Abstract
Background
Serologic tests for specific antibody nowadays are widely employed for the diagnosis of parasitic diseases. Recently, an increasing numbers of kits have adopted enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the detection of parasitic antibodies. In this study, we evaluated two ELISA reagents for the diagnosis of parasitic diseases.
Methods
A total of 553 serum and 156 CSF samples were assayed using an in-house micro-ELISA and GenediaⓇ Ab ELISA (Green cross PBM, Korea) for Cysticercus, Paragonimus westermani, Clonorchis sinensis, and Sparganum. We reviewed the medical records of all patients. The results from GenediaⓇ Ab ELISA kit were compared with those from the in-house micro-ELISA method.
Results
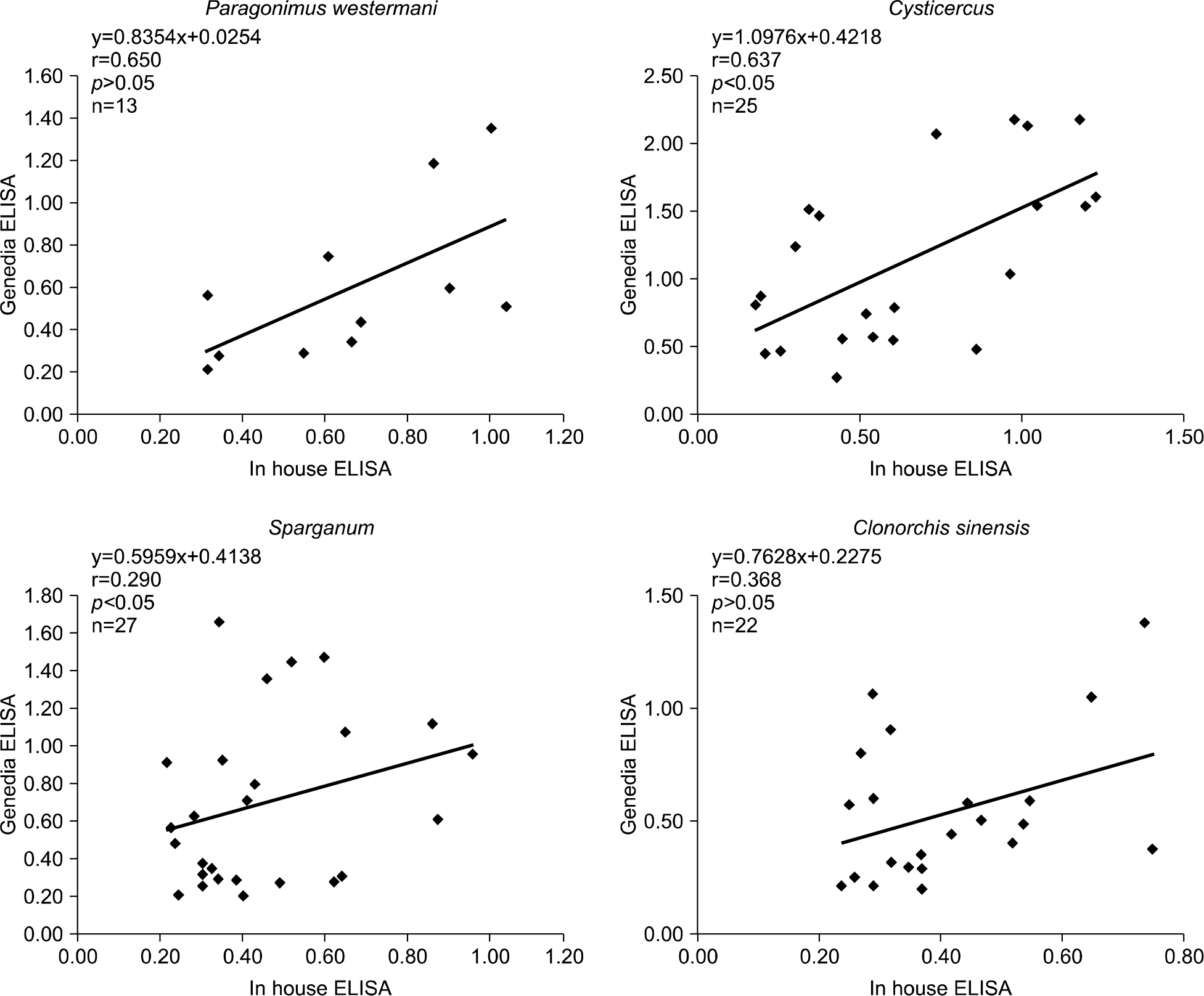
The overall concordance rate between the two ELISA tests was 95.5%. When compared with the clinical information, the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of the in-house micro-ELISA were 100%, 99.0∼99.6%, 82.4∼96.4%, and 100%, and the respective figures for GenediaⓇ Ab ELISA kit were 92.9∼100%, 88.0∼ 97.3%, 41.7∼50%, and 99.9∼100% with kappa agreement of 0.53–0.63. Comparison of two ELISA methods showed a significant difference (P<0.05). Retesting of 85 discordant samples showed that the concordance rate of the in-house ELISA was 97.7% and that of GenediaⓇ Ab ELISA was 28.2%.
Go to : 
References
1. Ministry of Health and Welfare and Korea Association of Health. Prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections in Korea-The sixth Report. 1997.
2. Kim SH, Chung JY, Bae YA, Cai GB, Na BK, Kim NJ, et al. Functional identification of a protein inhibitor of neuronal nitric oxide synthase of Taenia solium metacestode. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2007; 151:41–51.

