Abstract
We report a rare case of fungemia due to Exophiala (Wangiella) dermatitidis in a 4-month-old female infant who was admitted to an intensive care unit with sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). E. dermatiti-diswas repeatedly isolated from blood cultures (on the 28th and 32nd day of hospitalization) of the patient, who died on the 44th day of hospitalization. The fungus was identified by its morphological characteristics and DNA sequencing of both the D1/D2 domain and the ITS region of rDNA. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of E. dermatitidis fungemia in Korea.
REFERENCES
1. Nachman S, Alpan O, Malowitz R, Spitzer ED. Catheter-associated fungemia due to Wangiella (Exophiala) dermatitidis. J Clin Microbiol. 1996; 34:1011–3.

2. Hohl PE, Holley HP Jr, Prevost E, Ajello L, Padhye AA. Infections due to Wangiella dermatitidis in humans: report of the first documented case from the United States and a review of the literature. Rev Infect Dis. 1983; 5:854–64.

3. Vlassopoulos D, Kouppari G, Arvanitis D, Papaefstathiou K, Dounavis A, Velegraki A, et al. Wangiella dermatitidis peritonitis in a CAPD patient. Perit Dial Int. 2001; 21:96–7.

4. Chang CL, Kim DS, Park DJ, Kim HJ, Lee CH, Shin JH. Acute cerebral phaeohyphomycosis due to Wangiella dermatitidis accompanied by cerebrospinal fluid eosinophilia. J Clin Microbiol. 2000; 38:1965–6.
5. Kim DS, Yoon YM, Kim SW. Phaeohyphomycosis due to Exophiala dermatitidis successfully treated with itraconazole. Korean J Med Mycol. 1999; 4:79–83.
6. Hong KH, Kim JW, Jang SJ, Yu E, Kim EC. Liver cirrhosis caused by Exophiala dermatitidis. J Med Microbiol. 2009; 58:674–7.

7. Sugita T, Nishikawa A, Ikeda R, Shinoda T. Identification of medically relevant Trichosporon species based on sequences of internal transcribed spacer regions and construction of a database for Trichosporon identification. J Clin Microbiol. 1999; 37:1985–93.
8. Kurtzman CP and Robnett CJ. Identification of clinically important ascomycetous yeasts based on nucleotide divergence in the 5' end of the large-subunit (26S) ribosomal DNA gene. J Clin Microbiol. 1997; 35:1216–23.

9. Untereiner WA. Fruiting studies in species of Capronia (Herpo- trichiellaceae). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1995; 68:3–17.
10. Al-Obaid I, Ahmad S, Khan ZU, Dinesh B, Hejab HM. Catheter-associated fungemia due to Exophiala oligosperma in a leukemic child and review of fungemia cases caused by Exophiala species. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2006; 25:729–32.

11. Lim WH, Shin JH, Suh SP, Ryang DW. Diagnosis of central venous catheter-related sepsis using differential quantitative blood cultures. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1998; 18:208–14.
12. de Hoog GS, Matos T, Sudhadham M, Luijsterburg KF, Haase G. Intestinal prevalence of the neurotropic black yeast Exophiala (Wangiella) dermatitidis in healthy and impaired individuals. Mycoses. 2005; 48:142–5.

13. Woollons A, Darley CR, Pandian S, Arnstein P, Blackee J, Paul J. Phaeohyphomycosis caused by Exophiala dermatitidis following intra-articular steroid injection. Br J Dermatol. 1996; 135:475–7.

