Abstract
We report a pair of atypical rhomboideus muscles which originated higher than normal observed in a 49-year-old Korean male. Rhomboid muscles were not paralleogram shape but trapezoid with rhomboideus tertius attached inferior to the rhomboideus major muscles. Rhomboideus minor originated as tendon from the ligamentum nuchae of fourth and sixth cervical vertebrae level. The upper end of the origin of the rhomboideus major was the ligamentum nuchae between fifth and sixth cervical vertebrae level on the left side and the ligamentum nuchae at the sixth cervical vertebra level on the right side. The lower end of the origin of the rhomboideus major was the spinous process of the fourth thoracic vertebra on the left side and the spinous process of the second thoracic vertebra on the right side. The upper end of the origin of the rhomboideus tertius were the same as the lower end of the rhomboideus major and the lower end of the origin of the rhomboideus tertius were the spinous process of the fifth thoracic vertebrae on both sides. Whole rhomboideus muscle spanned over nine vertebrae. We compared these rhomboidei with previously reported variations and discussed its embryological and clinical significance.
References
1. Standring S. Gray's Anatomy. 40th ed.Philadelphia: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone;2008. p. 810–1. 925.
2. Chung IH, Oh CS, Han SH, Kim HJ. Human anatomy. 5th ed.Seoul: Hyunmoonsa;2011. p. 176–8.
3. Bergman RA, Afifi AK, Miyauchi R. Opus I: muscular system. illustrated encyclopedia of human anatomic variation. [Internet]. Anatomy atlases;c1995–2015. [cited 2015 Sep 3]. Available from:. http://www.anatomyatlases.org/Anatomic-Variants/MuscularSystem/Text/R/23Rhomboideus.shtml.
4. von Haffner H. Eine seltene doppelseitige anomalie des trapezius. Internationale monatsschrift für anatomie und physiologie. 1903; 20:313–8.
5. Mori M. Statistics on the musculature of the Japanese. Okajimas folia anatomica japonica. 1964; 40:195–300.

6. Jelev L, Landzhov B. A rare muscular variation: the third of the rhomboids. Anatomy. 2012-2013; 6-7:63–64. DOI: 10.2399/ana.11.218.

7. Valerius KP, Frank A, Kolster BC, Hamilton C, Lafont EA, Kreutzer R. The muscle book: anatomy, testing, movement. 1st ed. Berlin: Quintessence Publishing Co:;2011. p. 18–24.
8. Oxnard C. The scientific bases of human anatomy. Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell;2015. p. 173, 183.
9. Keibel F, Mall FP. Manual of human embryology I. Philadelphia: Lippincott Company;1910. p. 485. p.
Fig. 1.
Photograph and drawing of the atypical rhomboid muscles. The rhomboideus minors arose from ligamentum nuchae of 4–6th cer-vical vertebrae level. The origin of the left rhomboideus major was from ligamentum nuchae of 5th–6th cervical vertebrae level to spinous process of the 4th thoracic vertebra, and the right rhomboideus major was from ligamentum nuchae of 5th cervical vertebra level to the spi-nous process of the 2nd thoracic vertebra. The left rhomboideus tertius arose from the spinous processes of the 4–5th thoracic vertebrae, and the right rhomboideus tertius arose from the spinous processes of the 2–5th thoracic vertebrae. RMj, rhomboideus major; Rmi, rhomboideus minor; RT, rhomboideus tertius; SPS, serratus posterior superior; LS, levator scapulae; C4, spinous process of 4th cervical vertebra; C7, spinous process of 7th cervical vertebra; T5, spinous process of 5th thoracic vertebra.
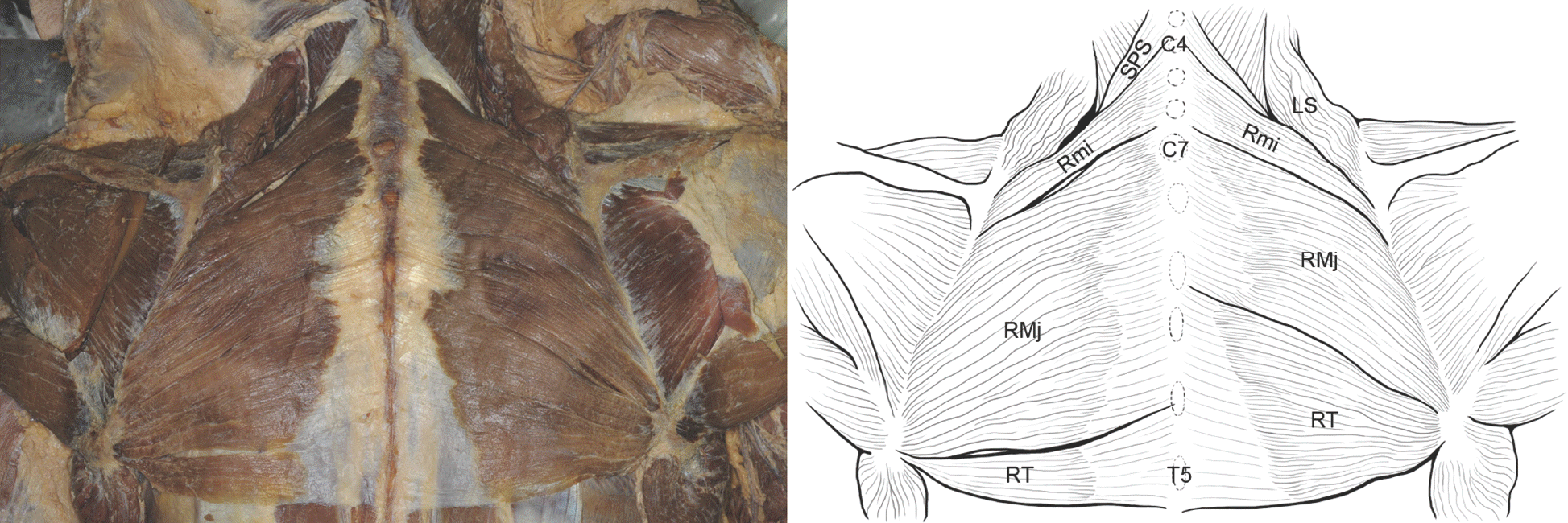
Fig. 2.