3. Na BK, Kim SH, Lee EG, Kim TS, Bae YA, Kang I, et al. Critical roles for excretory-secretory cysteine proteases during tissue invasion of Paragonimus westermani newly excysted metacercariae. Cell Microbiol. 2006; 8:1034–46.

4. Chang KH, Cha SH, Han MH, Kim HD, Cho SY, Kong Y, et al. An imaging diagnosis of cerebral paragonimiasis: CT and MR findings and correlation with ELISA antibody test. J Korean Radiol Soc. 1993; 29:345–54.

5. Cho SY, Kim SI, Kang SY, Choi DY, Suk JS, Choi KS, et al. Evaluation of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay in serological diagnosis of human neurocysticercosis using paired samples of serum and cerebrospinal fluid. Korean J Parasitol. 1986; 24:25–41.
6. Tsang VC, Brand JA, Boyer AE. An enzyme-linked immunoe-lectrotransfer blot assay and glycoprotein antigens for diagnosing human cysticercosis (Taenia solium). J Infect Dis. 1989; 159:50–9.

7. Hong ST. Changes of anti-Clonorchis sinensis IgG antibody in serum after praziquantel treatment in human clonorchiasis. Korean J Parasitol. 1988; 26:1–8.

8. Ishida MM, Peralta RH, Livramento JA, Hoshini-shimizu S, Peralita JM, Vaz AJ. Serodiagnosis of neurocysticercosis in patients with epileptic seizure using ELISA and immunoblot assay. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2006; 48:343–6.

9. Cho SY, Hong ST, Rho YH, Choi SY, Han YC. Application of micro ELISA in serodiagnosis of Human paragonimiasis. Korean J Parasitol. 1981; 19:151–6.
10. Kim H, Kim SI, Cho SY. Serological Diagnosis of Human Sparganosis by means of micro-ELISA. Korean J Parasitol. 1984; 22:222–8.

11. Lee YK, Ryu JS, Lee KT, Im KI. Comparison of TIA with ELISA for circulating antibody detection in clonorchiasis. Korean J Parasitol. 1983; 21:265–9.

12. Maclure M and Willett WC. Misinterpretation and misuse of the Kappa statistic. Am J Epidemiol. 1987; 126:161–9.
13. Jekel JF, Elmore JG, Katz DL. Epidemiology, Biostatistics and Preventive Medicine. Philadelphia; W.B. Saunders Company. 2006. 96–7.
14. Shin BM and Choi KI. Diagnostic significance of intradermal test compared with radiologic findings for clonorchiasis. Korean J Clin Pathol. 2000; 20:81–6.
15. Kim SI. Immune reactions between excretory-secretory antigens and specific antibodies of Clonorchis sinensis before and after praziquantel treatment in experimentally infected rabbits. Korean J Parasitol. 1994; 32:35–42.

16. Cho SY, Kim SI, Kang SY, Kong Y, Han SK, Shim YS, et al. Antibody changes in paragonimiasis patients after preziquantel treatment as observed by ELISA and immunoblot. Korean J Parasitol. 1989; 27:15–21.
17. Lee SH, Kim MN, Back BY, Choi JY, Kim TH, Hwang YS. Analysis of parasite-specific antibody positive patients for Clonorchis sinensis, Paragonimus westermani, Cysticercus and Sparganum using ELISA. Korean J Lab Med. 2003; 23:126–31.
18. Soh CT, Min DY, Ryu JS, Yong TS. Study on the reproducibility of ELISA technique for the diagnosis of clonorchiasis and paragonimiasis. Yonsei Rep Trop Med. 1985; 16:1–10.
19. Detrick B, Hamilton RG, Folds JD. eds. Manual of Molecular and clinical laboratory immunology. 7th ed.Washington D. C.: American Society for Microbiology;2006. p. 561–4.
20. Choi SH, Kang SY, Kong Y, Cho SY. Antigenic protein fractions reacting with sera of sparganosis patients. Korean J Parasitol. 1988; 26:163–7.

21. Lee JH, Kong Y, Ryu JY, Cho SY. Applicability of ABC-ELISA and protein A-ELISA in serological diagnosis of cysticercosis. Korean J Parasitol. 1993; 31:49–56.

22. Reed SG, Shreffler WG, Burns JM, Scott JM Jr, Orge Mda G, Ghalib HW, et al. An improved serodiagnostic procedure for visceral leishmaniasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1990; 43:632–9.

23. Odashima NS, Takayanagui OM, Figueiredo JF. Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of IgG, IgM, IgE and IgA against cysticersus cellulosae in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neurocysticercosis. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2002; 60:400–5.
Go to : 
Table 1.
Procedures and conditions of 2 different ELISAs employed in this study
Table 2.
Comparison of in-house ELISA and Genedia ELISA by kappa agreement and McNemar test
Table 3.
Clinical information on the discrepancy between in-house ELISA and Genedia ELISA
Table 4.
Diagnostic performances (sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values) of Genedia ELISA and in-house ELISA




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download