Abstract
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a typical pathogen of nosocomial infection, and has recently emerged as an important community-acquired pathogen. MRSA is notorious as a multidrug-resistant organism. Its resistance to all β-lactams is mediated by PBP2a which is encoded by mecA, and it is also resistant to many antimicrobials of other classes due to frequently co-carrying resistance genes, which accounts for becoming a clinical and laboratory issue. This article reviews the microbiological characteristics, surveillance methods, and molecular epidemiology of MRSA.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; Nineteenth informational supplement. CLSI document M100-S19; Philadelphia, CLSI. 2009.
2. Lee H, Kim CK, Lee J, Lee SH, Ahn JY, Hong SG, et al. Antimicrobial resistance of clinically important bacteria isolated from 12 hospitals in Korea in 2005 and 2006. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2007; 10:59–69.
3. Lee H, Yong D, Lee K, Hong SG, Kim EC, Jeong SH, et al. Antimicrobial resistance of clinically important bacteria from 12 hospitals in Korea in 2004. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 8:66–73.
4. Livermore DM. Antibiotic resistance in staphylococci. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2000; 16(Suppl 1):S3–10.

5. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically; Approved standard-eighth edition. CLSI document M7-A8; Philadelphia, CLSI. 2008.
6. Lee Y, Kim CK, Kim M, Yong D, Lee K, Chong Y. Detection of mecA in strains with oxacillin and cefoxitin disk tests for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus. Korean J Lab Med. 2007; 27:276–80.

7. Kim JS, Kim HS, Song W, Cho HC, Lee KM, Kim EC. Antimicrobial resistance profiles of Staphylococcus aureus isolated in 13 Korean hospitals. Korean J Lab Med. 2004; 24:223–9.
8. Kim HB, Jang HC, Nam HJ, Lee YS, Kim BS, Park WB, et al. In vitro activities of 28 antimicrobial agents against Staphylococcus aureus isolates from tertiary-care hospitals in Korea: a nationwide survey. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004; 48:1124–7.
9. Kim EC, Jung HJ, Oh MD, Lee HJ, Oh HS, Choe KW. Epidemiological typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus outbreak isolates by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and antibiogram. Yonsei Med J. 1998; 39:587–94.
10. Kim HB, Lee YS, Kim BS, Cha JO, Kwon SU, Lee HJ, et al. Prevalence and clinical implications of Staphylococcus aureus with a vancomycin MIC of 4 microg/ml in Korea. Microb Drug Resist. 2006; 12:33–8.
11. 질병관리본부. 2008년 반코마이신내성 황색포도상구균(VRSA) 실 험실 표본감시. VRSA Newsletter. 2008.
12. Kim HB, Shin DH, Park KU, Oh MD, Kim EC, Choe KW. The methicillin-resistance rate of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from anterior nares of healthy adults in the community. Korean J Infect Dis. 1998; 30:527–31.
13. Oh HS, Lee SE, Kim EC, Lee HJ, Oh MD, Choe KW. Health care workers' nasal carriage and outbreak control of epidemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Korean J Infect Dis. 2001; 33:194–201.
14. Davis KA, Stewart JJ, Crouch HK, Florez CE, Hospenthal DR. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) nares colonization at hospital admission and its effect on subsequent MRSA infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2004; 39:776–82.

15. Desai D, Desai N, Nightingale P, Elliott T, Neuberger J. Carriage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is associated with an increased risk of infection after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2003; 9:754–9.

16. Garrouste-Orgeas M, Timsit JF, Kallel H, Ben Ali A, Dumay MF, Paoli B, et al. Colonization with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in ICU patients: morbidity, mortality, and glycopeptide use. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2001; 22:687–92.

17. Harbarth S, Fankhauser C, Schrenzel J, Christenson J, Gervaz P, Bandiera-Clere C, et al. Universal screening for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus at hospital admission and nosocomial infection in surgical patients. J Am Med Assoc. 2008; 299:1149–57.
18. Harbarth S, Masuet-Aumatell C, Schrenzel J, Francois P, Akakpo C, Renzi G, et al. Evaluation of rapid screening and pre-emptive contact isolation for detecting and controlling methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in critical care: an interventional cohort study. Crit Care. 2006; 10:R25.
19. Robicsek A, Beaumont JL, Paule SM, Hacek DM, Thomson RB Jr, Kaul KL, et al. Universal surveillance for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in 3 affiliated hospitals. Ann Intern Med. 2008; 148:409–18.

21. Bohach G. Staphylococcus aureus Exotoxins. Fischetti VA, Novick RP, Ferratti JJ, Portnoy DA, Rood JI, editors. Gram-positive Pathogens. 2nd ed.Washington, D.C.: ASM Press;2006. p. 464–77.

22. Kim JS, Song W, Kim HS, Cho HC, Lee KM, Choi MS, et al. Association between the methicillin resistance of clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus, their staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) subtype classification, and their toxin gene profiles. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2006; 56:289–95.

23. Kim JS, Kim HS, Song W, Cho HC, Lee KM, Kim EC. Molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates with toxic shock syndrome toxin and staphylococcal enterotoxin C genes. Korean J Lab Med. 2007; 27:118–23.

24. Kim ES, Song JS, Lee HJ, Choe PG, Park KH, Cho JH, et al. A survey of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Korea. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007; 60:1108–14.

25. Kim JS, Park JS, Song W, Kim HS, Cho HC, Lee KM, et al. Panton-Valentine leukocidin positive Staphylococcus aureus isolated from blood in Korea. Korean J Lab Med. 2007; 27:286–91.

26. Wang R, Braughton KR, Kretschmer D, Bach TL, Queck SY, Li M, et al. Identification of novel cytolytic peptides as key virulence determinants for community-associated MRSA. Nature Med. 2007; 13:1510–4.

