Abstract
Modiolus is convergence of the facial muscles at the angle of the mouth, and its shape and size varying with individual, age, sex and ethnicity. In the previous study, the modiolus was usually located under the horizontal line at the mouth angle. In most medical schools, the cadavers are of later ages and their facial muscles have lost their elasticity as they got older. The purpose of this study is to identify the location of the modiolus in live young Korean and to compare it with that of Korean cadavers from the previous study. Participants were one hundred students of the catholic medical school with a mean age of 24 years. Experi-menter palpated the modiolus of each student with thumb and index finger. The average young live Korean modiolus was located at 14.4mm lateral to mouth angle and 1.6mm below the horizontal line of the mouth angle. Commonly, it is located below the mouth angle in 124 sides(62%). There was difference between horizontal distance of female and of male, and vertical distance of right and of left. The location of the modiouls was symmetric in 67%. These results were consistent with the previous study using Korean cadavers. Therefore these results suggest that the location of the modiolus is below to the mouth angle in large number of Koreans.
Go to : 
References
1. Chung IH, Oh CS, Han HS, Kim HJ. Human Anatomy. 5th ed.Seoul: Hyunmoon;2011. p. 550.
2. Berkovitz BKB, Moxham BJ. A textbook of head and neck anatomy. Chicago: Year Book Medical Publishers Inc.;1988. p. 157.
3. Williams PL, Bannister LH, Berry MM, Collins P, Dyson M, Dussek JE, et al. Gray's anatomy. 38th ed.New York: Churchill Livingstone;1995. p. 796–9.
4. Zufferey JA. Importance of the modiolus in plastic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002; 110:331–4.

5. Demiryurek D, Bayramoglu A, Erbil KM, Onderoglu S, Sargon MF, Aldur MM, et al. Three-dimensional structure of the modiolus. A computerized reconstruction study. Saudi Med J. 2003; 24:846–9.
6. Al-Hoqail RA, Abdel Meguid EM. An anatomical and analytical study of the modiolus: enlightening its relevance to plastic surgery. Aesth Plast Surg. 2009; 33:147–52.

7. Shimada K, Gasser RF. Variations in the facial muscles at the angle of the mouth. Clin Anatomy. 1989; 2:129–34.

8. Hu KS, Yang SJ, Kwak HH, Park HD, Youn KH, Jung HS, et al. Location of the modiolous and the morphologic variations of the risorius and zygomaticus major muscle related to the facial expression in Koreans. Korean J Phys Anthropol. 2005; 18:1–11. Korean.

9. Sato I, Ueno R, Sunohara M, Sato T. Quantitative morphology of dermal elastic fibers system of the human face durin g aging. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn. 1997; 74:65–73.
10. Yu SK, Lee MH, Kim HS, Park JT, Kim HJ, Kim HJ. Histo-morphologic approach for the modiolus with reference to reconstructive and aesthetic surgery. J Craniofac Surg. 2013; 24:1414–7.

11. Greyling LM, Meiring JH. Morphological study on the convergence of the facial muscles at the angle of the mouth. Acta Anat (Basel). 1992; 143:127–9.

12. Johnson PJ, Bajaj-Luthra A, Llull R, Johnson PC. Quantitative facial motion analysis after functional free muscle reanimation procedures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997; 100:1710–9.

13. Zufferey JA. Anatomical variations of the nasolabial fold. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1992; 89:225–31.
Go to : 
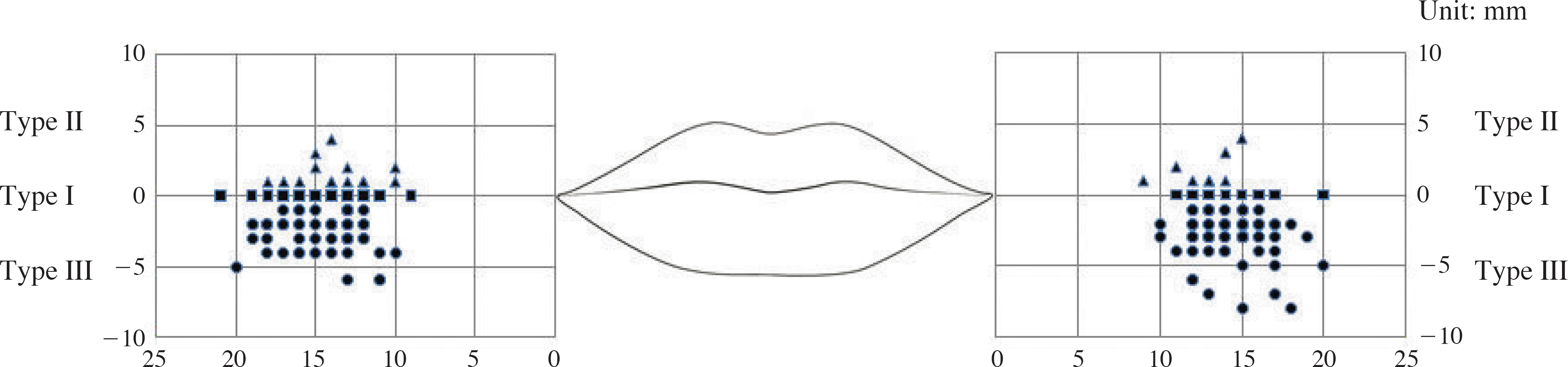 | Fig. 1.The location of the modiolus in living young Korean. Type I (�): modiolus is horizontal line to the mouth angle, Type II (▲): modiolus is above to the mouth angle, Type III(●): modiolus is below to the mouth angle. |
 | Fig. 2.The type of smile according to Rubin(1974). (A) “Mona Lisa” smile, (B) “canine” smile, (C) “full denture” smile. |
 | Fig. 3.The location change of the modiolus according to expression (sex: male, age: 23, (A) absence of expression, (B) pull the mouth angle up, (C) pull the mouth angle down (D) pull the mouth angle both side). |
Table 1.
The location of the modilous from the mouth angle in living Korean(mean±SD, unit: mm, ∗P⁄0.05)
| Horizontal distance | Vertical distance | |
|---|---|---|
| Male | 14.8±2.2∗ | –1.3±2.2 |
| Female | 13.8±2.2∗ | –1.9±1.7 |
| Right | 14.5±2.5 | –1.3±1.9∗ |
| Left | 14.4±2.1 | –1.9±2.1∗ |
| Total | 14.4±2.3 | –1.6±2.1 |
Table 2.
The type of location of the modiolus according to Shi-mada and Gasser method(1989)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download