INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Preparation of mesenchymal stem cells
TAA-induced liver fibrosis
Transplanted materials to evaluate the hepatic fibrosis and repair
Isolated MSCs
HGF-treated MSCs
Histological study
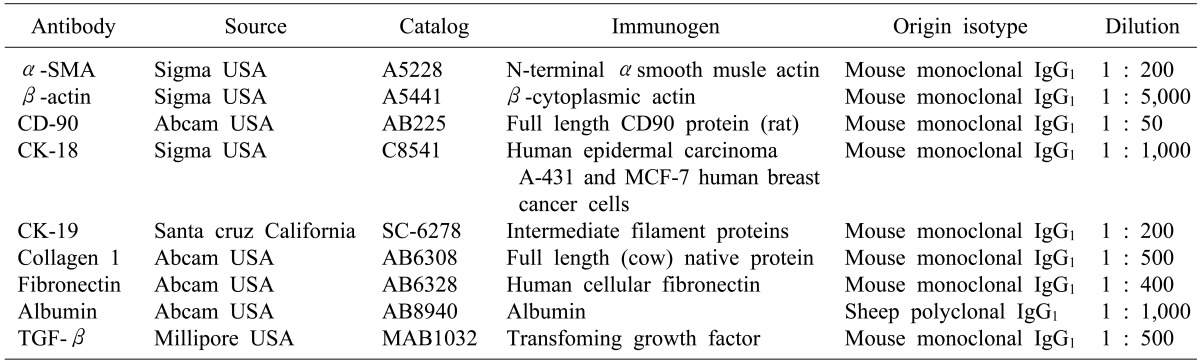
Immunohistochemistry
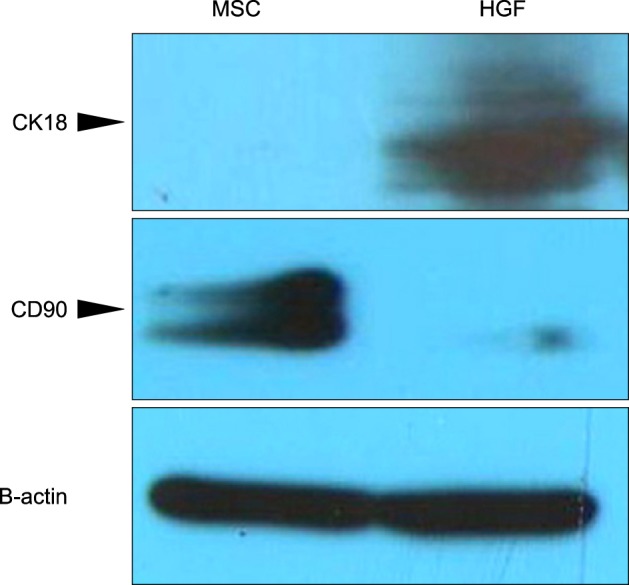
Western blot analysis
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Histological differences between the TAA/MSCs and TAA/HGF-treated MSCs
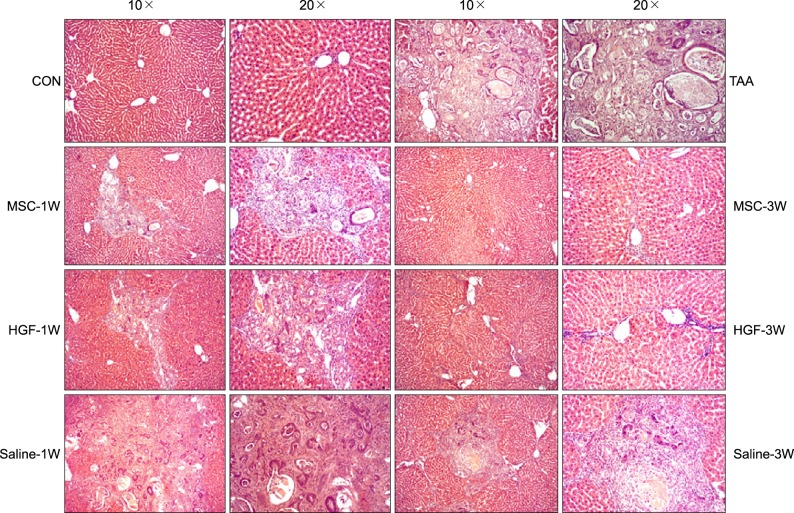 | Fig. 1Histological appearances in the TAA-induced cirrhotic livers. For comparing isolated MSCs group with normal saline group or HGF-treated MSC group, each specimen was stained with H&E stain (Original magnification: ×10, ×20); more prominent hepatocyte regeneration and decreased hepatic fibrosis were detected in isolated MSCs group, but not normal saline or HGF-treated MSCs group. |
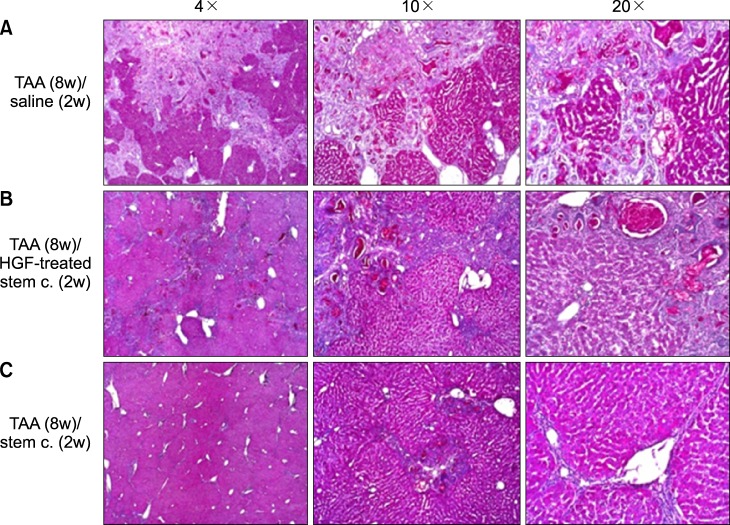 | Fig. 2Histological appearances in the TAA-induced cirrhotic livers. For comparing isolated MSCs group with normal saline group or HGF-treated MSC group, each specimen was stained with PAS stain (Original magnification: ×4, ×10, ×20); more prominent hepatocyte regeneration and glycogen storage were detected in isolated MSCs group, but not normal saline or HGF-treated MSCs group. |
