Abstract
Purpose
Nail insertion is the treatment of choice for subtrochanteric femoral fracture, but displacement of proximal bone fragment makes it difficult to find an ideal entry point. Therefore, in this study we aimed to determine the usefulness of treatment of subtrochanteric femoral fracture using Steinmann pin assisted reduction, internal fixation, and insertion of intramedullary nails.
Materials and Methods
We evaluated 33 patients who were followed-up more than a year with a displaced subtrochanteric femoral fracture treated with closed reduction and intramedullary nail fixation between January 2008 and March 2013. In addition, we studied postoperative bone union time, postoperative reduction status, change of the femur neck shaft angle, evaluation of hip joint function, return to daily life, and complications.
Results
All fractures with Steinmann pin assisted reduction were united but they included three cases of delayed union. In Fogagnolo classification, all cases were up to acceptable states and the varus change of femur neck shaft angle was 0.94°±3.1°; no significant difference in Harris hip score was observed between preoperative and last follow-up (p>0.05).
Figures and Tables
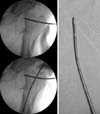
Fig. 1
(A) Typical external rotation, abduction, and flexion deformity of the proximal fragment in subtrochanteric fracture. (B-D) Reduction is carried out by Steinmann pin and induction of a guide wire and gradual reaming is performed. (E) Nail insertion and proximal fixation. (F-G) Distal fixation.

References
1. Nikolaou VS, Papathanasopoulos A, Giannoudis PV. What's new in the management of proximal femoral fractures? Injury. 2008; 39:1309–1318.

2. Perren SM. Evolution of the internal fixation of long bone fractures. The scientific basis of biological internal fixation: choosing a new balance between stability and biology. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84:1093–1110.
3. Tornetta P 3rd, Ritz G, Kantor A. Femoral torsion after interlocked nailing of unstable femoral fractures. J Trauma. 1995; 38:213–219.

4. Winquist RA, Hansen ST Jr, Clawson DK. Closed intramedullary nailing of femoral fractures. A report of five hundred and twenty cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984; 66:529–539.

5. Russell TA, Mir HR, Stoneback J, Cohen J, Downs B. Avoidance of malreduction of proximal femoral shaft fractures with the use of a minimally invasive nail insertion technique (MINIT). J Orthop Trauma. 2008; 22:391–398.

6. de Vries JS, Kloen P, Borens O, Marti RK, Helfet DL. Treatment of subtrochanteric nonunions. Injury. 2006; 37:203–211.

7. Gugenheim JJ, Probe RA, Brinker MR. The effects of femoral shaft malrotation on lower extremity anatomy. J Orthop Trauma. 2004; 18:658–664.

8. Parker MJ, Dutta BK, Sivaji C, Pryor GA. Subtrochanteric fractures of the femur. Injury. 1997; 28:91–95.

9. Siebenrock KA, Müller U, Ganz R. Indirect reduction with a condylar blade plate for osteosynthesis of subtrochanteric femoral fractures. Injury. 1998; 29:Suppl 3. C7–C15.

10. Sims SH. Subtrochanteric femur fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2002; 33:113–126. viii
11. Vanderschot P, Vanderspeeten K, Verheyen L, Broos P. A review on 161 subtrochanteric fractures: risk factors influencing outcome: age, fracture pattern and fracture level. Unfallchirurg. 1995; 98:265–271.
12. Nungu KS, Olerud C, Rehnberg L. Treatment of subtrochanteric fractures with the AO dynamic condylar screw. Injury. 1993; 24:90–92.

13. Rohilla R, Singh R, Magu NK, Siwach RC, Sangwan SS. Mini-incision dynamic condylar screw fixation for comminuted subtrochanteric hip fractures. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2008; 16:150–155.

14. Kinast C, Bolhofner BR, Mast JW, Ganz R. Subtrochanteric fractures of the femur. Results of treatment with the 95 degrees condylar blade-plate. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; (238):122–130.
15. Kyle RF, Cabanela ME, Russell TA, et al. Fractures of the proximal part of the femur. Instr Course Lect. 1995; 44:227–253.

16. Asher MA, Tippett JW, Rockwood CA, Zilber S. Compression fixation of subtrochanteric fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976; (117):202–208.

17. Trafton PG. Subtrochanteric-intertrochanteric femoral fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 1987; 18:59–71.

18. Krettek C, Miclau T, Schandelmaier P, Stephan C, Möhlmann U, Tscherne H. The mechanical effect of blocking screws (Poller screws) in stabilizing tibia fractures with short proximal or distal fragments after insertion of small-diameter intramedullary nails. J Orthop Trauma. 1999; 13:550–553.

19. Krettek C, Stephan C, Schandelmaier P, Richter M, Pape HC, Miclau T. The use of Poller screws as blocking screws in stabilising tibial fractures treated with small diameter intramedullary nails. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999; 81:963–968.

20. Stedtfeld HW, Mittlmeier T, Landgraf P, Ewert A. The logic and clinical applications of blocking screws. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86:Suppl 2. 17–25.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download