Abstract
Distraction osteogenesis with an Ilizarov external fixator is one of the most successful treatment options for large segmental bone defects after extensive debridement of chronic osteomyelitis in the tibial shaft. Its complications include skin irritation, pin tract infection, and non-union due to infection. There are few case reports on chronic osteomyelitis occurring in the distraction osteogenesis area. The authors experienced a chronic osteomyelitis in the distraction osteogenesis area of the tibial shaft and report this case with references.
Figures and Tables
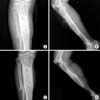
Fig. 1
Preoperative antero-posterior (A) and lateral (B) radiographs showing the distraction osteogenesis area of the proximal tibial shaft with old bone fracture deformity. Left arrow (A) indicates a radiolucent lesion in the distraction osteogenesis area, and right arrow (B) indicates an anterior corticocancellous bone defect of the distraction osteogenesis area.
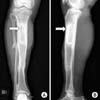
Fig. 2
(A) Coronal T1-weighted image shows a low signal intensity lesion on metadiaphysis of the right proximal tibia. (B) Coronal enhanced T2-weighted image shows a high signal intensity lesion with peripheral irregular enhancement and sequestrum of dark signal intensity. (C) Axial enhanced T2-weighted image shows sequestrum of dark signal intensity, defect of anterior bony cortex and fistular tract (arrow) from bone to skin.
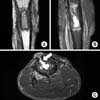
Fig. 3
Antero-posterior (A) and lateral (B) radiographs showing insertion of the wire, which is wrapped in antibioticmixed cement beads, after saucerization of an osteomyelitic lesion in the proximal tibia.
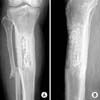
Fig. 4
(A) Clinical photograph, nine months after autoiliac bone graft operation, showing wound healing with crust formation, with no sign of discharge or infection in the proximal shin. (B) Wound healing with crust formation is more zoomed out.
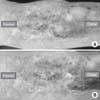
Fig. 5
Antero-posterior (A) and lateral (B) radiographs showing insertion of an autoiliac cancellous bone graft after removal of antibioticmixed cement beads in the proximal tibia. Antero-posterior (C) and lateral (D) radiographs from the final follow up X-ray, seven months after autoiliac bone graft operation, showing further healing of the autoiliac cancellous bone graft site in the proximal tibia.
References
1. Liu T, Zhang X, Li Z, Peng D. Management of combined bone defect and limb-length discrepancy after tibial chronic osteomyelitis. Orthopedics. 2011; 34:e363–e367.

2. Magadum MP, Basavaraj Yadav CM, Phaneesha MS, Ramesh LJ. Acute compression and lengthening by the Ilizarov technique for infected nonunion of the tibia with large bone defects. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2006; 14:273–279.

3. Cierny G 3rd, Zorn KE. Segmental tibial defects. Comparing conventional and Ilizarov methodologies. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994; (301):118–123.
4. Gateley DR, Irby SJ, Martin DL, Simonis RB. Ilizarov bone transport for the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis: a rare complication. J R Soc Med. 1996; 89:348P–350P.

6. Song HR, Kale A, Park HB, et al. Comparison of internal bone transport and vascularized fibular grafting for femoral bone defects. J Orthop Trauma. 2003; 17:203–211.

7. Uçkay I, Assal M, Legout L, et al. Recurrent osteomyelitis caused by infection with different bacterial strains without obvious source of reinfection. J Clin Microbiol. 2006; 44:1194–1196.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download