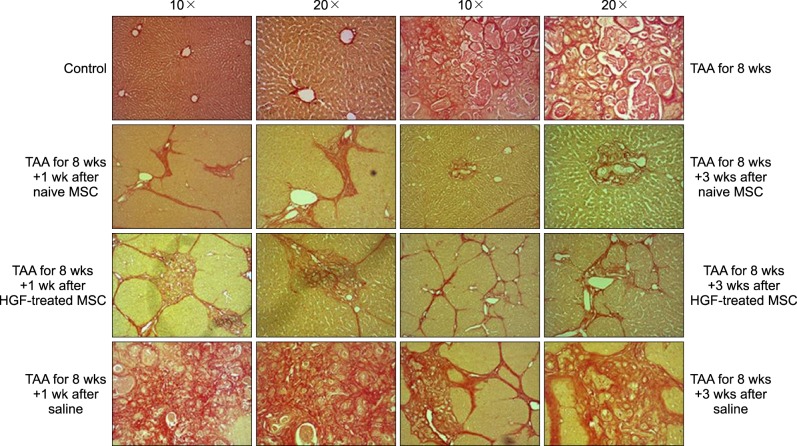 | Fig. 3Histological appearances in the TAA-induced cirrhotic livers. For comparing isolated MSCs group with normal saline group or HGF-treated MSC group, each specimen was stained with Sirius-red stain (Original magnification: ×10, ×20); Alleviated septal fibrosis and less collagen deposition were detected in isolated MSCs group, thickened fibrosis and more collagen deposition in normal saline or HGF-treated MSCs group. |
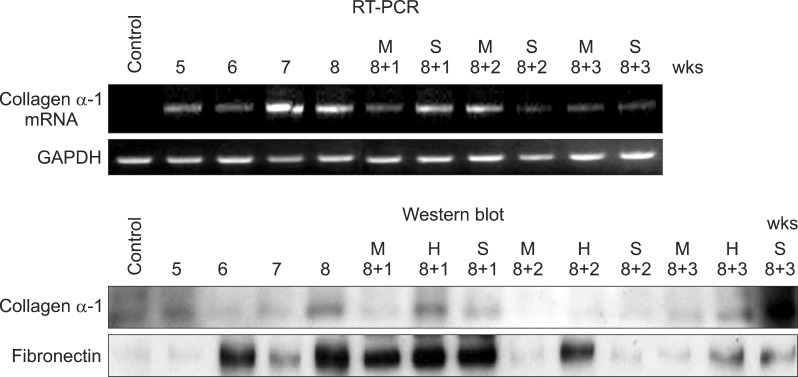 | Fig. 4Western blot analysis and RT-PCR study also showed these serial changes of fibrosis, Quantification of fibrosis induction and MSC-associated effects were assessed through antibody studies for collagen α-1 and fibronectin and RT-PCR for collagnen α-1 messanger ribonucleic andi (mRNA). The expressed amount of collagen α-1 and fibronectin were increased in 8 weeks after TAA ingestion and more decreased in additional 2 weeks after MSC infusion, contrary to control group. |
The change and migration of stem cell after HGF-treatment
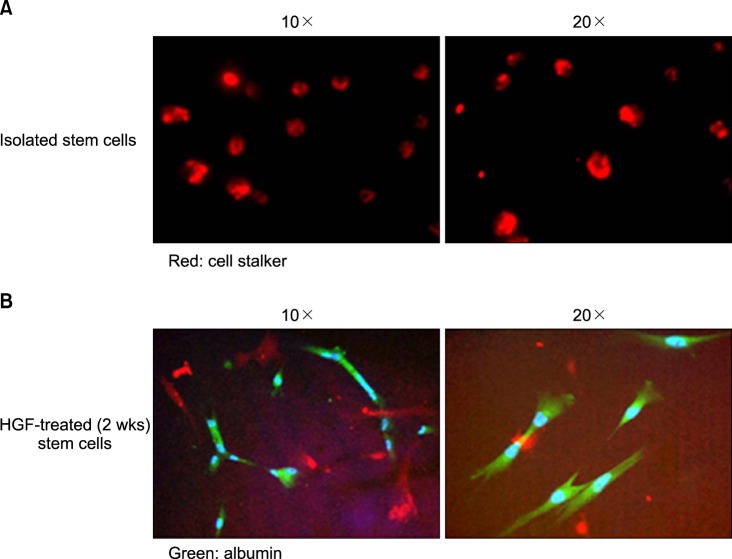 | Fig. 5Fluorescence microscope image showed that stem cells differentiate to hepatocyte and express the albumin in 2 weeks after HGF treatment. (A) Stem cells themselves without differentiation to hepatocyte-like cell (CELL STALKER-CSR dye staining, red; Original magnification: ×10, ×20). (B) Stems cells with differentiation to hepatocyte and albumin expression (Anti-albumin staining, green; Original magnification: ×10, ×20). |
