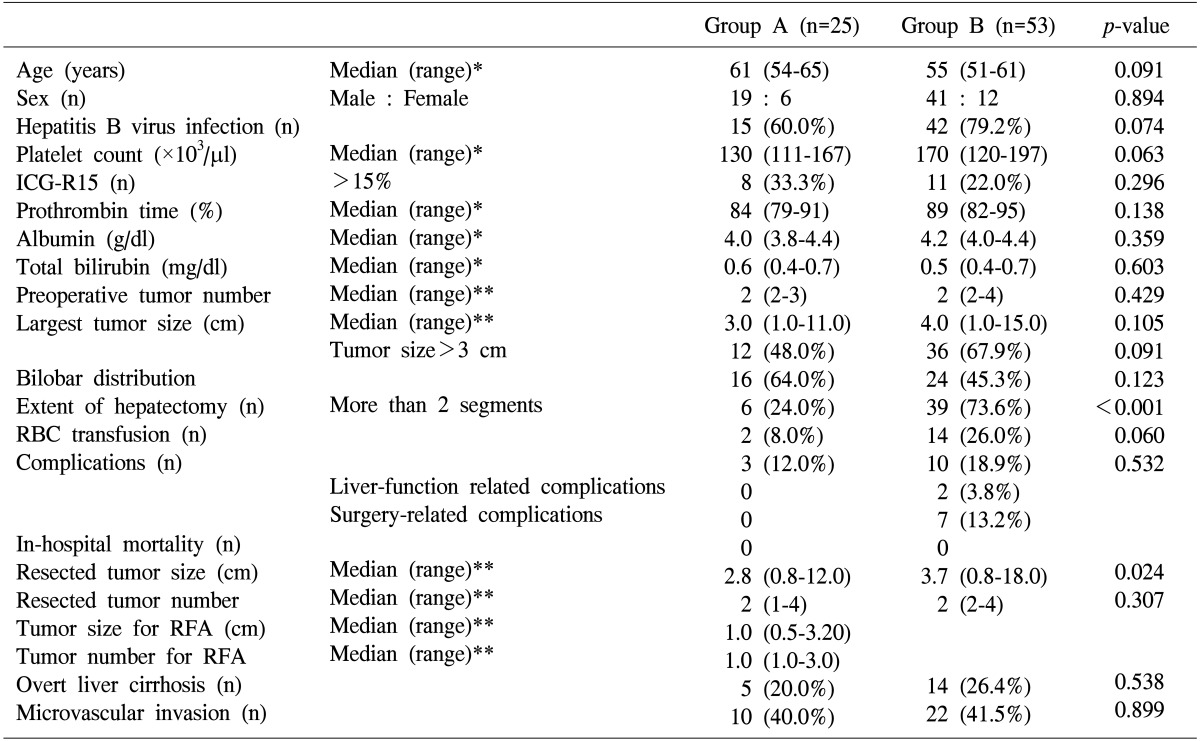
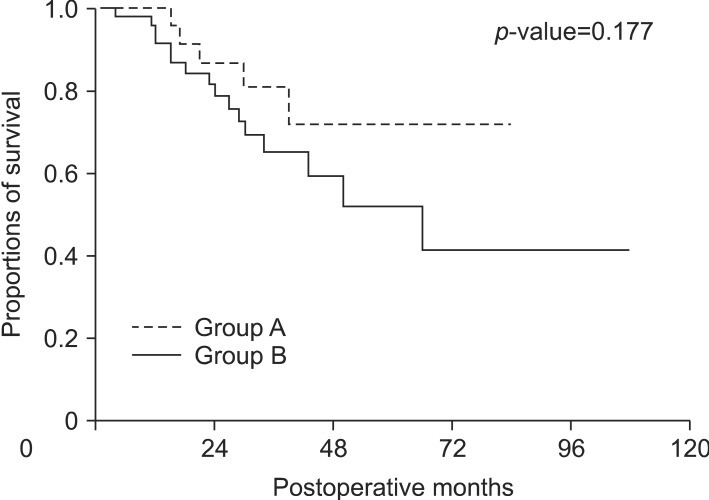
Patients in group A had more limited resections (less than 2 segments) than those in group B (p<0.001). Patients in group A also tended to have fewer red blood cell transfusions than those in group B (p=0.060). Liver function- and surgery-related complications occurred only in group B. There were no in-hospital mortalities in both groups. The overall survival and disease-free survival outcomes were not significantly different between groups A and B (p=0.177 and p=0.305, respectively).
Go to : 
Hepatic resection is generally considered the gold standard for the treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).1234 However, previous studies report a low rate of resectability for HCC, in the range of 20% to 40%.45 Surgical treatment is not considered appropriate for most patients, because of poor remnant hepatic function, distant metastasis, major vascular invasion, unsuitable tumor location, and multinodular tumor distribution.12345 Moreover, palliative treatments have produced disappointing survival benefits for patients with unresectable HCCs;678 studies show that surgical resection produces a better prognosis than palliative treatments.910
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) has been recently established as an effective treatment method, and is regarded as one of the curative treatment options for select HCC patients.111213 According to a recent study, RFA is a safe and effective method for managing HCC patients with cirrhosis, especially for patients with a tumor size ≤2 cm, and poor hepatic reservoir function.12 Intraoperative RFA has some theoretical advantages over percutaneous RFA, including better visualization of the tumor on intraoperative ultrasonography.13 Intraoperative RFA also enables more accurate placement of the electrodes, and reduces the risk of bleeding.13 Hepatic failure, due to intraoperative RFA, is less likely to occur in this circumstance than after a hepatectomy of wider extent.11121314
Multiple tumorectomies, or an extended hepatectomy, are indicated for patients with multiple HCC. However, they involve a higher risk of hepatic failure, perioperative massive transfusion, and postoperative complications. Therefore, hepatectomy combined with intraoperative RFA (H-RFA) has the advantage of reducing operative risk after the hepatectomy. Additionally, H-RFA may broaden the applicability of surgery for multiple HCC treatments.
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of H-RFA for multiple HCCs.
Go to : 
Between January 2004 and December 2013, 78 patients underwent surgery for multiple HCC, in the Department of Surgery at our hospital. Among them, 25 underwent H-RFA and 53 underwent hepatectomy alone; these patients were defined as group A and group B, respectively. Their medical records were reviewed retrospectively. The evaluated patient characteristics included age, sex, hepatitis B virus infection, and preoperative radiologic findings (such as the total tumor number, tumor distribution, and largest tumor size). The preoperative laboratory variables included an indocyanine green (ICG) test retention rate at 15 minutes (ICG-R15), a platelet count, the prothrombin time, albumin, and the total bilirubin. The surgical variables included the extent of resection, perioperative red blood cell transfusion, postoperative complications, and in-hospital mortality. The pathologic variables included the size of the largest tumor and the total number of tumors among the resected specimens, microvascular invasion, and the presence of liver cirrhosis. The tumor size and number of RFA procedures performed were also included.
We determined the extent of the hepatectomy based on the patient's clinical data, such as the Child-Pugh classification, the status of the portal hypertension, the preoperative laboratory results, and the tumor distribution. The Child-Pugh classification of all patients was Child A. The indications for intraoperative RFA were as follows: the tumor size was less than 3 cm (without closed vascular or biliary structure), there were multiple tumors located in both lobes of the liver that would lead to an inadequate expected remnant liver volume, and there were situations in which a percutaneous RFA approach would have been challenging.
