Abstract
The management of infected nonunion is based on a detailed evaluation of patients, the involved bone and soft tissues, stability of fixation, and type of bacterial pathogens. Preoperative surgical planning and strategies for each step is mandatory for the successful treatment of infected nonunion. The radical debridement of infected tissues, including the unstable implant, is one of the most important procedures. Adequate soft tissue coverage should be considered for the appropriate management of infection; a reconstructive procedure and stable skeletal stabilization by internal or external fixation is also necessary later. A restoration of bone defects and bony union can be accomplished with bone grafting, distraction osteogenesis, vascularized fibular grafting, and induced membrane technique.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
A 33-year-old male suffered from open femoral shaft fracture associated with complete femoral artery (arrow).
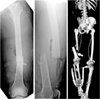
Fig. 2
(A) A temporary external fixation was carried out after wound debridement and vascular reconstruction. (B) External fixation was converted to bridging-plate fixation after soft tissue healing.
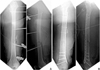
Fig. 3
(A) Plain X-ray taken 6 months after the injury shows delayed healing of the fracture without implant loosening. Tissue biopsy from the nonunion site revealed an infection, but there was no significant instability of the fracture, and infection was localized around the fracture site. After meticulous debridement of the infected tissue, autogenous cancellous bone graft and plate augmentation was performed. (B) Plain X-ray taken 12 months after revision surgery shows a solid bony union without recurrence of infection.
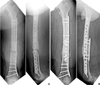
Fig. 4
Open type IIIc distal tibia and fibular fracture of a 31-year-old male was treated with vascular reconstruction and temporary external fixation.
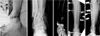
Fig. 5
(A) Internal fixation with intramedullary nail was carried out after soft tissue healing. (B) Plain X-ray taken 7 months after the injury shows atrophic nonunion, and there was pus discharge from the previously open wound on the medial side.
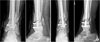
Fig. 6
(A) Under the diagnosis of infected nonunion, radical debridement of the infected tissue was performed and the fracture was stabilized by an external fixator. The bone defect after debridement was filled by an anti-cement bead. (B) An X-ray from the final follow-up showed a solid bony union after autogenous bone graft and plate fixation.
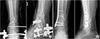
Fig. 7
(A) Clinical photography and X-ray show open comminuted proximal tibia fracture of a 72-year-old male. (B) Due to associated multiple injury, the fracture was stabilized by a temporary external fixator.

Fig. 8
(A) An X-rays and clinical photography taken 5 months after the injury showed infected nonunion after definite plate fixation with soft tissue defect. (B) The radical debridement of infected bone and soft tissue was carried out. The bone defect was filled by an anti-cement spacer (induced membrane technique) and soft tissue defect was covered by a free flap.

References
2. Motsitsi NS. Management of infected nonunion of long bones: the last decade (1996-2006). Injury. 2008; 39:155–160.

3. Patzakis MJ, Wilkins J. Factors influencing infection rate in open fracture wounds. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; (243):36–40.

5. Schmidt AH, Swiontkowski MF. Pathophysiology of infections after internal fixation of fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2000; 8:285–291.

6. Kim JH, Yoon YC, Kim YW, Jung SH, Oh JK. Diagnosis and management of posttraumatic chronic osteomyelitis. J Korean Fract Soc. 2014; 27:88–104.

7. Perry CR, Pearson RL, Miller GA. Accuracy of cultures of material from swabbing of the superficial aspect of the wound and needle biopsy in the preoperative assessment of osteomyelitis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991; 73:745–749.

8. Bose D, Kugan R, Stubbs D, McNally M. Management of infected nonunion of the long bones by a multidisciplinary team. Bone Joint J. 2015; 97:814–817.

9. Patzakis MJ, Zalavras CG. Chronic posttraumatic osteomyelitis and infected nonunion of the tibia: current management concepts. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2005; 13:417–427.

10. Maini L, Chadha M, Vishwanath J, Kapoor S, Mehtani A, Dhaon BK. The Ilizarov method in infected nonunion of fractures. Injury. 2000; 31:509–517.

11. Kim HM, Park IJ, Kim YS, et al. Free vascularized fibular grafts for treatment of infected nonunion of the tibia. J Korean Fract Soc. 2006; 19:163–169.

12. Ko HS, Kang YH, Kim DW, Ha JK. The treatment of infected non-union of long bones with plate and screws. J Korean Fract Soc. 2006; 19:72–77.

13. Sadek AF, Laklok MA, Fouly EH, Elshafie M. Two stage reconstruction versus bone transport in management of resistant infected tibial diaphyseal nonunion with a gap. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016; 136:1233–1241.

14. Prasarn ML, Ahn J, Achor T, Matuszewski P, Lorich DG, Helfet DL. Management of infected femoral nonunions with a single-staged protocol utilizing internal fixation. Injury. 2009; 40:1220–1225.

15. Han SK, Choi NY, Park SJ, Lee SK, Jang G, Lee IJ. Antibiotic cement-coated unreamed nailing for treatment of infected nonunion of long bone. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2000; 35:699–703.

16. Holtom PD, Patzakis MJ. Newer methods of antimicrobial delivery for bone and joint infections. Instr Course Lect. 2003; 52:745–749.
17. McKee MD, Wild LM, Schemitsch EH, Waddell JP. The use of an antibiotic-impregnated, osteoconductive, bioabsorbable bone substitute in the treatment of infected long bone defects: early results of a prospective trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2002; 16:622–627.

18. Swiontkowski MF, Hanel DP, Vedder NB, Schwappach JR. A comparison of short- and long-term intravenous antibiotic therapy in the postoperative management of adult osteomyelitis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999; 81:1046–1050.

19. Virani SR, Dahapute AA, Bava SS, Muni SR. Impact of negative pressure wound therapy on open diaphyseal tibial fractures: A prospective randomized trial. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2016; 7:256–259.

20. Chen CE, Ko JY, Pan CC. Results of vancomycin-impregnated cancellous bone grafting for infected tibial nonunion. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005; 125:369–375.

21. Stafford PR, Norris BL. Reamer-irrigator-aspirator bone graft and bi Masquelet technique for segmental bone defect nonunions: a review of 25 cases. Injury. 2010; 41:Suppl 2. S72–S77.

22. Yin P, Zhang L, Li T, et al. Infected nonunion of tibia and femur treated by bone transport. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015; 10:49.

23. Oh CW, Song HR, Roh JY, et al. Bone transport over an intramedullary nail for reconstruction of long bone defects in tibia. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008; 128:801–808.

24. Oh CW, Apivatthakakul T, Oh JK, et al. Bone transport with an external fixator and a locking plate for segmental tibial defects. Bone Joint J. 2013; 95:1667–1672.

25. Fischer C, Doll J, Tanner M, et al. Quantification of TGF-β1, PDGF and IGF-1 cytokine expression after fracture treatment vs. non-union therapy via masquelet. Injury. 2016; 47:342–349.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download