Abstract
Background
The referral hospital is somewhat isolated from the mainland due to its island status; thus, microorganisms isolated from blood cultures might have a distinct pattern in their frequency and anti-biogram. We attempted to uncover these characteristics.
Methods
The isolates from blood cultures at the Cheju University Hospital during 2003∼2007 were analysed. After inoculation in aerobic and anaerobic bottles, blood specimens were cultured using BacT/ Alert system, and the isolates were identifieded and antimicrobial susceptibilities were tested using Vitek II system.
Results
The overall positive rate of blood cultures was 9.6% and contamination rate was 3.6%. The most commonly isolated pathogens were Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Gram positive rod, gram negative cocci, and anaerobes were not isolated, but fungi were isolated in 0.6% of blood cultures. The prevalence of methi-cillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) was 68.0% in 2003, 41.4% in 2004, 48.1% in 2005, 54.5% in 2006, and 65.2% in 2007. The prevalence of vancomycin-resistant enterococcus (VRE) was 0% in 2003 and 2004, 16.7% in 2005, 10.0% in 2006, and 9.5% in 2007.
Conclusion
The most commonly isolated pathogens were similar to those from other hospitals, but the isolation rates of MRSA and VRE by year showed different patterns. Also, gram positive rods, gram negative cocci and anaerobes were not isolated. To help the choice of empirical antibiotic treatments, we need complementary measures to upgrade microorganism isolation systems and further studies in-cluding the monitoring of antibiotic use.
Go to : 
References
1. Bryan CS. Clinical implications of positive cultures. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989; 2:329–53.
2. Lee GI, Hong KS, Kim OK. Results of blood cultures at Ewha Womans' University Hospital in Recent 5 years. Korean J Lab Med. 1988; 8:169–75.
3. Ahn GY, Jang SJ, Lee SH, Jeong OY, Chaulagain BP, Moon DS, et al. Trends of the species and antimicrobial susceptibility of microorganisms isolated from blood cultures of patients. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2006; 9:42–50.
4. Koh EM, Lee SG, Kim CK, Kim M, Yong D, Lee K, et al. Microorganisms isolated from blood cultures and their antimicrobial susceptibility patterns at a university hospital during 1994–2003. Korean J Lab Med. 2007; 27:265–75.

5. National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System. National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance (NNIS) System Report, data summary from January 1992 through June 2004, issued October 2004. Am J Infect Control. 2004; 32:470–85.
6. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; tenth informational supplement M 100-S10. Wayne, PA; National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. 2005.
7. Kim HO, Kang CG, Chong YS, Lee SY. Organisms isolated from blood at the Yonsei medical center. 1974–1983. Infect Chemother. 1985; 17:15–32.
8. Kim HK, Lee KW, Chong YS, Kwon OH, Kim JM, Kim DS. Blood culture results at the Severance Hospital during 1984–1993. Infect Chemother. 1996; 28:151–66.
9. Mylotte JM and Tayara A. Blood cultures: clinical aspects and controversies. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000; 19:157–63.
11. Edmond MB, Wallace SE, McClish DK, Pfaller MA, Jones RN, Wenzel RP. Nosocomial bloodstrem infections in United States hospitals: a three-year analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 1999; 29:239–44.
13. Kim KA, Shin SM, Moon HG, Park YH. Causative organisms of neonatal sepsis. Yeungnam Univ J Med. 1999; 16:60–8.

14. Orrett FA and Changoor E. Bacteremia in children at a regional hospital in Trinidad. Int J Infect Dis. 2007; 11:145–51.
15. Uh Y, Lee HH, Lee KW, Chong YS. The species and antimicrobial susceptibility of microorganisms isolated from blood cultures of patients. J Korean Soc Microbiol. 1991; 26:417–30.
16. Leclercq R, Derlot E, Duval J, Courvalin P. Plasmid-mediated resistance to vancomycin and teicoplanin in Enterococcus faecium. N Engl J Med. 1988; 319:157–61.

17. Hong SG, Kim S, Jeong SH, Chang CL, Cho SR, Ahn JY, et al. Prevlence and diversity of extended-spectrum β-lactamase -producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in Korea. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2003; 6:149–55.