An intraoperative RFA was performed using a 200 W generator in the impedance control mode, and a monopolar single or clustered internally cooled electrode with a 3 cm-long exposure tip (Valleylab, Burlington, MA, USA). A single radiologic specialist performed the intraoperative RFA procedure.
All patients underwent follow-up examinations that included measuring tumor markers, and a 3-phase liver computed tomography or abdominal ultrasonography. Follow-up visits were conducted 4 weeks after surgery, and every 3 months thereafter. After 2 years, follow-up examinations were conducted every 4 to 6 months, depending on the particulars of each case.
Continuous variables were measured as the median (interquartile range or minimal to maximal range) and analyzed using the Mann-Whitney U test. Categorical variables were analyzed with the Chi-square test or Fisher's exact test. Survival outcomes were compared between the two groups, using the Kaplan-Meier method, with a log-rank test. SPSS for Windows (Korean version 14.0; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for the statistical analyses. P-values of less than 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of our institution.
Go to : 
The clinicopathological data for the 78 patients enrolled in this study are summarized in Table 1. The median follow-up period was 24 months. The median ages of the patients in groups A and B were 61 years and 55 years, respectively (p=0.091). The male sex was dominant in both groups, although the difference was not significant (p=0.894). The hepatitis B virus infection was the most common etiology of HCC in both groups (p=0.074). The median preoperative platelet count values were 130×103/µl in group A and 170×103/µl in group B (p=0.063). There were no statistically significant differences in other laboratory variables, such as ICG-R15 values greater than 15% (p=0.296), prothrombin time (p=0.138), albumin (p=0.359), and total bilirubin (p=0.603).
With respect to the preoperative variables, the median number of tumors was 2 in both groups (p=0.429). There was no statistically significant difference in the median diameter of the largest tumor between the two groups (p=0.105). Bilobar tumor distribution was observed in 16 patients (64.0%) in group A, and 24 patients (45.3%) in group B, although this difference was also not statistically significant (p<0.123).
The analysis of the surgical variables showed that major hepatic resections (more than 2 segments) were performed in 24.0% of the patients in group A, and 73.6% of the patients in group B; this difference was statistically significant (p<0.001). The patients in group B tended to have more frequent perioperative red blood cell transfusions than those in group A (p=0.060). There was no postoperative mortality among patients in both groups. The postoperative complication rates were 12.0% in group A, and 18.9% in group B; the difference was not statistically significant (p=0.532). Liver function-related complications, such as hepatic failure or ascites, as well as surgery related complications, such as biloma or intra-abdominal bleeding, occurred only in group B.
Regarding pathological variables, the median diameter of the largest tumor in the resected liver specimens was significantly smaller in group A (2.8 cm) than in group B (3.7 cm; p=0.024). The median total number of tumors was 2 in both the groups (p=0.307). The median tumor size for the RFA was 1.0 cm (range, 0.5-3.2 cm) and the median tumor number for the RFA was 1.0 cm (range, 1.0-3.0). There were no statistically significant differences in the presence of cirrhosis or microvascular invasion between the two groups (p=0.538 and p=0.899, respectively).
Moreover, there were no statistically significant differences in the overall or disease-free survival rates between groups A and B (Figs. 1, 2). The overall survival rate, at 5 years, was 72.1% in group A and 52.0% in group B (p=0.177). The disease-free survival rate at 5 years was 29.7% in group A and 23.9% in group B (p=0.305). Furthermore, the marginal recurrence following the intraoperative RFA was 16.7%.
Go to : 