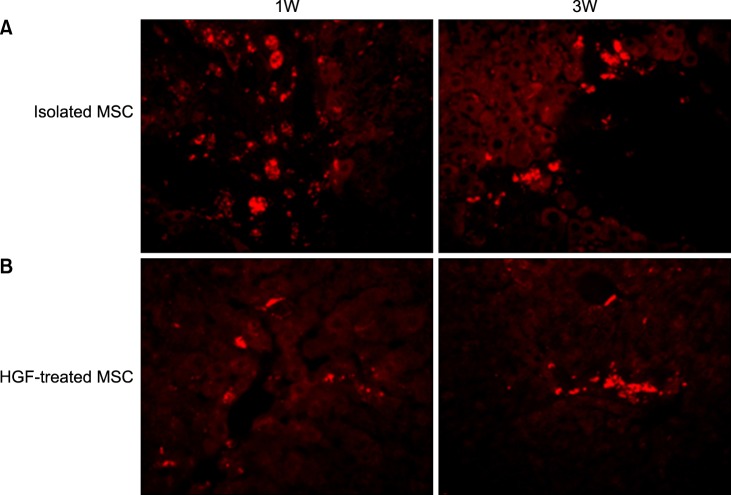 | Fig. 7Transplanted donor cell distribution to the recipient livers. High fluorescence microscope images (×20). (A) A number of Red autofluorescence is mainly localized near hepatic sinusoids in stem cell group, which indicated better engraftment (B). A few red autofluorescence is localized near peripheral hepatic sinusoids in HGF-treated stem cells group, indicated poor engraftment. |
Comparing the serial differentiation phase between Isolated MSCs and HGF-treated MSCs
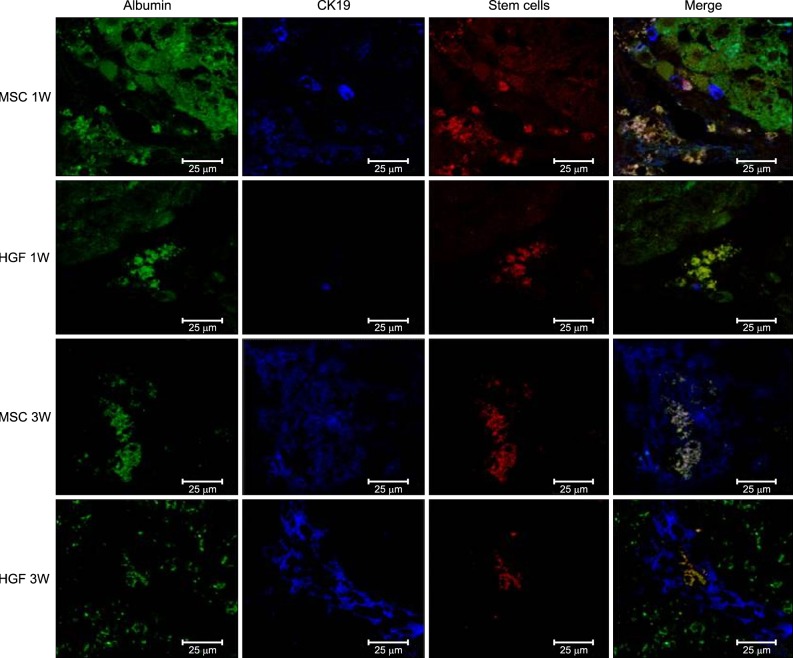 | Fig. 8Transplanted donor cell engraftment to the recipient liver and differentiation into the hepatocytes. High fluorescence microscope images (×20). Anti-CK19 staining, green. MSCs with CELL STALKER-CSR dye staining, red. Albumin positive stem cells in the merged images, yellow. Hepatogenic differentiation-related analyses showed that infusion of isolated MSCs advanced the appearance of oval cells in 1 week, leading to a higher population of hepatic progenitor cells and a lower population of MSCs at 3 weeks. |