14. de Hoog GS and Vitale RG. Bipolaris, Exophiala, Scedosporium, Sporothriz, and Other Dematiaceous Fungi. Murray PR, Baron EJ, Jeorgensen JH, Landry ML, Pfaller MA, editors. Manual of Clinical Microbiology. 9th ed.Washington D.C.: ASM Press;2006. p. 1898–917.
15. Petti CA. Detection and identification of microorganisms by gene amplification and sequencing. Clin Infect Dis. 2007; 44:1108–14.
Fig. 1.
Two weeks after incubation at 30°C on the potato dextrose agar, the colonies appeared as black, reverse black, wet, and mucoid.
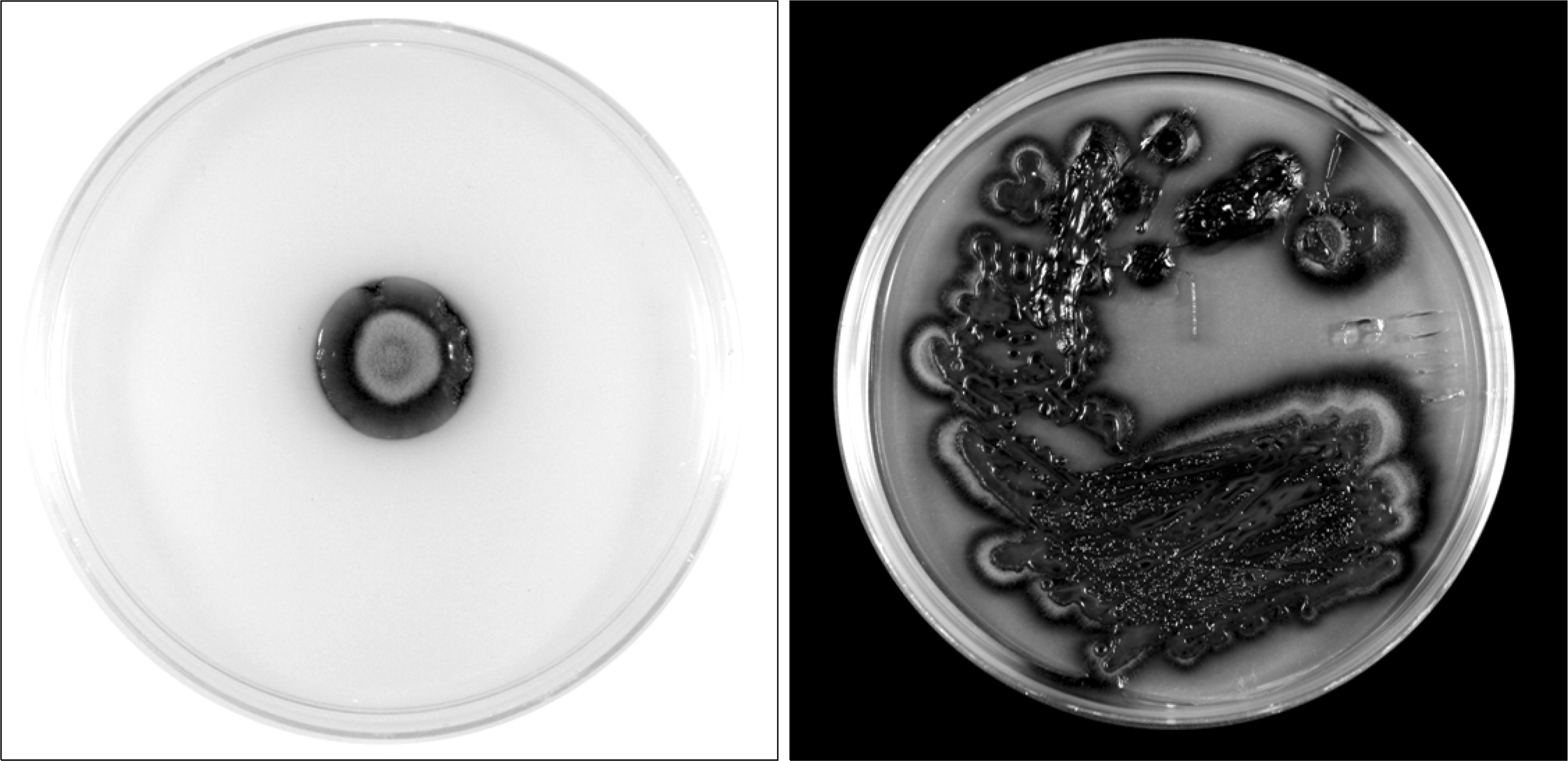
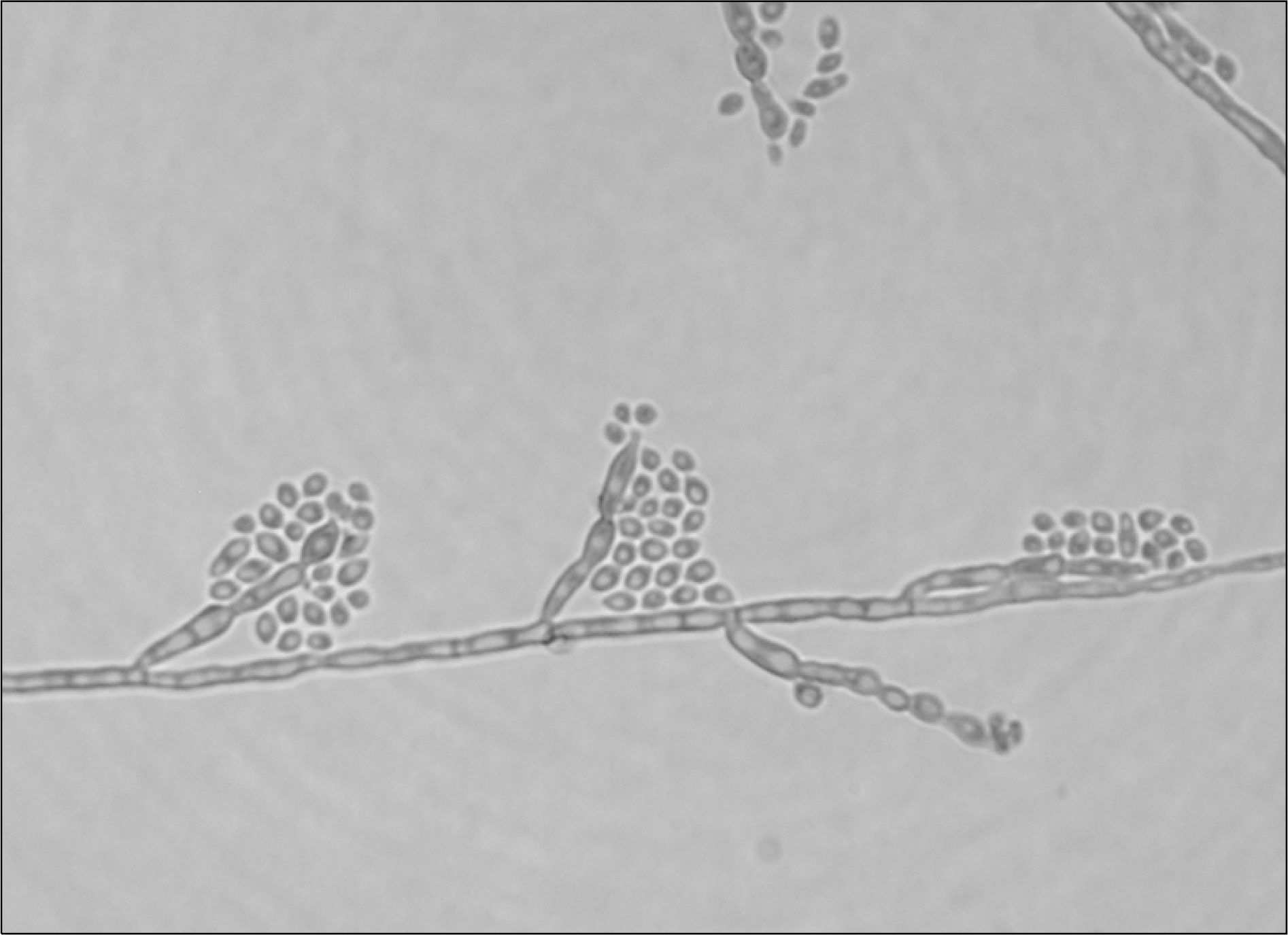
Fig. 2.
Microscopically, septate, and pale olivaceous hyphae and black yeast synanarmorphs were found. Conidiogenous cells were cylindrical, with rounded apeces producing one-celled conidia. Round to ovoid, pale brown conidia accumulated in balls or slipped down the side of conidiophores (Lactophenol cotton blue stain, ×400).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download