27. Suzuki, Kato, Owada, Hayakawa, Terada. Genetic heterogeneity of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Jpn Soc Clin Microbiol. 2007; 17:115.
28. 식품의약품안전청. PFGE 검사매뉴얼. 2007.
29. 이경원, 정윤섭, 용동은, 염종화, 정소영. 항균제 내성 진화와 다약 제 내성 세균의 확산. 서울, 서흥출판사;. 2006. 213–42.
30. Huh JY, Yi J, Hong KH, Kim EC. Multilocus sequence typing of clonal changes of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from intensive care unit patients: 1996 versus 2004. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2006; 9:84–9.
31. Cha HY, Moon DC, Choi CH, Oh JY, Jeong YS, Lee YC, et al. Prevalence of the ST230 clone of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and differences in antimicrobial susceptibilities of ST239 and ST5 clones identified in a Korean hospital. J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 43:3610–4.
32. Enright MC, Robinson DA, Randle G, Feil EJ, Grundmann H, Spratt BG. The evolutionary history of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002; 99:7687–92.

33. Shopsin B, Gomez M, Montgomery SO, Smith DH, Waddington M, Dodgw DE, et al. Evaluation of protein A gene polymorphic region DNA sequencing for typing of Staphylococcus aureus strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1999; 37:3556–63.
34. Cookson BD, Robinson DA, Monk AB, Murchan S, de Deplano A, Ryck R, et al. Evaluation of molecular typing methods in characterizing a European collection of epidemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains: the HARMONY collection. J Clin Microbiol. 2007; 45:1830–7.
Go to : 
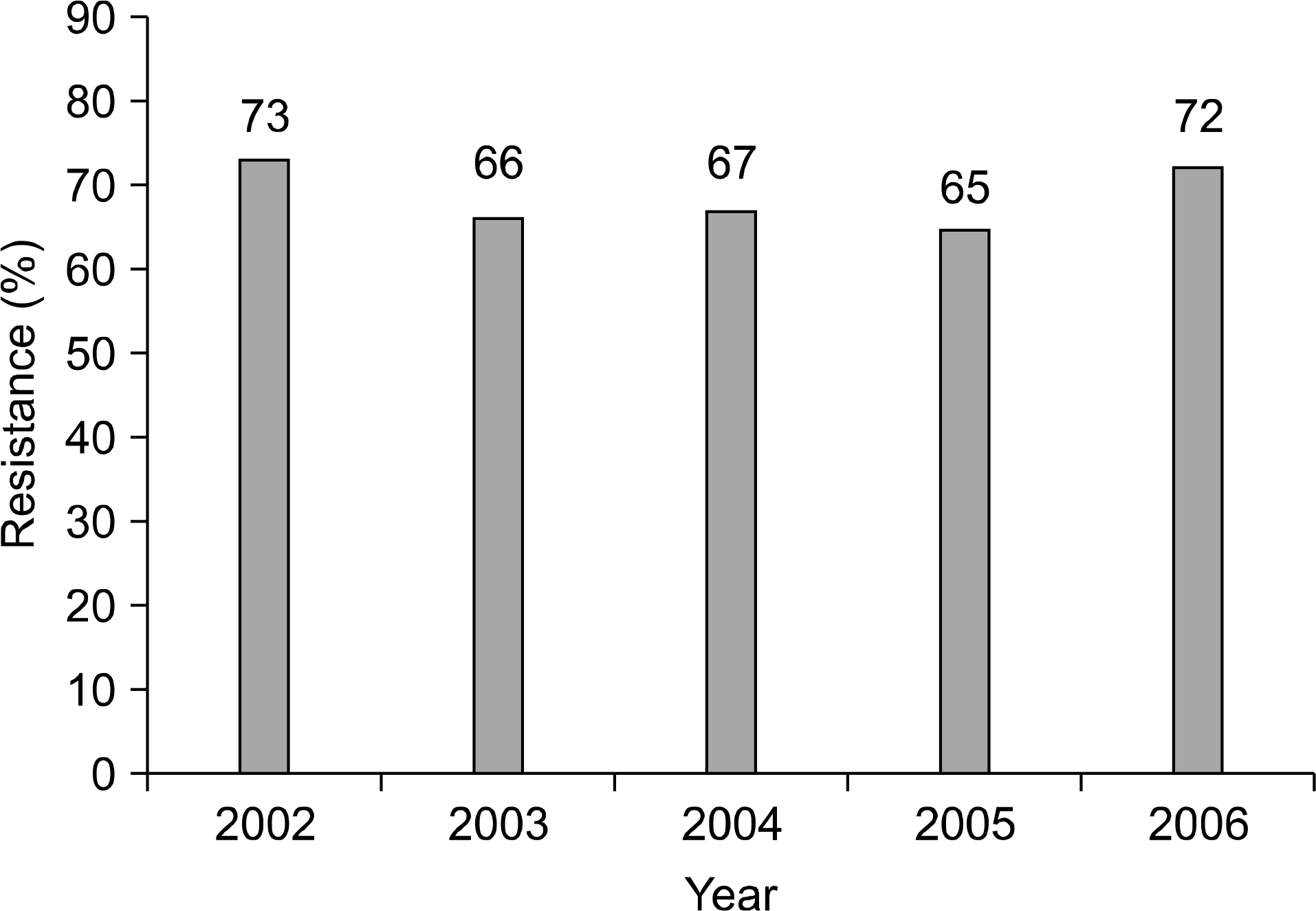 | Fig. 1.Yearly oxacillin resistance of S. aureus isolated from 12 hospitals in Korea during the period from 2002 to 2006. |
Table 1.
Staphylococcus aureus exotoxins and genetic loci
Table 2.
Characteristics of CA-MRSA versus HA-MRSA




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download