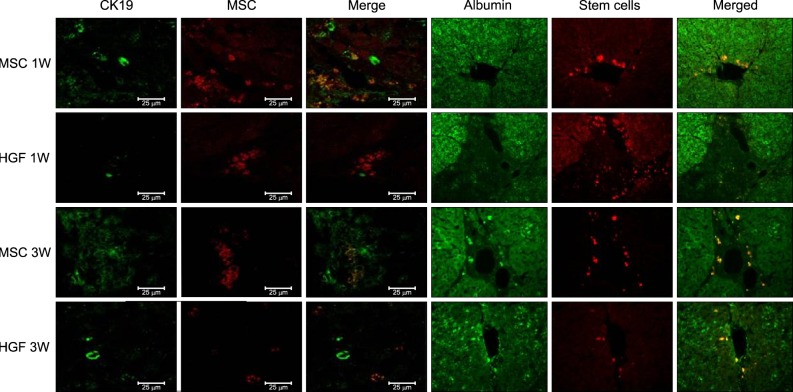 | Fig. 9Transplanted donor cell engraftment to the recipient liver and differentiation into the hepatocytes. High fluorescence microscope images (×20). Hepatogenic differentiantion of implanted MSCs was assessed by immunohistochemistry using Antibody to albunin, CK-19 and CELL STALKKER-CSR dye to assess the MSCs. One week after MSC implantation, CK19 stained oval cells derived from MSCs were located around the portal veins. At 3 weeks, more differentiated MSCs or hepatocyte-like cells were located toward the hepatic parenchyma, and albumin-stained areas had expanded and overlapped the MSC-stained areas. Nearly all the CK19/thy1- and albumin-stained areas overlapped the MSC-stained areas, indicating that most MSCs had transdifferentiated into oval progenitor cells and then into functional hepatocyte-like cells after hepatic implantation. |
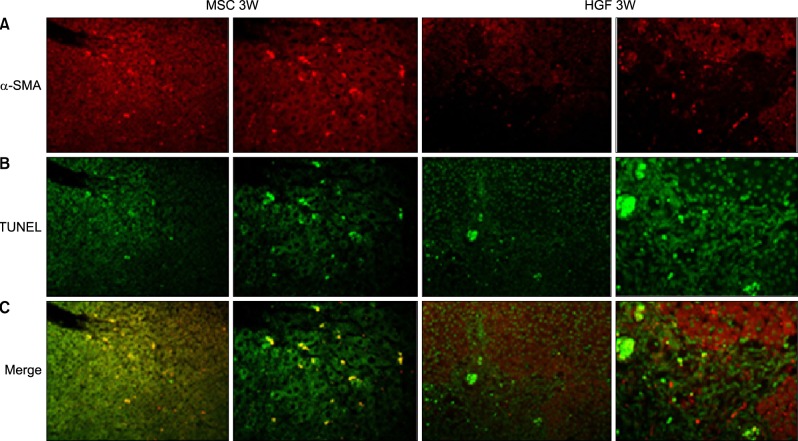 | Fig. 10Hepatic fibrosis and repair by transplanted donor cell engraftment to the recipient liver. High fluorescence microscope images: Engrafted isolated MSC groups express lower α-SMA and higher TUNEL compared with HGF-treated MSCs group. (A) Anti-α-SMA staining, red. (B) TUNEL staining, green. (C) α-SMA and TUNEL positive stem cells in the merged images, yellow. The merged images of TUNEL and α-SMA stains also revealed that apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells was less evident after HGF treatment. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download