Abstract
Brevundimonas diminuta is a lactose non-fermenting Gram-negative rod associated with infection in immunocompromised patients. In three patients from two general wards, B. diminuta was isolated in blood culture sample. The clinical features of the patients did not coincide with the blood culture result, and pseudo-outbreak was suspected. These isolated were biochemically identified as Brevundimonas diminuta, and 16S rRNA sequencing confirmed their identification. The PFGE result showed a single pattern, and their clonality was assumed.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Lipuma JJ, Currie BJ, et al. Miscellaneous gram-negative bacteria. Murray PR, Baron EJ, editors. Manual of Clinical Microbiology. 9th ed.Washington DC: American Society for Microbiology;2006. p. 749–69.
2. Lee MR, Huang YT, Liao CH, Chuang TY, Lin CK, Lee SW, et al. Bacteremia caused by Brevundimonas species at a tertiary care hospital in Taiwan, 2000-2010. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis.http://www.springerlink.com/content/ht12661xw20u4251/fulltext.pdf. [Online] (last visited on April 2011).
3. Yang ML, Chen YH, Chen TC, Lin WR, Lin CY, Lu PL. Case report: infective endocarditis caused by Brevundimonas vesicularis. BMC Infect Dis. 2006; 6:179.

4. Sofer Y, Zmira S, Amir J. Brevundimonas vesicularis septic arthritis in an immunocompetent child. Eur J Pediatr. 2007; 166:77–8.

5. Kwak SD, Choi SY, Park JY, Yim JK, Chun JH, Kim TW, et al. A case of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis peritonitis due to Brevundimonas vesicularis. Korean J Nephrol. 2009; 28:365–9.
6. Han XY and Andrade RA. Brevundimonas diminuta infections and its resistance to fluoroquinolones. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005; 55:853–9.
Go to : 
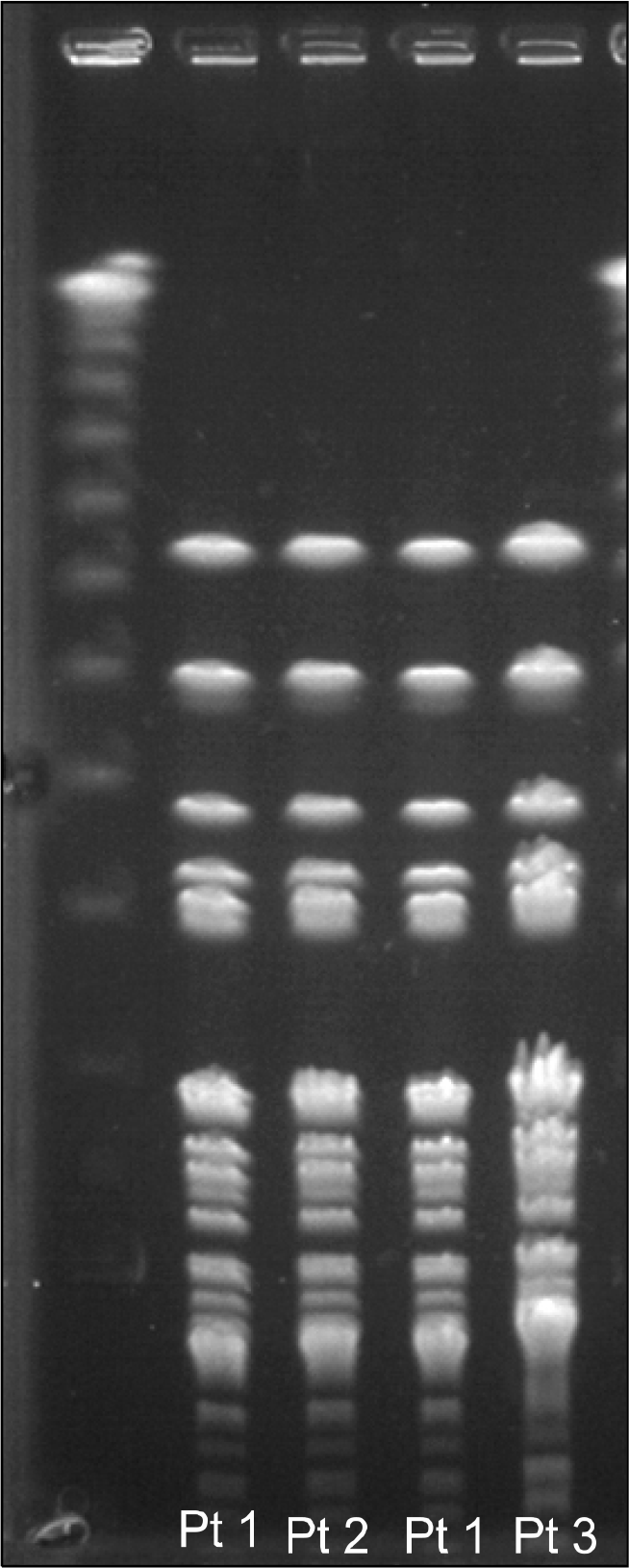 | Fig. 1.Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) patterns of Brevundimonas diminuta isolates. |
Table 1.
Description of cases




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download