The reasons for the lack of curative treatments for patients with multiple HCCs include insufficient hepatic reservoirs after resection, impaired hepatic function with cirrhosis, and an improper surgical approach for bilobar tumor distribution. However, the survival benefits after palliative treatment for these patients have been disappointing, as documented in previous studies.67 Cammá et al.6 reported that, in randomized studies, the survival benefit of hepatic arterial chemoembolization in these patients was relatively small. Llovet et al7. showed that chemoembolization improved the overall survival for only 20% of responders. A study of the palliative treatment in 268 HCC patients, who did not satisfy the Milan criteria, yielded poor survival outcomes with only 24% being alive at 5 years.15 Additionally, sorafenib was reported to improve the survival period by only 3 months in patients with advanced HCCs.8
However, Ng et al.9 reported favorable survival outcomes after hepatic resection for large or multiple HCCs, with 5-year overall survival rates of 39%. They suggested that the long-term survival outcomes in patients without poor prognostic variables were comparable to those with early HCC. Yin et al.10 suggested that hepatic resection may be the treatment of choice for resectable multiple HCCs that do not meet the Milan criteria. Furthermore, they reported a 3-year overall survival rate of 51.5%. These studies indicate that hepatic resection could be a curative treatment option for patients with resectable HCC.
Recently, RFA has been recommended for patients with early HCC as a curative treatment option.1234 Kim et al.16 reported excellent long-term survival outcomes for patients with early HCC after percutaneous RFA; the 10-year survival rate was 38.2%. However, they also reported that tumor recurrence after RFA was frequent, with 10-year intrahepatic and extrahepatic recurrence rates of 88.5% and 38.2%, respectively. Intraoperative RFA has some theoretical advantages- it provides a better visualization of the tumor for accurate placement of the ablation probe, is painless, and is safer than a percutaneous approach. Therefore, H-RFA may be the treatment of choice for HCC patients with surgical limitations, such as those with poor hepatic reservoir function or bilobar tumor distribution.
Pawlik et al.17 reported the first study of H-RFA, in 172 patients with hepatic metastases from colorectal or other cancers. They showed that the ablated tumor size and number did not influence the survival outcomes or local recurrence after H-RFA. They, therefore, suggested that H-RFA was a safe treatment option for multiple hepatic metastases from gastrointestinal cancers.
Choi et al.18 described the long-term survival outcomes of patients with multifocal HCC, who underwent H-RFA. They reported that the 5-year overall survival rate, after H-RFA, was 55% and that the intrahepatic marginal recurrence rate was 3%. They also reported no hospital mortalities, and an RFA-related complication rate of 2%. A resected tumor size ≥5 cm was the only independent prognostic factor for survival.
In this present study, there were no significant differences in the overall and disease-free survival outcomes, between patients who underwent H-RFA and those who underwent hepatectomy alone. Furthermore, the marginal recurrence rate was 16.7%, which is consistent with the previous study reported by Kim et al.16 Thus, we conclude that H-RFA is an effective treatment modality for patients with multiple HCC. Expanding the possibilities for the curative resection of HCC will lead to better prognoses for patients with multiple HCC. Additionally, patients with H-RFA experienced a lower complication rate than those with hepatectomy alone, although this difference was not statistically significant. Liver function-related or surgery-related complications occurred only in patients who underwent hepatectomy alone.
In conclusion, the results of our study suggest that H-RFA is a safe and effective treatment option for patients with multiple HCCs, comparable to extended hepatectomy alone.
Go to : 
References
1. Lee JM, Park JW, Choi BI. 2014 KLCSG-NCC Korea Practice Guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: HCC diagnostic algorithm. Dig Dis. 2014; 32:764–777. PMID: 25376295.