The rhomboid muscle group in non-human primate (A) and in human (B) (redrawn and modified from figure in Ref. 8). In primate, the rhomboideus muscles show extensive origins including skull and the entire cervical and thoracic vertebrae in contrast to human with limited origin. RO, rhomboideus occipitalis; RC, rhomboideus cervicis; RT, rhomboideus thoracis; Rmi, rhomboide-us minor, RMj; rhomboideus major.
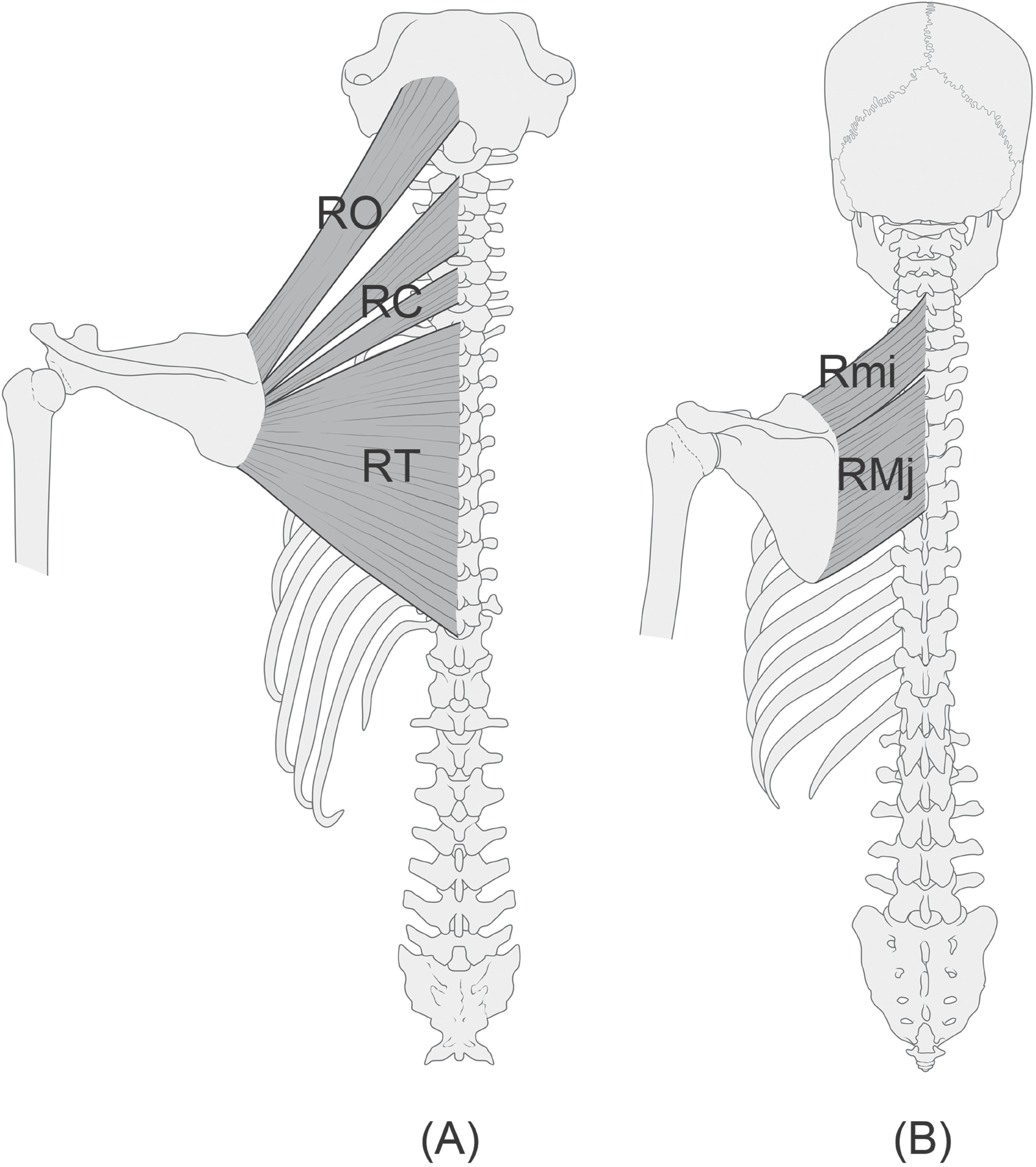
Table 1.
Measurement of rhomboid muscles
| Measurements | Rhomboideus minor | Rhomboideus major | Rhomboideus tertius | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left | Right | Left | Right | Left | Right | |
| Muscle width at origin (mm) | 32.58 | 31.64 | 136.46 | 59.78 | 25.13 | 90.50 |
| Muscle width at insertion (mm) | 18.34 | 11.14 | 98.27 | 84.77 | 4.46 | 10.14 |
| Muscle length of upper margin (mm) | 101.23 | 104.62 | 102.99 | 103.04 | 115.93 | 124.32 |
| Muscle length of lower margin (mm) | 100.64 | 99.95 | 117.35 | 128.76 | 116.69 | 107.66 |
| Muscle thickness∗ (mm) | 4.90 | 4.89 | 7.58 | 7.18 | 1.30 | 2.39 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download