Abstract
In the distal third of the tibia, the anterior tibial artery runs close to the anterolateral surface of the tibial cortex. In a clinical situation, without vascular evaluation, injury or entrapment of the anterior tibial artery is difficult to detect. Because, an intact dorsalis pedis pulse is supplied with the collateral vessels of the posterior tibial artery. An entrapped anterior tibial artery can be injured during closed reduction in an emergency room or open reduction and internal fixation in the operating room. Care must be taken to prevent iatrogenic anterior tibial artery. In this case, an entrapped anterior tibial artery was observed in a simple radiograph and computed tomograph without contrast media for the vessel. We report on a rare case of calcified anterior tibial artery entrapment in a distal tibial fracture.
Figures and Tables
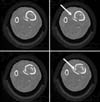
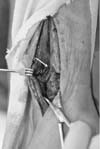
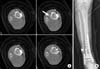
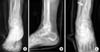 | Fig. 1An 80-year-old female patient with a spiral distal tibial fracture. (A) Antero-posterior view. (B) Lateral view. (C) Oblique view. Entrapped vessel is shown at the fracture site in the plain radiograph (arrow). |
References
1. Brinker MR, Bailey DE Jr. Fracture healing in tibia fractures with an associated vascular injury. J Trauma. 1997; 42:11–19.

2. Segal D, Brenner M, Gorczyca J. Tibial fractures with infrapopliteal arterial injuries. J Orthop Trauma. 1987; 1:160–169.

3. Tan ET, Tan TJ, Poon KB. Entrapment of the deep peroneal nerve and anterior tibial vessels by a spiral tibial fracture causing partial non-union: a case report. Skeletal Radiol. 2015; PMID: 26408316. [epub].

4. Court-Brown CM, McBirnie J. The epidemiology of tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995; 77:417–421.

5. Labler L, Wedler V, Mica L, Trentz O. Entrapment of the anterior tibial artery in a distal tibial fracture after intramedullary nailing. Unfallchirurg. 2006; 109:156–159.

6. Miki RA, Lawrence JP, Gillon TJ, Lawrence BD, Zell RA. Anterior tibial artery and deep peroneal nerve entrapment in spiral distal third tibia fracture. Orthopedics. 2008; 31:DOI: 10.3928/01477447-20081201-13. cited 2008 Dec. [Internet]. Available from: http://www.healio.com/orthopedics/trauma/journals/ortho/2008-12-31-12/%7B75123d28-e2b6-42a5-95b9-07ee2cb7b83f%7D/anterior-tibial-artery-and-deep-peroneal-nerve-entrapmentin-spiral-distal-third-tibia-fracture.

7. Sanders RJ, Alston GK. Variations and anomalies of the popliteal and tibial arteries. Am J Surg. 1986; 152:531–534.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download