2. Bruix J, Sherman M. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology. 2011; 53:1020–1022. PMID: 21374666.

3. Kudo M, Matsui O, Izumi N, Iijima H, Kadoya M, Imai Y, et al. JSH consensus-based clinical practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: 2014 update by the liver cancer study group of Japan. Liver Cancer. 2014; 3:458–468. PMID: 26280007.

4. European Association for Study of Liver. European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 2012; 48:599–641. PMID: 22424278.
5. Bruix J, Llovet JM. Prognostic prediction and treatment strategy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2002; 35:519–524. PMID: 11870363.

6. Cammà C, Schepis F, Orlando A, Albanese M, Shahied L, Trevisani F, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Radiology. 2002; 224:47–54. PMID: 12091661.

7. Llovet JM, Real MI, Montaña X, Planas R, Coll S, Aponte J, et al. Barcelona Liver Cancer Group. Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002; 359:1734–1739. PMID: 12049862.

8. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, et al. SHARP Investigators Study Group. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:378–390. PMID: 18650514.

9. Ng KK, Vauthey JN, Pawlik TM, Lauwers GY, Regimbeau JM, Belghiti J, et al. International Cooperative Study Group on Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Is hepatic resection for large or multinodular hepatocellular carcinoma justified? Results from a multi-institutional database. Ann Surg Oncol. 2005; 12:364–373. PMID: 15915370.

10. Yin L, Li H, Li AJ, Lau WY, Pan ZY, Lai EC, et al. Partial hepatectomy vs. transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for resectable multiple hepatocellular carcinoma beyond Milan Criteria: a RCT. J Hepatol. 2014; 61:82–88. PMID: 24650695.

11. Feng K, Yan J, Li X, Xia F, Ma K, Wang S, et al. A randomized controlled trial of radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012; 57:794–802. PMID: 22634125.

12. Cabibbo G, Maida M, Genco C, Alessi N, Peralta M, Butera G, et al. Survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) treated by percutaneous radio-frequency ablation (RFA) is affected by complete radiological response. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e70016. PMID: 23922893.

13. Santambrogio R, Opocher E, Zuin M, Selmi C, Bertolini E, Costa M, et al. Surgical resection versus laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and Child-Pugh class a liver cirrhosis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009; 16:3289–3298. PMID: 19727960.

14. Rhim H, Yoon KH, Lee JM, Cho Y, Cho JS, Kim SH, et al. Major complications after radio-frequency thermal ablation of hepatic tumors: spectrum of imaging findings. Radiographics. 2003; 23:123–134. PMID: 12533647.

15. Grieco A, Pompili M, Caminiti G, Miele L, Covino M, Alfei B, et al. Prognostic factors for survival in patients with early-intermediate hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing non-surgical therapy: comparison of Okuda, CLIP, and BCLC staging systems in a single Italian centre. Gut. 2005; 54:411–418. PMID: 15710992.

16. Kim YS, Lim HK, Rhim H, Lee MW, Choi D, Lee WJ, et al. Ten-year outcomes of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation as first-line therapy of early hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis of prognostic factors. J Hepatol. 2013; 58:89–97. PMID: 23023009.

17. Pawlik TM, Izzo F, Cohen DS, Morris JS, Curley SA. Combined resection and radiofrequency ablation for advanced hepatic malignancies: results in 172 patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 2003; 10:1059–1069. PMID: 14597445.

18. Choi D, Lim HK, Joh JW, Kim SJ, Kim MJ, Rhim H, et al. Combined hepatectomy and radiofrequency ablation for multifocal hepatocellular carcinomas: long-term follow-up results and prognostic factors. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007; 14:3510–3518. PMID: 17653800.

Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download