Abstract
Thoracic outlet syndrome is a relatively common disease. However, costoclavicular syndrome as a condition secondary to nonunion of a displaced fracture of the clavicle is very rare. Most clavicular fractures in adults are united with no or minimal persistent symptoms. Also, symptomatic nonunion of a displaced fracture of the clavicle is rare. A 55-year-old male initially presented with persistent forearm pain after slip-down was initially diagnosed with simple muscle strain. However, he was given a delayed diagnosis of costoclavicular syndrome, caused by compression of the subclavian artery due to trauma in the fibrotic nonunion of the right clavicle without apparent symptoms. We obtained satisfactory results by surgical treatment. Here we report this case with a review of the literature.
Figures and Tables
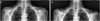 | Fig. 1Preoperative radiograph shows a fibrous nonunion and displacement with shortening of the clavicle shaft. |
 | Fig. 2Preoperative 3dimension computed tomography shows displacement and shortening of the clavicle shaft. |
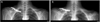
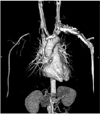 | Fig. 3Preoperative angio computed tomography shows the discontinuous subclavian artery under the fracture site. |
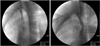 | Fig. 4Preoperative angiogram shows the discontinuous subclavian artery beneath the fracture site with little collateral circulation. |
References
1. Davidovic LB, Kostic DM, Jakovljevic NS, Kuzmanovic IL, Simic TM. Vascular thoracic outlet syndrome. World J Surg. 2003. 27:545–550.

2. Garnier D, Chevalier J, Ducasse E, Modine T, Espagne P, Puppinck P. Arterial complications of thoracic outlet syndrome and pseudarthrosis of the clavicle: three patients. J Mal Vasc. 2003. 28:79–84.
4. Lee YM, Song SW, Choi KB, Rhee SK. The treatment of thoracic outlet syndrome. J Korean Soc Microsurg. 2011. 20:102–107.
5. Mulder DS, Greenwood FA, Brooks CE. Posttraumatic thoracic outlet syndrome. J Trauma. 1973. 13:706–715.

8. Sohn SK, Kim SS, Song CG, Kwak JI. Costoclavicular syndrome: a case report. J Korean Fract Soc. 2007. 20:86–89.

9. Tindall SC. Youmans JR, editor. Chronic injuries of peripheral nerves by entrapment. Neurological surgery. 1996. 4th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co;2182–2187.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download