Abstract
Background
Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP) is a major cause of community-acquired pneumonia in children. Currently, no study exists regarding the frequency of the mycoplasmal antibody on Jeju Island. The aim of the present study was to investigate the frequency of mycoplasmal antibody among children living on Jeju Island.
Methods
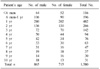
From March 2009 to February 2011, the frequency of mycoplasmal antibody among 1580 pediatric (<10 years old) patients who were tested for the mycoplasmal antibody titer in Cheju Halla Hospital were retrospectively investigated. The authors also analyzed the positive rates according to age, sex, and season.
Results
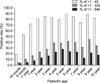
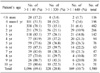
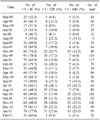
The frequency of mycoplasmal antibody titers were 69.4% for an antibody titer >1:40, 20.8% in an antibody titer >1:320, and 10.7% in an antibody titer >1:640. The positive rates of each antibody titer were lowest in children under the age of 6 months, and the positive rates increased gradually with age until 4 years, where the frequency showed a "plateau." There were minor cyclic increases of positive rate (>1:320, >1:640) every three months from August 2009 to June 2010, and there was a major increase of positive rate (>1:320, >1:640) from July 2010 to January 2011. However, there was no positive rate cyclic pattern of mycoplasmal antibody in the lower titer (>1:40) patients.
Conclusion
The frequency of mycoplasmal antibody titer is lowest under the age of 6 months. The positive rates rise gradually with age until the age of 4 years. The present study showed minor peaks of mycoplasmal antibody titer every three months and a major peak of mycoplasmal antibody titer. The results can be helpful for the interpretation and diagnosis of MP among pediatric patients on Jeju Island.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Hadi N, Kashef S, Moazzen M, Pour MS, Rezaei N. Survey of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in Iranian children with acute lower respiratory tract infections. Braz J Infect Dis. 2011. 15:97–101.
2. Yu J, Yoo Y, Kim DK, Kang H, Koh YY. Distributions of antibody titers to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in Korean children in 2000-2003. J Korean Med Sci. 2005. 20:542–547.
3. Kim JH, Chae SA, Lee DK. Clinical findings of Mycoplasma pneumonia in children, from 1998 to 2003. Korean J Pediatr. 2005. 48:969–975.
4. Kim JW, Seo HK, Yoo EG, Park SJ, Yoon SH, Jung HY, et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in Korean children, from 1979 to 2006-a meta-analysis. Korean J Pediatr. 2009. 52:315–323.
5. Kim SS, Kang H, Ahn BM, Lee WW, Kim ER, Kim SY, et al. Study of exchange phenomenon of mycoplasma pneumoniae in children from 1997-2002. Korean J Pediatr. 2004. 47:24–30.
6. Yoo SJ, Oh HJ, Shin BM. Evaluation of four commercial IgG- and IgM-specific enzyme immunoassays for detecting Mycoplasma pneumoniae antibody: comparison with particle agglutination assay. J Korean Med Sci. 2007. 22:795–801.
7. Bae SM, Jang MJ, Song HJ, Jeon DY, Kweon SS, Kang YH. Prevalence of mycoplasma pneumoniae antibodies in healthy residents of jeonnam province. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2007. 10:109–113.
8. Kim KW. Mycoplasma and chlamydia infection in Korea. Korean J Pediatr. 2009. 52:277–282.
9. Eun BW, Kim NH, Choi EH, Lee HJ. Mycoplasma pneumoniae in Korean children: the epidemiology of pneumonia over an 18-year period. J Infect. 2008. 56:326–331.
10. Hyun DS, Kwon WT. The study on the regional characteristics of climate change in Jeju Island. 2009. National institute of Meteorological Research, Korea meteorological administration.
11. Kasper DL, Braunwald E, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 2005. 16th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill companies;1008–1010.
12. Xu YC, Zhu LJ, Xu D, Tao XF, Li SX, Tang LF, et al. Epidemiological characteristics and meteorological factors of childhood Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in Hangzhou. World J Pediatr. 2011. 7:240–244.
13. Onozuka D, Hashizume M, Hagihara A. Impact of weather factors on Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Thorax. 2009. 64:507–511.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download