Abstract
Dorsal dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal joint is a common injury in the orthopedic department. In most cases, the joint is reduced simply by closed manipulation. However, in rare cases, the joint is not reducible by closed manipulation, therefore, surgery is required. We report on a case of irreducible open dorsal dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal joint which was surgically treated. Because the flexor tendon interposed between the head of the proximal phalanx and the base of the middle phalanx, we could reduce the joint only after repositioning of the flexor tendon.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 2
Preoperative magnetic resonance imagings. The flexor digitorum profundus tendon interposed between the head of the proximal phalanx and the base of the middle phalanx. (A) Sagittal images. (B) Coronal images.
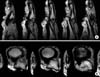
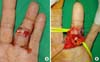
Fig. 3
Intraoperative photographs. (A) The head of the proximal phalanx protruded through the palmar open wound. (B) Flexor digitorum profundus tendon (black arrow head) had slipped behind the condyle of the proximal phalanx.
References
1. Merrell G, Slade JF. Dislocations and Ligament Injuries in the Digits. In : Wolfe SW, Hotchikiss RN, Pederson WC, Kozin SH, editors. Green's operative hand surgery. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier;2011. p. 291–332.
2. Calfee RP, Sommerkamp TG. Fracture-dislocation about the finger joints. J Hand Surg Am. 2009; 34:1140–1147.

3. Muraoka S, Furue Y, Kawashima M. Irreducible open dorsal dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal joint: a case report. Hand Surg. 2010; 15:61–64.

4. Kilgore ES Jr, Newmeyer WL, Brown LG. Post-traumatic trapped dislocations of the proximal interphalangeal joint. J Trauma. 1976; 16:481–487.

5. Takami H, Takahashi S, Ando M. Irreducible open dorsal dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal joint. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2001; 121:232–233.

6. Green SM, Posner MA. Irreducible dorsal dislocations of the proximal interphalangeal joint. J Hand Surg Am. 1985; 10:85–87.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


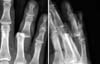
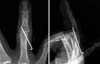

 XML Download
XML Download