Go to : 
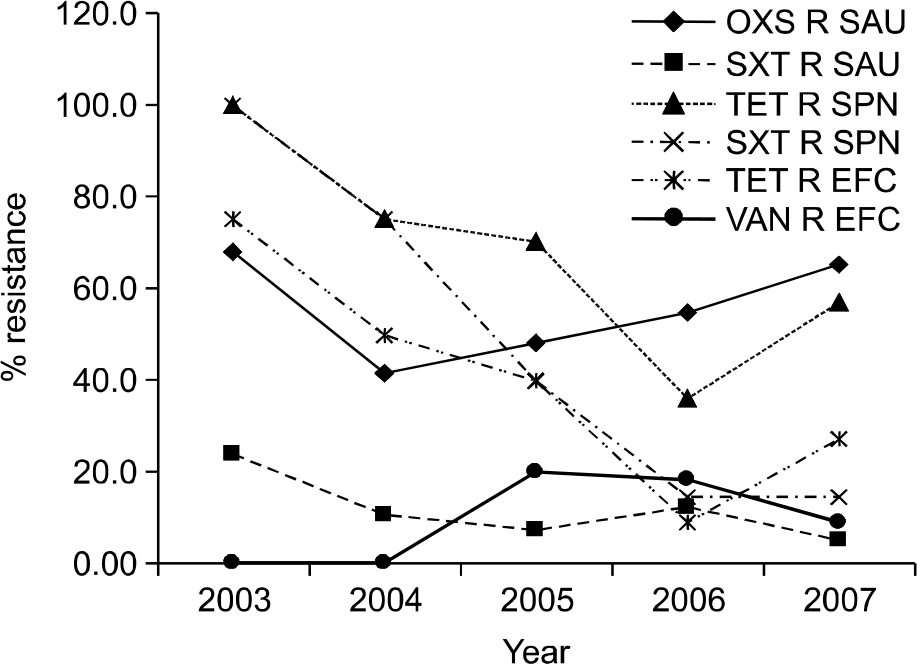 | Fig. 1.Trend of antimicrobial resistance of S. aureus, S. pneumoniae and E. faecalis by year. Abbreviations: OXS R SAU, oxacillin-resistant S. aureus; SXT SAU, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole-resistant S. aureus; TET R SPN, tetracycline-resistant S. pneumoniae; SXT R SPN, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole-resistant S. pneumoniae; TET R EFC, tetracycline-resistant E. faecalis; VAN R EFC, vancomycin-resistant E. faecalis. |
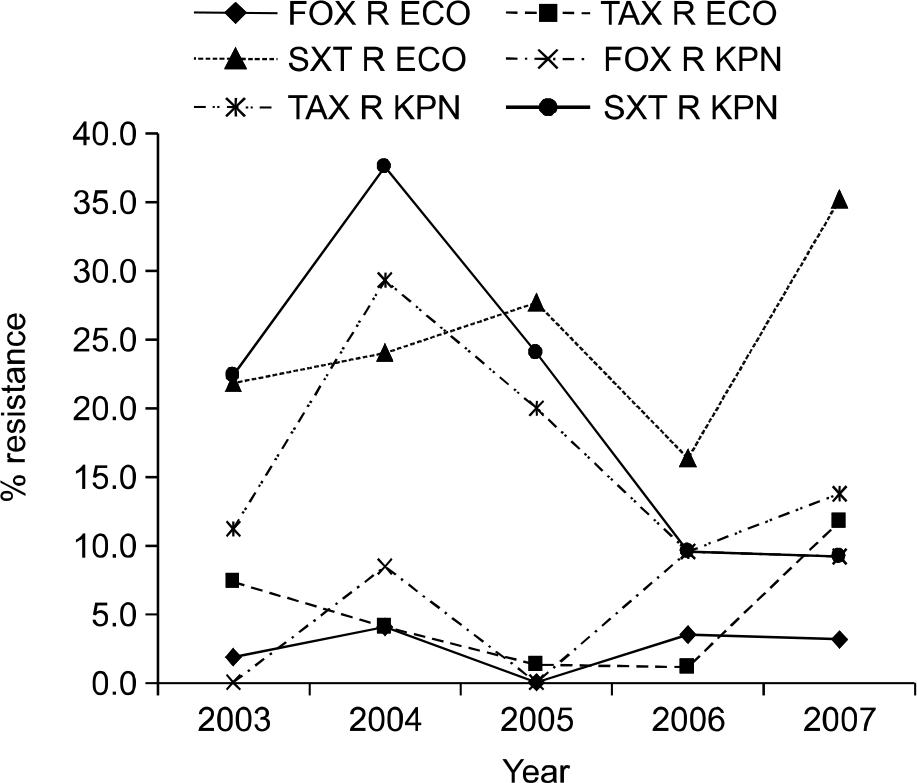 | Fig. 2.Trend of antimicrobial resistance of E. coli and K. pneumoniae by year. Abbreviations: FOX R ECO, cefoxitin-resistant E. coli; TAX R ECO, cefotaxime-resistant E. coli; SXT R ECO, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole-resistant E. coli; FOX R KPN, cefoxitin-resistant K. pneumoniae; TAX R KPN, cefotaxime-resistant K. pneumoniae; SXT R KPN, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole-resistant K. pneumoniae. |
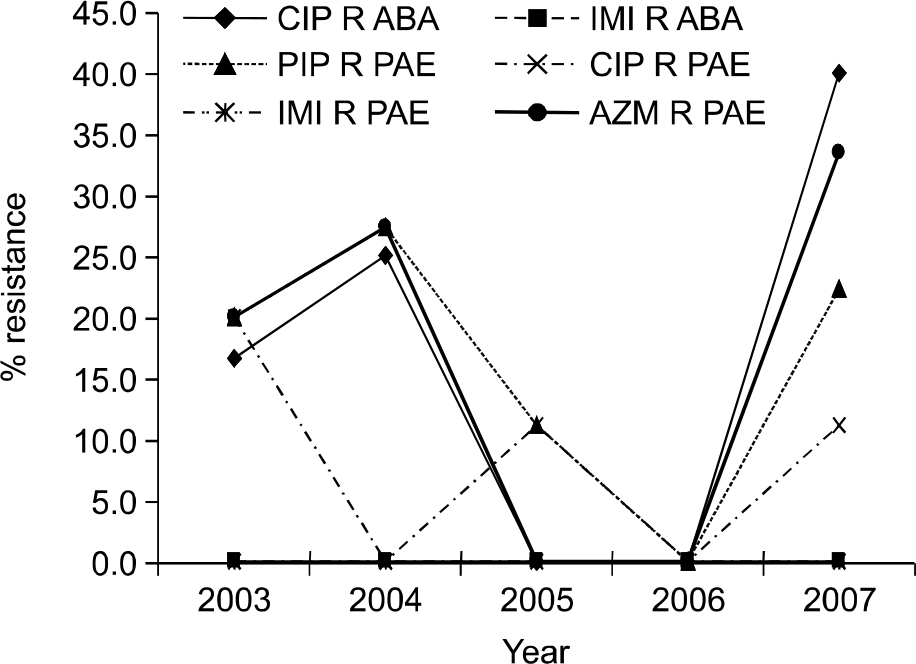 | Fig. 3.Trend of antimicrobial resistance of A. baumannii and P. aeruginosa by year. Abbreviations: CIP R ABA, ciprofloxacin-resistant A. baumannii; IMI R ABA, imipenem-resistant A. baumannii; PIP R PAE, piperacillin-resistant P. aeruginosa; CIP R PAE, ciprofloxacin-resistant P. aeruginosa; IMI R PAE, imipenem-resistant P. aeruginosa; AZM R PAE, aztreonam-resistant P. aeruginosa. |
Table 1.
Microorganisms isolated from blood in an island region during 2003∼2007
Table 2.
Species of aerobic gram-positive cocci, bacilli and gram-negative cocci from blood in an island region during 2003∼2007
Table 3.
Species of aerobic and facultative anaerobic gram-negative bacilli from blood in an island region during 2003∼2007
Table 4.
Species of glucose-nonfermenting gram-negative bacilli solated from blood in an island region during 2003∼2007
Table 5.
Species of fungi isolated from blood in an island region during 2003∼2007
Table 6.
Annual isolation rate of relatively common bacteria isolated from blood in an island region during 2003∼2007
Table 7.
Distribution of relatively common bacteria isolated from blood in an island region by age group of patients
Table 8.
Association between the number of blood culture and blood culture-positive patients and CNS and BCP isolated from blood




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download