Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to examine incidence of recompression and risk factors in the patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture (OVCF) after vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty.
Materials and Methods
This study was conducted on 179 vertebral bodies of 126 patients who underwent vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty on OVCF from January 2004 to August 2013.
Results
When anterior vertebral height of fractured vertebrae declined by more than 3 mm from the height immediately after vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty, it was judged that recompression had occurred. Recompression was observed in a total of 58 vertebrae (32.4%). Recompression occurrences were found to be decreasing significantly when fractured vertebrae were the thoracic spine. In addition, osteonecrosis occurred in the preoperative vertebrae and restoration degree of anterior vertebral height immediately after vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty affected recompression occurrences significantly. The other factors (age, sex, bone mineral density, steroid medication history, follow-up duration, cement volume, vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty, and approach method) were compared, but no statistical significance was found.
Conclusion
The risk of vertebral recompression is more common, especially when osteonecrosis occurred in preoperative vertebrae or when vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty achieved remarkable restoration of anterior vertebra height. When performing vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty, such conditions should be considered carefully.
Figures and Tables
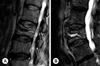 | Fig. 1Sagittal thoracic vertebra (T2)-weigted magnetic resonance imaging showing (A) the intervertebral cleft with surrounding bone edema signal intensity, (B) high signal lesion (fluid collection). |
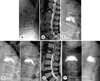 | Fig. 2A 65-year-old female with lumbar vertebra (L1) osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture (dual energy x-ray absorptiometry T-score: -4.4). (A) Initial lateral radiograph. (B) Sagittal thoracic vertebra (T2)-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) shows intervertebral cleft (osteonecrosis). (C) Immediately postoperative lateral radiograph. (D) At 6 weeks after vertebroplasty, lateral dynamic radiograph (flexion and extension) shows recompression with resorption of the inferior portion of the vertebral body. (E) Postoperative sagittal T2-weighted MRI shows fluid collection around cement. (F) Postoperative (2nd vertebroplasty) radiograph. |
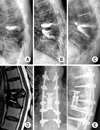 | Fig. 3A 60-year-old male with thoracic vertebra (T8, 9) osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture (dual energy x-ray absorptiometry T-score: -3.2). (A) Postoperative (vertebroplasty T8) lateral radiograph. (B) Postoperative (vertebroplasty T9) lateral radiograph. (C) At 2 years after 2nd vertebroplasty, local kyphotic angle was 55° with severe back pain. (D) Postoperative sagittal T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging shows fluid collection around cement. (E) Postoperative radiograph. |
References
1. Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P, Le Gars D. Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty. Neurochirurgie. 1987; 33:166–168.
2. McKiernan F, Faciszewski T, Jensen R. Quality of life following vertebroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86:2600–2606.

3. Belkoff SM, Mathis JM, Jasper LE, Deramond H. The biomechanics of vertebroplasty. The effect of cement volume on mechanical behavior. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:1537–1541.
4. Teng MM, Wei CJ, Wei LC, et al. Kyphosis correction and height restoration effects of percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24:1893–1900.
5. Syed MI, Patel NA, Jan S, Harron MS, Morar K, Shaikh A. New symptomatic vertebral compression fractures within a year following vertebroplasty in osteoporotic women. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:1601–1604.
6. Gaughen JR Jr, Jensen ME, Schweickert PA, Marx WF, Kallmes DF. The therapeutic benefit of repeat percutaneous vertebroplasty at previously treated vertebral levels. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:1657–1661.
7. Jensen ME, Evans AJ, Mathis JM, Kallmes DF, Cloft HJ, Dion JE. Percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral body compression fractures: technical aspects. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997; 18:1897–1904.
8. Jun DS, Shin WJ, Kim KH. The usefulness of bone scan in the osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture patients treated with kyphoplasty. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2008; 15:18–22.

9. Yu SW, Chen WJ, Lin WC, Chen YJ, Tu YK. Serious pyogenic spondylitis following vertebroplasty: a case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29:E209–E211.
10. Ryu KS, Park CK, Kim MC, Kang JK. Dose-dependent epidural leakage of polymethylmethacrylate after percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Neurosurg. 2002; 96:1 Suppl. 56–61.

11. Tanigawa N, Komemushi A, Kariya S, Kojima H, Shomura Y, Sawada S. Radiological follow-up of new compression fractures following percutaneous vertebroplasty. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2006; 29:92–96.

12. Uppin AA, Hirsch JA, Centenera LV, Pfiefer BA, Pazianos AG, Choi IS. Occurrence of new vertebral body fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with osteoporosis. Radiology. 2003; 226:119–124.

13. Leung Y, Samartzis D, Cheung KM, Luk KD. Osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: the clinical impact of "intravertebral clefts". Spine J. 2010; 10:1035–1036.

14. Kim YY, Park CG, Rhyu KW. Recompression of vertebral bodies after balloon kyphoplasty for vertebral compression fractures: preliminary report. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2009; 16:89–94.

15. Lin CC, Shen WC, Lo YC, et al. Recurrent pain after percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 194:1323–1329.

16. Wagner AL, Baskurt E. Refracture with cement extrusion following percutaneous vertebroplasty of a large interbody cleft. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:230–231.
17. Tsai TT, Chen WJ, Lai PL, et al. Polymethylmethacrylate cement dislodgment following percutaneous vertebroplasty: a case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:E457–E460.

18. Huang KY, Yan JJ, Lin RM. Histopathologic findings of retrieved specimens of vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacrylate cement: case control study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:E585–E588.
19. Lin CC, Yen PS, Wen SH. Fluid sign in the treated bodies after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Neuroradiology. 2008; 50:955–961.

20. Lin WC, Lee YC, Lee CH, et al. Refractures in cemented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty: a retrospective analysis. Eur Spine J. 2008; 17:592–599.

21. Heo DH, Chin DK, Yoon YS, Kuh SU. Recollapse of previous vertebral compression fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Osteoporos Int. 2009; 20:473–480.

22. Lin CC, Wen SH, Chiu CH, Chen IH, Yu TC. The clinical influence of fluid sign in treated vertebral bodies after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Radiology. 2009; 251:866–872.

23. Kim MJ, Lindsey DP, Hannibal M, Alamin TF. Vertebroplasty versus kyphoplasty: biomechanical behavior under repetitive loading conditions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31:2079–2084.

24. He SC, Teng GJ, Deng G, et al. Repeat vertebroplasty for unrelieved pain at previously treated vertebral levels with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33:640–647.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download