Abstract
Backgrounds/Aims
Recently many studies have been reported the early results of a hepatectomy for various intrahepatic lesions. Also various types of laparoscopic hepatectomies are being performed in many centers. Some reports about the safety of laparoscopic parenchymal dissection of the liver have been published. In this study, we reported our experiences of laparoscopic left hepatectomies in patients with an intrahepatic duct (IHD) stone with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis (RPC), and investigated whether the total laparoscopic parenchymal dissection is as safe as open surgery.
Methods
From April 2008 to December 2010, 25 patients had been admitted for left IHD stones with RPC. Preoperatively, the type of surgery was decided with the intention of treating each patient. Initially 10 patients underwent a laparoscopy-assisted left hepatectomy and the next 15 patients underwent total laparoscopic left hepatectomy as our experience grew. Demographics, peri- and postoperative results were collected and analyzed comparatively.
Results
The mean age, gender ratio, preoperative American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) score, accompanied acute cholangitis and biliary pancreatitis, and the number of preoperative percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage (PTBD) inserted cases were not different between the two groups who had undergone laparoscopy-assisted and totally laparoscopic left hepatectomy. The operation time, intraoperative transfusions and postoperative complications also showed no difference between them. The postoperative hospital stay did not show a significant difference statistically.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
A 54-year old female with multiple IHD stones with RPC. (A) On preoperative abdominal CT, there were severe atrophic change of the left lobe of the liver (white arrow head). (B) She underwent a totally laparoscopic left hepatectomy. In a postoperative abdominal CT, there were no postoperative complications.
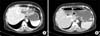
Fig. 2
The incisions to retrieve the specimen. (A) An upper midline incision was made in the laparoscopy-assisted left hepatectomy. (B) A right lower transverse incision was made in the totally laparoscopic left hepatectomy. (C) A Pfannenstiel incision was made in the totally laparoscopic surgery.

References
1. Kim BW, Lee HW, Kim IG, et al. New surgical technique for hepatolithiasis: ventral hilar exposure method. Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2005. 9:23–30.
2. Chen MF, Jan YY, Wang CS, et al. A reappraisal of cholangiocarcinoma in patient with hepatolithiasis. Cancer. 1993. 71:2461–2465.
3. Kubo S, Kinoshita H, Hirohashi K, et al. Hepatolithiasis associated with cholangiocarcinoma. World J Surg. 1995. 19:637–641.
4. Liu CL, Fan ST, Wong J. Primary biliary stones: diagnosis and management. World J Surg. 1998. 22:1162–1166.
5. Hwang JH, Yoon YB, Kim YT, et al. Risk factors for recurrent cholangitis after initial hepatolithiasis treatment. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2004. 38:364–367.
6. John TG, Greig JD, Crosbie JL, et al. Superior staging of liver tumors with laparoscopy and laparoscopic ultrasound. Ann Surg. 1994. 220:711–719.
7. Kaneko H, Takagi S, Shiba T. Laparoscopic partial hepatectomy and left lateral segmentectomy: technique and results of a clinical series. Surgery. 1996. 120:468–475.
8. Ferzli G, David A, Kiel T. Laparoscopic resection of a large hepatic tumor. Surg Endosc. 1995. 9:733–735.
9. Song YJ, Kim KJ, Moon HG, et al. The feasibility of laparoscopic hepatectomy for the patients with left intrahepatic stones. J Korean Surg Soc. 2010. 78:35–40.
10. Hüscher CG, Lirici MM, Chiodini S. Laparoscopic liver resections. Semin Laparosc Surg. 1998. 5:204–210.
11. Min SK, Han HS, Lee HK, et al. Totally laparoscopic anatomic liver resection. J Korean Surg Soc. 2003. 64:390–395.
12. Kim CG, Yoon YS, Han HS, et al. Experience of total laparoscopic hepatectomy. J Korean Surg Soc. 2007. 73:490–495.
13. Cai X, Wang Y, Yu H, et al. Laparoscopic hepatectomy for hepatolithiasis: a feasibility and safety study in 29 patients. Surg Endosc. 2007. 21:1074–1078.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download